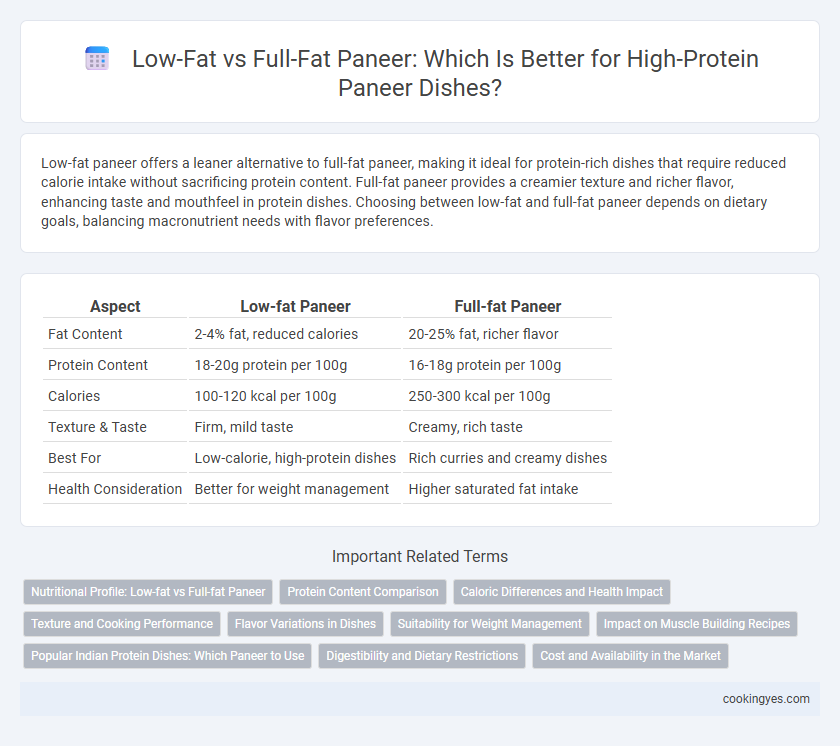
Low-fat paneer offers a leaner alternative to full-fat paneer, making it ideal for protein-rich dishes that require reduced calorie intake without sacrificing protein content. Full-fat paneer provides a creamier texture and richer flavor, enhancing taste and mouthfeel in protein dishes. Choosing between low-fat and full-fat paneer depends on dietary goals, balancing macronutrient needs with flavor preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Low-fat Paneer | Full-fat Paneer |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 2-4% fat, reduced calories | 20-25% fat, richer flavor |
| Protein Content | 18-20g protein per 100g | 16-18g protein per 100g |
| Calories | 100-120 kcal per 100g | 250-300 kcal per 100g |
| Texture & Taste | Firm, mild taste | Creamy, rich taste |
| Best For | Low-calorie, high-protein dishes | Rich curries and creamy dishes |
| Health Consideration | Better for weight management | Higher saturated fat intake |
Nutritional Profile: Low-fat vs Full-fat Paneer
Low-fat paneer contains significantly fewer calories and saturated fats, making it ideal for protein dishes aimed at weight management and heart health without compromising on protein content. Full-fat paneer boasts higher levels of fat-soluble vitamins like A and D, alongside a creamier texture that enhances flavor and satiety in dishes. When choosing between low-fat and full-fat paneer, consider the balance of macronutrients to match dietary goals while maintaining the high-quality casein protein essential for muscle repair and growth.
Protein Content Comparison
Low-fat paneer contains approximately 18 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a lean option for high-protein dishes, whereas full-fat paneer offers around 16 grams of protein per 100 grams with higher fat content. The reduced fat in low-fat paneer supports muscle building and recovery without the extra calories from fat. Choosing low-fat paneer optimizes protein intake in meals aimed at weight management and fitness goals.
Caloric Differences and Health Impact
Low-fat paneer contains significantly fewer calories than full-fat paneer, making it a preferred choice for calorie-conscious individuals aiming to maintain or lose weight. Despite the lower fat content, low-fat paneer delivers a comparable amount of high-quality protein, essential for muscle repair and growth in protein-rich dishes. Choosing low-fat paneer over full-fat can reduce saturated fat intake, supporting heart health while still providing vital nutrients like calcium and phosphorus.
Texture and Cooking Performance
Low-fat paneer has a firmer, less creamy texture compared to full-fat paneer, making it ideal for dishes requiring a more robust consistency. Full-fat paneer melts more smoothly and retains moisture better during cooking, enhancing richness and mouthfeel in protein-rich dishes. Choosing between the two depends on the desired texture and cooking method to optimize protein content and culinary outcome.
Flavor Variations in Dishes
Low-fat paneer offers a milder taste and firmer texture, making it ideal for protein dishes that benefit from subtle flavor profiles and lower calorie content. Full-fat paneer contains richer creaminess and a buttery taste, enhancing the depth and mouthfeel of dishes like curries and grilled items. Choosing between low-fat and full-fat paneer significantly impacts the overall flavor intensity and nutritional balance in protein-rich recipes.
Suitability for Weight Management
Low-fat paneer contains significantly fewer calories and saturated fats compared to full-fat paneer, making it an ideal choice for weight management and protein-rich dishes. Its high protein content supports muscle maintenance while reducing overall fat intake, which helps in fat loss and metabolic health. Full-fat paneer, while richer in taste, may contribute to higher calorie consumption, thus less suitable for calorie-restricted diets aimed at weight control.
Impact on Muscle Building Recipes
Low-fat paneer contains reduced fat content while maintaining high-quality protein essential for muscle repair and growth, making it ideal for calorie-conscious muscle-building recipes. Full-fat paneer offers a richer taste and higher calorie density, providing additional energy but with increased fat content that may affect macros for lean muscle goals. Choosing between low-fat and full-fat paneer depends on individual dietary needs and muscle-building priorities, balancing protein intake with calorie and fat management.
Popular Indian Protein Dishes: Which Paneer to Use
Low-fat paneer offers a leaner protein option ideal for calorie-conscious dishes like palak paneer and paneer tikka, maintaining high protein content while reducing fat intake. Full-fat paneer provides a richer taste and creamier texture, enhancing dishes such as paneer butter masala and shahi paneer with higher fat and calorie levels. Choosing between low-fat and full-fat paneer depends on dietary goals and desired flavor intensity in popular Indian protein recipes.
Digestibility and Dietary Restrictions
Low-fat paneer offers easier digestibility compared to full-fat paneer, making it a preferred choice for those with sensitive stomachs or lactose intolerance. It provides a high protein content with reduced saturated fats, suitable for dietary restrictions like low-cholesterol or weight management diets. Full-fat paneer, while richer in flavor and essential fatty acids, may be less ideal for individuals requiring strict fat intake control.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Low-fat paneer generally costs more than full-fat paneer due to the additional processing required to reduce fat content, affecting overall market availability. Full-fat paneer is widely available in most local markets and grocery stores, making it a more accessible option for protein-rich dishes. Consumers seeking affordable and readily available protein sources often prefer full-fat paneer despite its higher fat content.
Low-fat Paneer vs Full-fat Paneer for protein dishes Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com