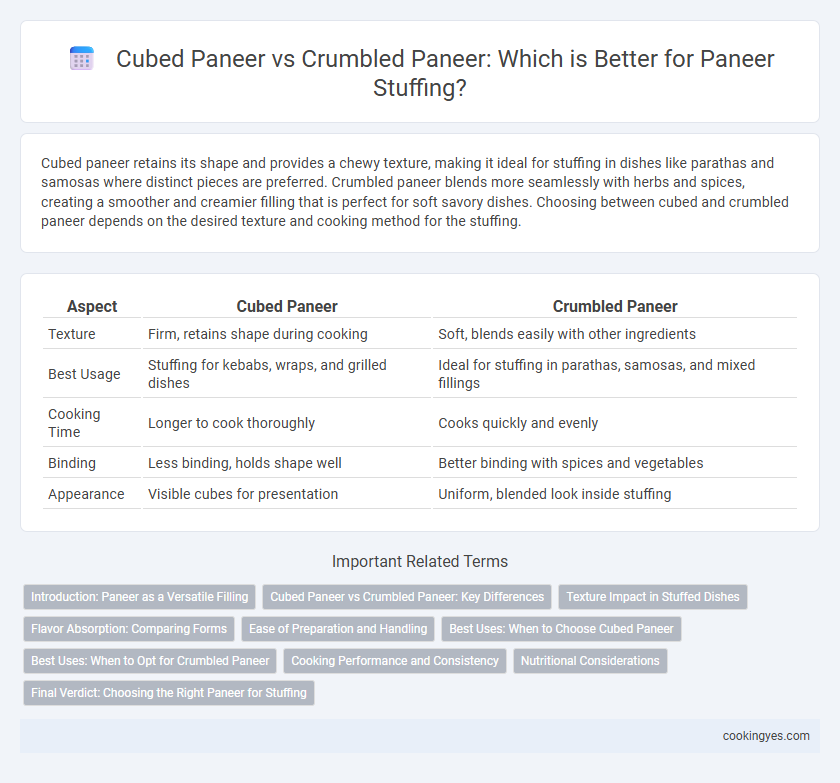
Cubed paneer retains its shape and provides a chewy texture, making it ideal for stuffing in dishes like parathas and samosas where distinct pieces are preferred. Crumbled paneer blends more seamlessly with herbs and spices, creating a smoother and creamier filling that is perfect for soft savory dishes. Choosing between cubed and crumbled paneer depends on the desired texture and cooking method for the stuffing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cubed Paneer | Crumbled Paneer |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Firm, retains shape during cooking | Soft, blends easily with other ingredients |
| Best Usage | Stuffing for kebabs, wraps, and grilled dishes | Ideal for stuffing in parathas, samosas, and mixed fillings |
| Cooking Time | Longer to cook thoroughly | Cooks quickly and evenly |
| Binding | Less binding, holds shape well | Better binding with spices and vegetables |
| Appearance | Visible cubes for presentation | Uniform, blended look inside stuffing |
Introduction: Paneer as a Versatile Filling
Paneer, a fresh Indian cheese known for its mild flavor and firm texture, serves as a versatile filling in various dishes. Cubed paneer maintains its shape and provides a satisfying bite, making it ideal for stuffed parathas and wraps. Crumbled paneer offers a softer texture that blends seamlessly with spices and vegetables, perfect for samosas and stuffing mixtures.
Cubed Paneer vs Crumbled Paneer: Key Differences
Cubed paneer retains its shape and provides a firm texture ideal for stuffing in parathas or kebabs, offering clear, distinct bites of cheese. Crumbled paneer is softer and blends seamlessly with spices and vegetables, creating a cohesive filling often used in dishes like stuffed peppers or koftas. The choice between cubed and crumbled paneer depends on the desired texture and consistency of the stuffing, with cubed paneer enhancing bite and crumbled paneer enhancing creaminess.
Texture Impact in Stuffed Dishes
Cubed paneer provides a firm, chewy texture that holds its shape well during cooking, making it ideal for stuffed dishes where distinct pieces are preferred. Crumbled paneer offers a softer, more crumbly texture that blends seamlessly with other filling ingredients, creating a creamy, cohesive stuffing. The choice between cubed and crumbled paneer significantly impacts the mouthfeel and structural integrity of paneer-stuffed culinary preparations.
Flavor Absorption: Comparing Forms
Cubed paneer retains its texture and absorbs marinades more slowly, making it ideal for stuffing that requires distinct cheese bites and balanced flavor release. Crumbled paneer, with its increased surface area, soaks up spices and sauces rapidly, intensifying the overall flavor profile in stuffed dishes. Choosing between cubed and crumbled paneer depends on whether a firmer texture or enhanced flavor absorption is preferred in the stuffing.
Ease of Preparation and Handling
Cubed paneer offers ease of preparation and handling, as it maintains its shape during stuffing and cooking, providing a firm texture that holds fillings securely. Crumbled paneer, while softer and easier to mix with spices and other ingredients, can be more challenging to manage due to its tendency to break apart and require gentle handling to avoid becoming mushy. Choosing between cubed and crumbled paneer depends on the desired texture and the specific stuffing technique used in dishes like stuffed parathas or paneer-stuffed peppers.
Best Uses: When to Choose Cubed Paneer
Cubed paneer retains its shape and firmness, making it ideal for stuffing dishes like stuffed parathas, bell peppers, or paneer-stuffed parathas where distinct texture is desired. Its solid form allows for even cooking without disintegration, perfect for recipes requiring intact pieces that absorb spices while maintaining bite. Choose cubed paneer when the stuffing benefits from visible paneer chunks and a chewy texture that contrasts with softer fillings.
Best Uses: When to Opt for Crumbled Paneer
Crumbled paneer is ideal for stuffing dishes like parathas, samosas, and stuffed peppers where a uniform texture and easy mixing with spices and herbs enhance the flavor profile. Its fine consistency allows it to blend seamlessly with other ingredients, ensuring each bite is consistent and flavorful. Choose crumbled paneer for recipes requiring soft, creamy stuffing that binds well without large chunks.
Cooking Performance and Consistency
Cubed paneer maintains its shape and provides a firm texture, making it ideal for stuffing in dishes like parathas and stuffed peppers where a distinct bite is desired. Crumbled paneer integrates smoothly into fillings, offering a creamy consistency that binds well with spices and vegetables, enhancing uniformity in taste and texture. The choice between cubed and crumbled paneer directly impacts the cooking performance by influencing moisture retention and mouthfeel in the final stuffed dish.
Nutritional Considerations
Cubed paneer retains more moisture and provides a richer texture with higher protein content per serving, making it ideal for stuffing that requires structure and bite. Crumbled paneer, while easier to mix with spices and vegetables, tends to have a slightly lower fat content due to increased surface area exposure and can absorb more flavor but may lose some protein density. Choosing between cubed and crumbled paneer impacts the nutritional balance of the dish, influencing protein retention, fat content, and texture in stuffed recipes.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Paneer for Stuffing
Cubed paneer retains its shape and provides a firmer texture suitable for stuffing in dishes like parathas and stuffed peppers, ensuring distinct bites and structural integrity. Crumbled paneer blends seamlessly with spices and other fillings, creating a creamier, more uniform stuffing ideal for soft rolls and samosas. Selecting between cubed and crumbled paneer depends on the desired texture and consistency of the final dish, with cubed paneer preferred for a chunky, textured stuffing and crumbled paneer for a smooth, cohesive filling.
Cubed Paneer vs Crumbled Paneer for stuffing Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com