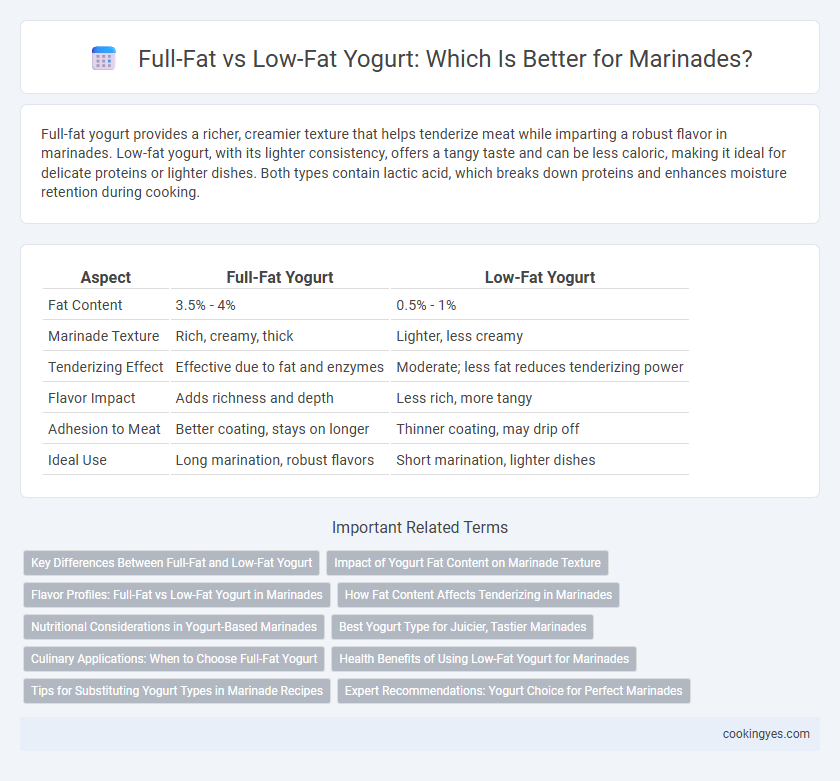
Full-fat yogurt provides a richer, creamier texture that helps tenderize meat while imparting a robust flavor in marinades. Low-fat yogurt, with its lighter consistency, offers a tangy taste and can be less caloric, making it ideal for delicate proteins or lighter dishes. Both types contain lactic acid, which breaks down proteins and enhances moisture retention during cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Full-Fat Yogurt | Low-Fat Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 3.5% - 4% | 0.5% - 1% |
| Marinade Texture | Rich, creamy, thick | Lighter, less creamy |
| Tenderizing Effect | Effective due to fat and enzymes | Moderate; less fat reduces tenderizing power |
| Flavor Impact | Adds richness and depth | Less rich, more tangy |
| Adhesion to Meat | Better coating, stays on longer | Thinner coating, may drip off |
| Ideal Use | Long marination, robust flavors | Short marination, lighter dishes |
Key Differences Between Full-Fat and Low-Fat Yogurt
Full-fat yogurt contains higher fat content, offering richer texture and creaminess that enhances moisture retention and tenderness in marinades. Low-fat yogurt has reduced fat, resulting in a lighter, tangier flavor and thinner consistency, which can lead to less tender meat but fewer calories. The fat in full-fat yogurt also helps dissolve fat-soluble flavors and contributes to better browning during cooking compared to low-fat versions.
Impact of Yogurt Fat Content on Marinade Texture
Full-fat yogurt creates a richer, creamier marinade texture due to its higher fat content, which helps tenderize meat more effectively and adds moisture. Low-fat yogurt produces a thinner marinade, resulting in less coating and potentially drier meat after cooking. The fat in full-fat yogurt also enhances flavor absorption, making it preferable for more intense and juicy marinades.
Flavor Profiles: Full-Fat vs Low-Fat Yogurt in Marinades
Full-fat yogurt adds a rich, creamy texture and a fuller flavor profile to marinades, enhancing the taste and tenderness of meats. Low-fat yogurt offers a lighter, tangier flavor but may lack the same depth and moisture retention as full-fat varieties. Using full-fat yogurt in marinades maximizes flavor complexity and juiciness in grilled or roasted dishes.
How Fat Content Affects Tenderizing in Marinades
Full-fat yogurt contains higher levels of fat that enhance the marinade's ability to retain moisture, resulting in juicier and more tender meats due to a slower protein breakdown. Low-fat yogurt, with reduced fat content, still provides lactic acid and enzymes necessary for tenderizing but may cause a firmer texture as it accelerates protein denaturation without the buffering effect of fat. The fat in full-fat yogurt also improves flavor absorption, making it a preferred choice for rich and tender marinated dishes.
Nutritional Considerations in Yogurt-Based Marinades
Full-fat yogurt contains higher levels of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, enhancing nutrient absorption in marinades compared to low-fat yogurt. Low-fat yogurt typically has reduced calories and fat content, appealing to calorie-conscious consumers but may lack the creamy texture that aids in tenderizing meats. Both types provide beneficial probiotics and protein, but the fat content in full-fat yogurt can improve flavor and moisture retention during cooking.
Best Yogurt Type for Juicier, Tastier Marinades
Full-fat yogurt contains higher fat content, which helps retain moisture and infuses richer flavors into meats, making it the superior choice for juicier, tastier marinades. Its creaminess enhances tenderness by breaking down protein fibers more effectively than low-fat yogurt, which tends to dry out during cooking. Choosing full-fat yogurt boosts both texture and flavor intensity in marinades, optimizing the final dish's overall succulence.
Culinary Applications: When to Choose Full-Fat Yogurt
Full-fat yogurt offers a richer texture and creamier consistency ideal for marinades that require a tenderizing effect on meats, especially chicken and lamb, due to its higher fat content and lactic acid concentration. Its dense composition enhances moisture retention and intensifies flavor absorption during marination, making it preferable for recipes seeking depth and succulence. Choose full-fat yogurt when the culinary goal is to create a luxurious mouthfeel and a robust, well-rounded marinade.
Health Benefits of Using Low-Fat Yogurt for Marinades
Low-fat yogurt offers a healthier option for marinades by reducing calorie and saturated fat intake while maintaining essential nutrients like calcium and protein. Its lower fat content aids digestion and promotes heart health compared to full-fat yogurt, which contains higher levels of saturated fats. Using low-fat yogurt in marinades also enhances meat tenderness and flavor without adding excessive calories, supporting balanced nutrition and weight management.
Tips for Substituting Yogurt Types in Marinade Recipes
Full-fat yogurt enhances marinade richness and tenderizes meat effectively due to its higher fat content and creamy texture, while low-fat yogurt provides a tangy flavor with fewer calories but may result in a thinner marinade. When substituting, adjust marinating time by reducing it slightly for low-fat yogurt to prevent over-tenderizing and consider adding a touch of olive oil to mimic the mouthfeel of full-fat versions. Balancing acidity and fat content ensures the marinade maintains its flavor profile and tenderizing properties regardless of yogurt type.
Expert Recommendations: Yogurt Choice for Perfect Marinades
Full-fat yogurt contains higher fat content which helps tenderize meat more effectively by breaking down proteins and retaining moisture, resulting in juicier and more flavorful dishes. Low-fat yogurt offers a tangy flavor with less richness, making it suitable for lighter marinades but may produce a slightly drier texture. Experts recommend full-fat yogurt for marinades when seeking optimal tenderness and depth of flavor, especially in recipes involving tougher cuts of meat.
Full-Fat Yogurt vs Low-Fat Yogurt for Marinades Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com