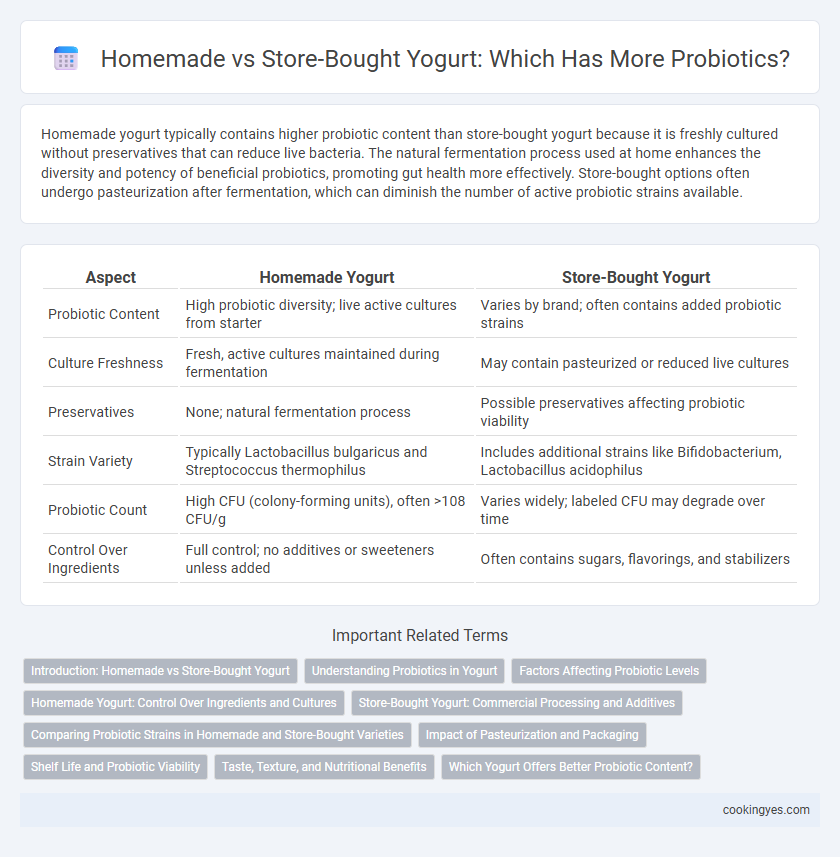
Homemade yogurt typically contains higher probiotic content than store-bought yogurt because it is freshly cultured without preservatives that can reduce live bacteria. The natural fermentation process used at home enhances the diversity and potency of beneficial probiotics, promoting gut health more effectively. Store-bought options often undergo pasteurization after fermentation, which can diminish the number of active probiotic strains available.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Homemade Yogurt | Store-Bought Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Probiotic Content | High probiotic diversity; live active cultures from starter | Varies by brand; often contains added probiotic strains |
| Culture Freshness | Fresh, active cultures maintained during fermentation | May contain pasteurized or reduced live cultures |
| Preservatives | None; natural fermentation process | Possible preservatives affecting probiotic viability |
| Strain Variety | Typically Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus | Includes additional strains like Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus acidophilus |
| Probiotic Count | High CFU (colony-forming units), often >108 CFU/g | Varies widely; labeled CFU may degrade over time |
| Control Over Ingredients | Full control; no additives or sweeteners unless added | Often contains sugars, flavorings, and stabilizers |
Introduction: Homemade vs Store-Bought Yogurt
Homemade yogurt often contains a higher diversity of probiotics due to the use of fresh starter cultures and controlled fermentation time. Store-bought yogurt may have added preservatives and varied probiotic strains, but the viability and concentration of live cultures can be inconsistent. Choosing homemade yogurt ensures a richer probiotic profile, promoting better gut health through naturally occurring beneficial bacteria.
Understanding Probiotics in Yogurt
Homemade yogurt often contains higher levels of live probiotics compared to many store-bought varieties, which may be pasteurized after fermentation, reducing beneficial bacteria. Probiotics like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus play a crucial role in improving gut health and immune response. Selecting yogurt with active cultures labeled on the packaging ensures effective probiotic intake, especially when aiming for digestive benefits.
Factors Affecting Probiotic Levels
Homemade yogurt typically contains higher probiotic levels due to the use of live bacterial cultures and shorter processing times, which preserve beneficial microbes. Store-bought yogurt often undergoes pasteurization and extended shelf life management, reducing viable probiotic counts. Factors affecting probiotic levels include fermentation temperature, duration, bacterial strain, and storage conditions, all of which influence the survival and activity of probiotics in yogurt.
Homemade Yogurt: Control Over Ingredients and Cultures
Homemade yogurt offers superior control over probiotic strains by allowing the use of specific live cultures such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which are essential for gut health and digestion. Unlike store-bought options that may contain added sugars, preservatives, and unknown bacterial strains, homemade yogurt ensures purity and customization of probiotic content. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of probiotics, promoting a balanced microbiome and improved immune function.
Store-Bought Yogurt: Commercial Processing and Additives
Store-bought yogurt often undergoes commercial processing that can reduce its natural probiotic content compared to homemade yogurt. Many commercial brands add stabilizers, sweeteners, and preservatives that may impact the viability of live bacterial cultures. Despite fortification in some cases, homemade yogurt typically offers higher concentrations of diverse probiotics like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus due to minimal processing and fresher fermentation.
Comparing Probiotic Strains in Homemade and Store-Bought Varieties
Homemade yogurt typically contains a limited variety of probiotic strains, often dominated by Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, due to the starter culture used. Store-bought yogurts frequently feature a broader spectrum of probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Lactobacillus casei, which can enhance gut microbiota diversity. The diversity and concentration of probiotics in store-bought options often provide more consistent health benefits compared to homemade versions.
Impact of Pasteurization and Packaging
Homemade yogurt typically contains higher probiotic content due to the absence of pasteurization, which can destroy beneficial bacteria found in store-bought varieties. Store-bought yogurt often undergoes heat treatment and packaging in airtight containers, reducing live cultures for extended shelf life. The impact of pasteurization and packaging methods directly affects the viability and diversity of probiotics in yogurt products.
Shelf Life and Probiotic Viability
Homemade yogurt often contains higher probiotic viability due to fresher live cultures compared to many store-bought options, which may undergo pasteurization or refrigeration periods that reduce bacterial activity. The shelf life of homemade yogurt typically ranges from 7 to 14 days under proper refrigeration, preserving its probiotic potency, whereas store-bought yogurt usually has a longer shelf life due to preservatives but may have diminished live cultures. Maintaining yogurt at consistent refrigeration temperatures around 4degC (39degF) is critical for optimizing probiotic survival in both homemade and commercial products.
Taste, Texture, and Nutritional Benefits
Homemade yogurt offers a richer probiotic profile due to the use of live cultures that are often fresher and more diverse than those in store-bought yogurt, enhancing gut health and digestion. The taste of homemade yogurt is typically tangier and creamier, with a customizable texture that can be adjusted by fermentation time, contrasting with the more consistent but sometimes overly processed flavor and texture of commercial products. Nutritionally, homemade yogurt often contains fewer additives, preservatives, and sugars, providing a more natural source of protein, calcium, and essential vitamins crucial for bone health and overall wellness.
Which Yogurt Offers Better Probiotic Content?
Homemade yogurt typically contains higher and more diverse probiotic strains compared to many store-bought varieties, which often undergo heat treatment that reduces live cultures. Strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum thrive better in homemade yogurt due to controlled fermentation conditions. Choosing homemade yogurt ensures a richer probiotic profile, enhancing gut health more effectively than some commercial options.
Homemade yogurt vs store-bought yogurt for probiotic content Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com