Live culture yogurt contains active probiotics that help maintain and restore a healthy gut microbiome, promoting digestion and boosting immune function. Heat-treated yogurt, on the other hand, has been pasteurized or boiled, which kills beneficial bacteria and reduces its effectiveness in supporting gut health. Choosing live culture yogurt ensures the presence of live bacteria essential for enhancing gut flora and improving overall digestive wellness.
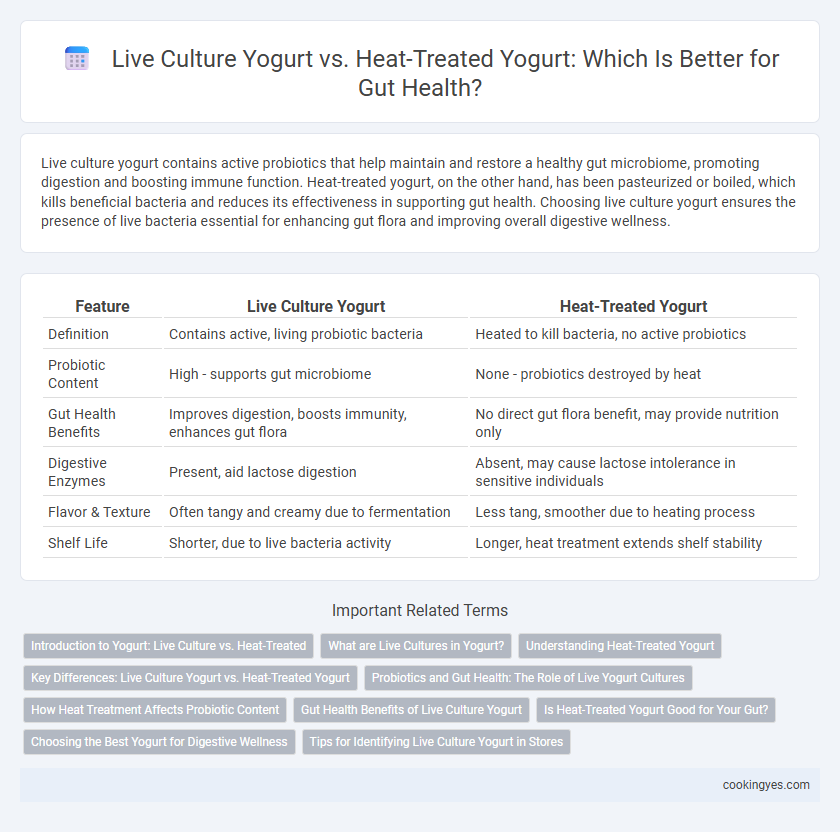
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Live Culture Yogurt | Heat-Treated Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contains active, living probiotic bacteria | Heated to kill bacteria, no active probiotics |
| Probiotic Content | High - supports gut microbiome | None - probiotics destroyed by heat |
| Gut Health Benefits | Improves digestion, boosts immunity, enhances gut flora | No direct gut flora benefit, may provide nutrition only |
| Digestive Enzymes | Present, aid lactose digestion | Absent, may cause lactose intolerance in sensitive individuals |
| Flavor & Texture | Often tangy and creamy due to fermentation | Less tang, smoother due to heating process |
| Shelf Life | Shorter, due to live bacteria activity | Longer, heat treatment extends shelf stability |
Introduction to Yogurt: Live Culture vs. Heat-Treated
Live culture yogurt contains active probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains that promote gut microbiota diversity and enhance digestive health. Heat-treated yogurt undergoes pasteurization after fermentation, which kills these beneficial bacteria, reducing its probiotic benefits. Choosing live culture yogurt supports improved gut barrier function, immune modulation, and overall intestinal well-being.
What are Live Cultures in Yogurt?
Live cultures in yogurt are beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, that remain active during fermentation and consumption. These probiotics enhance gut health by promoting a balanced intestinal microbiome, improving digestion, and boosting immune function. Heat-treated yogurt, in contrast, undergoes pasteurization after fermentation, which kills these live bacteria, reducing its probiotic benefits.
Understanding Heat-Treated Yogurt
Heat-treated yogurt undergoes pasteurization after fermentation, which eliminates live probiotic bacteria essential for promoting gut health. Unlike live culture yogurt, heat-treated varieties lack the beneficial microorganisms such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium that support digestion and enhance the gut microbiome. Consuming live culture yogurt preserves these probiotics, making it more effective for improving intestinal flora and overall digestive wellness.
Key Differences: Live Culture Yogurt vs. Heat-Treated Yogurt
Live culture yogurt contains active probiotic bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which support gut health by enhancing digestion and boosting the immune system. In contrast, heat-treated yogurt undergoes pasteurization after fermentation, killing beneficial probiotics and reducing its potential gut health benefits. Choosing live culture yogurt ensures intake of viable microorganisms essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
Probiotics and Gut Health: The Role of Live Yogurt Cultures
Live culture yogurt contains active probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains that enhance gut microbiota diversity and improve digestive health. Heat-treated yogurt lacks these viable bacteria, resulting in diminished probiotic benefits and reduced support for intestinal barrier function. Consuming live yogurt cultures promotes balanced gut flora, aiding in immune modulation and alleviating gastrointestinal disorders.
How Heat Treatment Affects Probiotic Content
Heat-treated yogurt undergoes pasteurization or high-temperature processing that significantly reduces or eliminates live probiotic bacteria essential for gut health. In contrast, live culture yogurt contains active strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum, which support digestion and enhance gut microbiota diversity. Consuming live culture yogurt is more effective for improving gut health than heat-treated varieties that lack viable probiotics.
Gut Health Benefits of Live Culture Yogurt
Live culture yogurt contains active probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains that enhance gut microbiota diversity and support digestive health by promoting beneficial bacteria growth. These live microorganisms help improve intestinal barrier function, reduce inflammation, and enhance nutrient absorption, contributing to overall gut health. Heat-treated yogurt lacks these live probiotics, making it less effective in providing the gut health benefits associated with live cultures.
Is Heat-Treated Yogurt Good for Your Gut?
Heat-treated yogurt lacks live probiotic cultures essential for improving gut microbiota diversity and enhancing digestive health. Live culture yogurt contains beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum that help restore gut flora balance and boost immune function. Consuming heat-treated yogurt offers limited gut health benefits compared to live culture yogurt due to the absence of active probiotics.
Choosing the Best Yogurt for Digestive Wellness
Live culture yogurt contains active probiotics such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum, which promote a healthy gut microbiome by enhancing digestion and boosting immune function. Heat-treated yogurt undergoes pasteurization after fermentation, which eliminates beneficial live bacteria, reducing its effectiveness for gut health. Choosing yogurt with live and active cultures ensures maximum probiotic benefits to support optimal digestive wellness.
Tips for Identifying Live Culture Yogurt in Stores
Live culture yogurt contains active probiotics essential for gut health, unlike heat-treated yogurt where beneficial bacteria are killed. To identify live culture yogurt in stores, check for labels stating "contains live and active cultures" or specific strains such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum. Look for refrigeration requirements and expiration dates to ensure the probiotics remain viable and effective for digestion.
Live culture yogurt vs heat-treated yogurt for gut health Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com