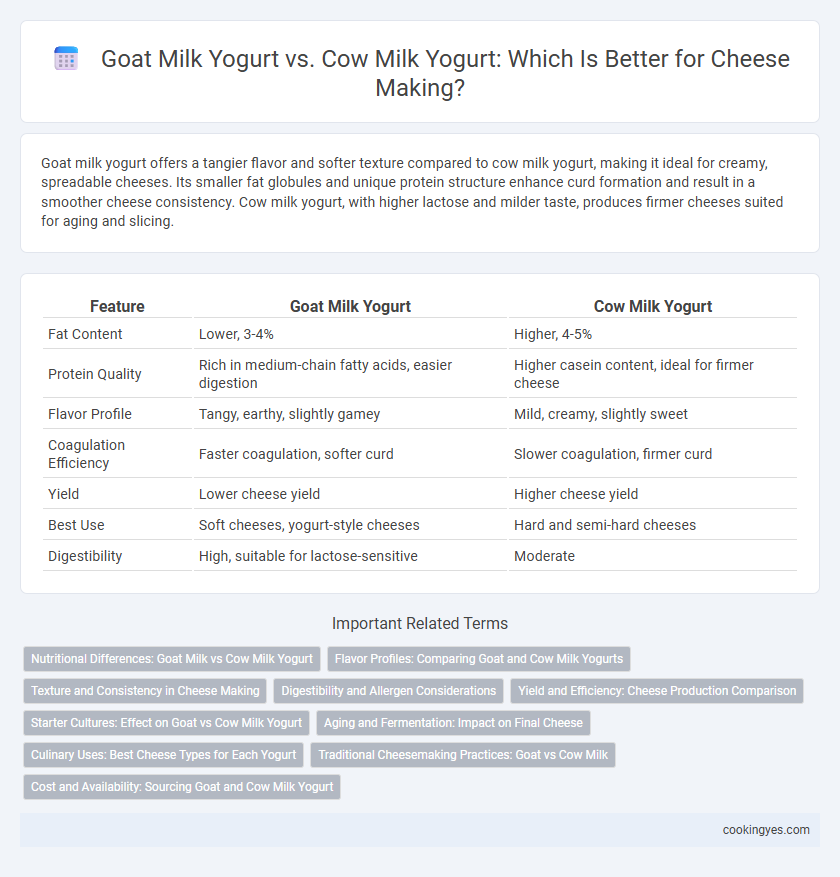
Goat milk yogurt offers a tangier flavor and softer texture compared to cow milk yogurt, making it ideal for creamy, spreadable cheeses. Its smaller fat globules and unique protein structure enhance curd formation and result in a smoother cheese consistency. Cow milk yogurt, with higher lactose and milder taste, produces firmer cheeses suited for aging and slicing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Goat Milk Yogurt | Cow Milk Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | Lower, 3-4% | Higher, 4-5% |
| Protein Quality | Rich in medium-chain fatty acids, easier digestion | Higher casein content, ideal for firmer cheese |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, earthy, slightly gamey | Mild, creamy, slightly sweet |
| Coagulation Efficiency | Faster coagulation, softer curd | Slower coagulation, firmer curd |
| Yield | Lower cheese yield | Higher cheese yield |
| Best Use | Soft cheeses, yogurt-style cheeses | Hard and semi-hard cheeses |
| Digestibility | High, suitable for lactose-sensitive | Moderate |
Nutritional Differences: Goat Milk vs Cow Milk Yogurt
Goat milk yogurt contains higher levels of medium-chain fatty acids, which are easier to digest and promote better absorption of nutrients compared to cow milk yogurt. It also provides more calcium, potassium, and vitamin A, essential for strong bones and immune support, while cow milk yogurt tends to have higher vitamin B12 and folate content. These nutritional differences influence the texture, flavor, and aging process of cheeses made from each milk type, making goat milk yogurt ideal for tangier, softer cheeses and cow milk yogurt suitable for richer, creamier varieties.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Goat and Cow Milk Yogurts
Goat milk yogurt offers a distinctive tangy and earthy flavor with a slight tartness, creating a bold and complex taste ideal for robust cheese varieties. Cow milk yogurt has a milder, creamier, and slightly sweet flavor, providing a smooth base for soft and fresh cheese types. The choice between goat and cow milk yogurts significantly influences the cheese's aroma, texture, and overall flavor intensity, with goat milk yielding a more pronounced character.
Texture and Consistency in Cheese Making
Goat milk yogurt produces cheese with a creamier and smoother texture due to its smaller fat globules and lower casein content compared to cow milk yogurt. Cow milk yogurt tends to yield firmer and denser cheese, attributed to higher alpha-s1 casein levels that enhance curd structure. The unique protein composition in goat milk yogurt results in a softer consistency, ideal for fresh cheeses, while cow milk yogurt supports aging and firmer cheese varieties.
Digestibility and Allergen Considerations
Goat milk yogurt generally offers better digestibility than cow milk yogurt due to its smaller fat globules and lower lactose content, making it suitable for individuals with mild lactose intolerance. It contains less alpha-S1-casein protein, which reduces allergenic potential compared to cow milk yogurt, often preferred by those with cow milk protein allergies. These factors make goat milk yogurt a favorable option for cheese making in allergen-sensitive and digestive-friendly diets.
Yield and Efficiency: Cheese Production Comparison
Goat milk yogurt generally produces a lower cheese yield compared to cow milk yogurt due to its smaller fat globules and higher moisture content, which affect curd formation and firmness. However, goat milk's unique protein structure allows for faster acidification and curdling, potentially improving production efficiency despite the reduced volume. Cow milk yogurt yields more cheese with a creamier texture, making it favorable for large-scale cheese production focused on maximizing output.
Starter Cultures: Effect on Goat vs Cow Milk Yogurt
Starter cultures significantly influence the texture and flavor profile of goat milk yogurt compared to cow milk yogurt in cheese making. Goat milk's unique protein and fat composition interacts differently with lactic acid bacteria like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, often resulting in tangier, creamier yogurt with a distinct aroma. Optimizing starter culture strains for goat milk can enhance fermentation efficiency and improve the sensory qualities of yogurt and cheese products.
Aging and Fermentation: Impact on Final Cheese
Goat milk yogurt typically ferments faster due to its lower fat content and different protein structure, leading to a tangier, softer cheese with a shorter aging period compared to cow milk yogurt. The higher casein content in cow milk yogurt supports a firmer texture and allows for longer aging, enhancing flavor complexity and depth in the final cheese. Variations in fermentation time and microbial activity between the two milk types significantly influence the cheese's taste profile, texture, and shelf life during the aging process.
Culinary Uses: Best Cheese Types for Each Yogurt
Goat milk yogurt produces tangy, creamy cheese varieties like chevre and feta, prized for their distinct flavors and crumbly texture, making it ideal for Mediterranean and artisanal dishes. Cow milk yogurt excels in creating smooth, mild cheeses such as cream cheese and ricotta, favored for their versatility in pastries, spreads, and rich sauces. The higher fat content in cow milk yogurt contributes to a silkier consistency, while goat milk yogurt's unique proteins enhance cheese fermentation and flavor complexity.
Traditional Cheesemaking Practices: Goat vs Cow Milk
Goat milk yogurt offers traditional cheesemaking advantages with its higher acidity and unique protein structure, resulting in a tangier flavor and creamier texture in cheeses like chevre. Cow milk yogurt, favored in classic cheesemaking due to its richer fat content and milder taste, produces a firmer curd ideal for varieties such as cheddar and mozzarella. Traditional cheesemaking practices leverage these distinct properties to influence the maturation process, curd consistency, and flavor profile of goat versus cow milk cheeses.
Cost and Availability: Sourcing Goat and Cow Milk Yogurt
Goat milk yogurt typically costs more than cow milk yogurt due to lower production volumes and higher feed expenses for goats. Cow milk yogurt is more widely available in supermarkets, benefiting from larger-scale dairy farming and established supply chains. These factors make cow milk yogurt more accessible and budget-friendly for cheese making, whereas goat milk yogurt may require sourcing from specialty suppliers or local farms.
Goat milk yogurt vs cow milk yogurt for cheese making Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com