Yogurt starter culture consists of specific live bacteria strains, such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which are essential for controlled and consistent fermentation. Commercial starters often contain standardized, high-quality bacteria blends that ensure reliable acidification, texture, and flavor development in yogurt production. Using a commercial starter for fermentation improves batch consistency and reduces contamination risks compared to traditional yogurt starter cultures derived from previous yogurt batches.
Table of Comparison
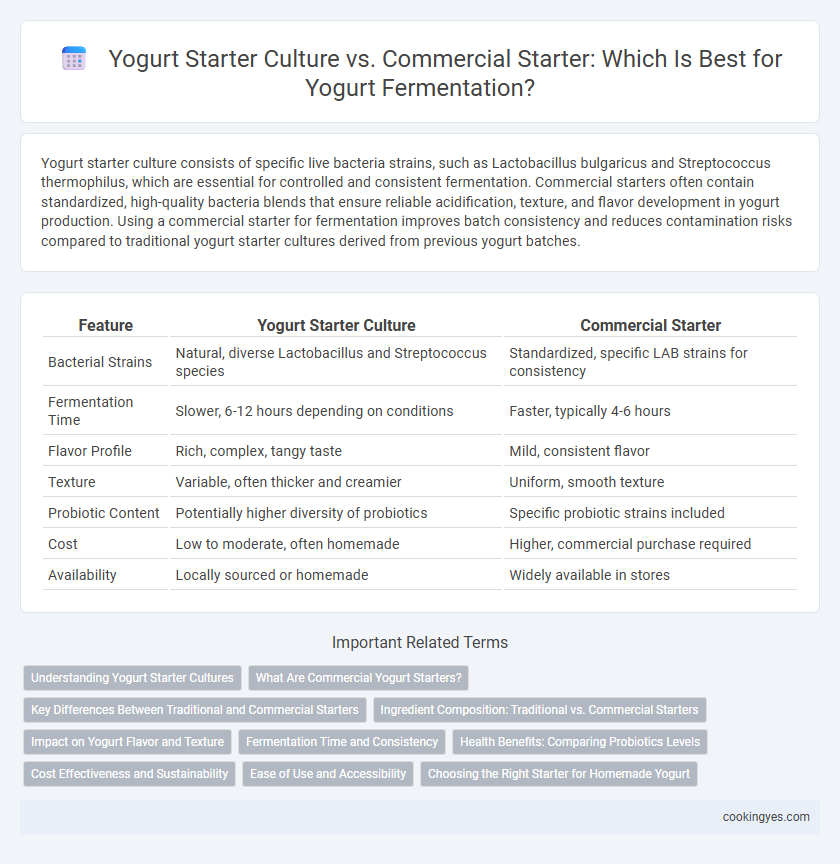
| Feature | Yogurt Starter Culture | Commercial Starter |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Strains | Natural, diverse Lactobacillus and Streptococcus species | Standardized, specific LAB strains for consistency |
| Fermentation Time | Slower, 6-12 hours depending on conditions | Faster, typically 4-6 hours |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, complex, tangy taste | Mild, consistent flavor |
| Texture | Variable, often thicker and creamier | Uniform, smooth texture |
| Probiotic Content | Potentially higher diversity of probiotics | Specific probiotic strains included |
| Cost | Low to moderate, often homemade | Higher, commercial purchase required |
| Availability | Locally sourced or homemade | Widely available in stores |
Understanding Yogurt Starter Cultures
Yogurt starter cultures consist of live microorganisms such as *Lactobacillus bulgaricus* and *Streptococcus thermophilus*, essential for initiating fermentation and developing yogurt's texture and flavor. Commercial starters often contain standardized, carefully selected strains that ensure consistent fermentation times and product quality. Understanding the specific bacterial strains and their interactions is crucial for optimizing yogurt fermentation and achieving desired probiotic benefits.
What Are Commercial Yogurt Starters?
Commercial yogurt starters contain a carefully selected blend of live bacterial strains, primarily Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, designed to ensure consistent fermentation and optimal texture and flavor. These starters are manufactured under controlled conditions to provide reliable acidification rates, enhanced probiotic benefits, and standardized yogurt quality for both home and industrial production. Unlike traditional yogurt starter cultures sourced from previous batches, commercial starters offer precise microbial composition and stability, reducing batch variability and contamination risks.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Commercial Starters
Traditional yogurt starter cultures primarily consist of naturally occurring Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus strains, promoting rich flavor and probiotic benefits. In contrast, commercial starters often include genetically selected or engineered bacterial strains designed for consistent fermentation time, texture, and shelf life. Key differences lie in microbial diversity, fermentation control, and the resulting yogurt's sensory and health properties.
Ingredient Composition: Traditional vs. Commercial Starters
Traditional yogurt starter cultures contain live, active strains of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which naturally ferment milk into yogurt with unique texture and flavor profiles. Commercial starters often include standardized blends of these primary bacteria along with additional probiotic strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, or other beneficial microbes to enhance health benefits and fermentation consistency. Ingredient composition in traditional starters emphasizes natural microbial diversity, while commercial starters prioritize controlled, reproducible fermentation and targeted functional properties.
Impact on Yogurt Flavor and Texture
Yogurt starter cultures, often containing specific strains like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, produce a distinctive tangy flavor and creamy texture due to precise bacterial activity during fermentation. Commercial starters may include a broader mix of probiotic strains, enhancing variety in flavor profiles but sometimes resulting in less consistent texture and acidity levels. The choice between yogurt starter and commercial starter significantly influences the balance of taste complexity and smooth, firm texture in the final product.
Fermentation Time and Consistency
Yogurt starter culture typically results in faster fermentation times, often completing within 4 to 6 hours, while commercial starters may require longer periods depending on their formulation. The starter culture's specific bacterial strains, such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, influence the consistency, producing a thicker, creamier texture compared to some commercial starters which can yield a more variable consistency. Controlled fermentation using yogurt starter cultures ensures uniform acidity and optimal viscosity, crucial for high-quality homemade yogurt.
Health Benefits: Comparing Probiotics Levels
Yogurt starter cultures typically contain a higher concentration and diversity of live probiotics such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which enhance gut health and improve digestion more effectively than many commercial starters. Commercial yogurt starters may use stabilized or heat-treated strains, resulting in lower probiotic viability and reduced health benefits. Consuming homemade yogurt with authentic starter cultures promotes stronger immune function and better nutrient absorption due to the presence of robust, active probiotic colonies.
Cost Effectiveness and Sustainability
Yogurt starter culture offers cost-effective fermentation by allowing multiple reuse cycles, reducing the need for frequent purchases compared to commercial starters. Its natural microbial diversity enhances sustainability through minimal processing and lower environmental impact, whereas commercial starters often involve industrial-scale production with higher energy consumption. Choosing yogurt starter culture supports eco-friendly practices and long-term savings without compromising product quality.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
Yogurt starter culture offers ease of use with pre-measured live bacteria, enabling consistent fermentation and reliable results, making it accessible for beginners. Commercial starters often come in convenient single-use packets that simplify the process further but may contain fewer strain varieties compared to specialized yogurt starter cultures. Both options provide accessible fermentation methods, with commercial starters typically more readily available in supermarkets while yogurt starter cultures can be sourced from specialty suppliers or homemade.
Choosing the Right Starter for Homemade Yogurt
Selecting the right starter for homemade yogurt is crucial for achieving desired texture and flavor; yogurt starter cultures typically contain live, active bacteria such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which are essential for fermentation. Commercial starters often offer convenience and consistency but may include additional strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus or Bifidobacterium for probiotic benefits. For optimal homemade yogurt, choose a starter with proven live cultures tailored to your taste preference and fermentation time, ensuring creamy texture and balanced tanginess.
Yogurt starter culture vs commercial starter for fermentation Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com