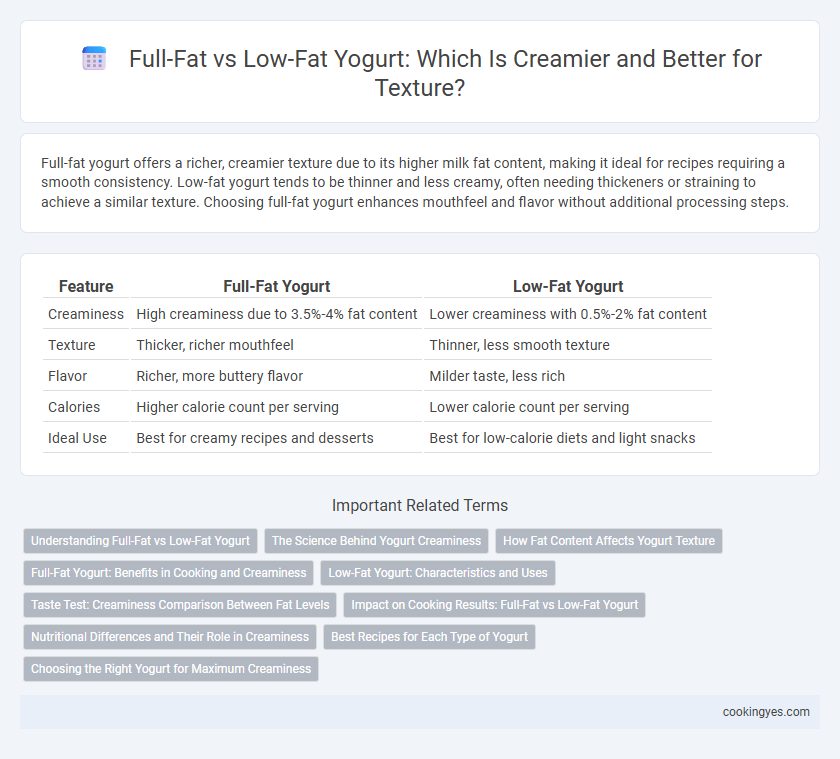
Full-fat yogurt offers a richer, creamier texture due to its higher milk fat content, making it ideal for recipes requiring a smooth consistency. Low-fat yogurt tends to be thinner and less creamy, often needing thickeners or straining to achieve a similar texture. Choosing full-fat yogurt enhances mouthfeel and flavor without additional processing steps.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Full-Fat Yogurt | Low-Fat Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Creaminess | High creaminess due to 3.5%-4% fat content | Lower creaminess with 0.5%-2% fat content |
| Texture | Thicker, richer mouthfeel | Thinner, less smooth texture |
| Flavor | Richer, more buttery flavor | Milder taste, less rich |
| Calories | Higher calorie count per serving | Lower calorie count per serving |
| Ideal Use | Best for creamy recipes and desserts | Best for low-calorie diets and light snacks |
Understanding Full-Fat vs Low-Fat Yogurt
Full-fat yogurt contains higher milk fat content, typically around 3.25%, contributing to a richer, creamier texture and enhanced mouthfeel compared to low-fat yogurt, which generally ranges from 0.5% to 2% fat. The fat in full-fat yogurt not only improves creaminess but also influences flavor profile and satiety, making it a preferred choice for culinary uses requiring thick, smooth consistency. Low-fat yogurt offers a lighter texture and fewer calories, appealing to those seeking reduced fat intake while still providing essential nutrients like protein and probiotics.
The Science Behind Yogurt Creaminess
Full-fat yogurt contains higher levels of milk fat, which contributes to its rich, creamy texture by enhancing the emulsion of fat globules and stabilizing the protein network during fermentation. Low-fat yogurt has reduced fat content, resulting in a thinner consistency due to less fat globule interaction and increased water mobility. The science behind yogurt creaminess involves the complex interplay between fat content, protein structure, and fermentation processes that influence texture and mouthfeel.
How Fat Content Affects Yogurt Texture
Full-fat yogurt contains higher fat content, which contributes to a richer, creamier texture compared to low-fat yogurt. The fat globules in full-fat yogurt create a smooth mouthfeel and enhance the overall viscosity, making it more velvety and dense. Low-fat yogurt tends to be thinner and less creamy, often requiring stabilizers or thickeners to mimic the texture of full-fat varieties.
Full-Fat Yogurt: Benefits in Cooking and Creaminess
Full-fat yogurt provides superior creaminess and richness, making it ideal for cooking applications that benefit from a smooth, velvety texture. Its higher fat content enhances mouthfeel and flavor, contributing to better emulsification in sauces, dressings, and baked goods. Choosing full-fat yogurt can improve the overall sensory experience of dishes by adding natural creaminess without the need for additional fats or thickeners.
Low-Fat Yogurt: Characteristics and Uses
Low-fat yogurt contains reduced milk fat, resulting in a lighter texture while maintaining a creamy mouthfeel through added stabilizers or protein content. It offers versatility in recipes, providing a rich consistency without the calorie density of full-fat options. Commonly used in smoothies, dressings, and desserts, low-fat yogurt balances creaminess with lower saturated fat levels for health-conscious consumers.
Taste Test: Creaminess Comparison Between Fat Levels
Full-fat yogurt delivers a richer, creamier texture due to its higher fat content, enhancing mouthfeel and flavor intensity in taste tests. Low-fat yogurt, while lighter and lower in calories, often lacks the same smoothness and depth, leading to a less satisfying creamy experience. Fat plays a crucial role in the sensory perception of yogurt, making full-fat varieties preferred for creaminess among consumers.
Impact on Cooking Results: Full-Fat vs Low-Fat Yogurt
Full-fat yogurt enhances creaminess in cooking due to its higher fat content, resulting in richer sauces and smoother textures. Low-fat yogurt, with reduced fat, can lead to a thinner consistency and may curdle more easily under heat, affecting dish stability. Chefs prefer full-fat yogurt for recipes requiring creamy texture and better emulsification during cooking.
Nutritional Differences and Their Role in Creaminess
Full-fat yogurt contains higher levels of milk fat, contributing to a richer, creamier texture compared to low-fat yogurt, which has reduced fat content that often results in a thinner consistency. The fat content in full-fat yogurt enhances mouthfeel and flavor, while low-fat varieties may compensate with added thickeners or stabilizers to mimic creaminess. Nutritionally, full-fat yogurt provides more calories and fat-soluble vitamins like A and D, whereas low-fat options offer lower calorie counts, making the choice dependent on dietary preferences and desired creaminess levels.
Best Recipes for Each Type of Yogurt
Full-fat yogurt offers rich creaminess ideal for indulgent desserts, creamy dressings, and smooth dips, enhancing texture and flavor in recipes like tzatziki and parfaits. Low-fat yogurt provides a lighter, tangier option perfect for health-conscious recipes such as smoothies, sauces, and baked goods where moisture without heaviness is desired. Each type complements different culinary uses, with full-fat excelling in richness and low-fat benefiting calorie-controlled dishes.
Choosing the Right Yogurt for Maximum Creaminess
Full-fat yogurt contains higher milk fat content, providing a naturally rich and creamy texture ideal for recipes requiring smooth consistency. Low-fat yogurt, while lower in calories and fat, often lacks the same dense mouthfeel and may contain stabilizers to mimic creaminess. Selecting full-fat yogurt enhances creaminess organically, making it the preferred choice for dishes like smoothies, dressings, and desserts where texture is paramount.
Full-fat yogurt vs low-fat yogurt for creaminess Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com