Paneer and cottage cheese differ significantly in texture and preparation, impacting their suitability for curry dishes. Paneer is a firm, non-melting cheese that holds its shape well during cooking, making it ideal for rich, spicy curries. Cottage cheese, with its soft, crumbly texture and higher moisture content, tends to dissolve and lose structure, which can affect the consistency and presentation of curry recipes.
Table of Comparison
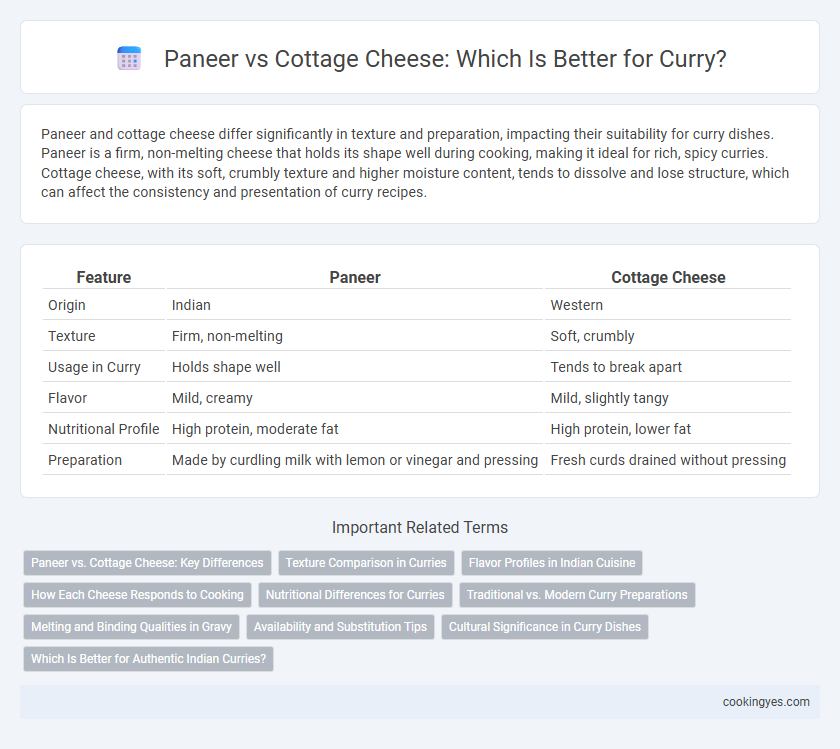
| Feature | Paneer | Cottage Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Indian | Western |
| Texture | Firm, non-melting | Soft, crumbly |
| Usage in Curry | Holds shape well | Tends to break apart |
| Flavor | Mild, creamy | Mild, slightly tangy |
| Nutritional Profile | High protein, moderate fat | High protein, lower fat |
| Preparation | Made by curdling milk with lemon or vinegar and pressing | Fresh curds drained without pressing |
Paneer vs. Cottage Cheese: Key Differences
Paneer is a fresh, non-melting Indian cheese made by curdling milk with lemon juice or vinegar, resulting in a dense and crumbly texture ideal for curries as it holds shape well during cooking. Cottage cheese, primarily consumed in Western countries, has a creamy, loose curd structure with higher moisture and curds that tend to dissolve or break apart when heated, making it less suitable for traditional Indian curries. Nutritionally, paneer offers higher protein content and lower sodium compared to cottage cheese, making it a preferred choice in rich, spiced curry preparations.
Texture Comparison in Curries
Paneer maintains a firm, crumbly texture when cooked in curries, preventing it from dissolving and ensuring it holds its shape during simmering. Cottage cheese, with its higher moisture content and softer consistency, tends to break down quickly, resulting in a creamier but less structured curry. The texture contrast significantly influences the mouthfeel and presentation, making paneer the preferred choice for dishes requiring distinct cheese pieces.
Flavor Profiles in Indian Cuisine
Paneer offers a mild, milky flavor with a firm, crumbly texture that absorbs curry spices well, making it a staple in Indian cuisine for rich, creamy dishes like palak paneer and paneer butter masala. Cottage cheese, often softer and saltier with a more granular texture, tends to break down quicker in curries, resulting in a less distinct texture and muted spice absorption. The balanced, subtle taste of paneer complements bold Indian spices without overpowering the dish, while cottage cheese's tangier flavor may alter the traditional curry flavor profile.
How Each Cheese Responds to Cooking
Paneer maintains its firm texture and shape when cooked, making it ideal for curries that require cubed cheese to hold up during simmering and frying. Cottage cheese, with higher moisture and softer curds, tends to dissolve and lose structure in hot dishes, resulting in a creamier but less distinct texture. For curries, paneer's heat resistance and ability to absorb spices without breaking apart provide a superior cooking experience compared to cottage cheese.
Nutritional Differences for Curries
Paneer contains higher protein content and a firmer texture compared to cottage cheese, making it ideal for curries that require frying or grilling without losing shape. Cottage cheese has more moisture and lower fat, resulting in a lighter curry but less richness and creaminess than paneer. Nutritionally, paneer provides more calcium and fat, enhancing the curry's texture and flavor profile, while cottage cheese offers fewer calories and a softer consistency.
Traditional vs. Modern Curry Preparations
Paneer, a traditional Indian cheese, offers a firmer texture and subtle tang that holds well in classic curry preparations like Palak Paneer or Paneer Butter Masala, providing authentic flavor and mouthfeel. Cottage cheese, often softer and more crumbly, suits modern or fusion curries where a lighter texture and quicker melting are preferred, but may lack the structural integrity and bite of paneer. The choice between paneer and cottage cheese significantly impacts the curry's texture and authenticity, with paneer preserving traditional culinary techniques while cottage cheese aligns with contemporary adaptations.
Melting and Binding Qualities in Gravy
Paneer retains its firm texture and does not melt in curry, providing a consistent bite and excellent binding properties that help thicken the gravy without disintegrating. Cottage cheese tends to lose its shape and melts easily, resulting in a creamier texture but less structural integrity in the curry. This difference makes paneer the preferred choice for recipes requiring cubes that hold their form and contribute to a rich, cohesive sauce.
Availability and Substitution Tips
Paneer, a fresh Indian cheese made by curdling milk with lemon juice or vinegar, is widely available in South Asian grocery stores, while cottage cheese is more common in Western markets. For curries, substituting paneer with cottage cheese requires draining excess liquid to prevent a watery texture and using firmer, less curdled varieties to better mimic paneer's dense, non-melting consistency. Storing paneer in water helps maintain its softness, whereas cottage cheese is best added towards the end of cooking to avoid curdling.
Cultural Significance in Curry Dishes
Paneer holds a distinct cultural significance in Indian curry dishes, prized for its firm texture and ability to absorb rich spices, which enhances traditional recipes like palak paneer and shahi paneer. Cottage cheese, while similar in protein content, is softer and often lacks the consistency needed for authentic Indian curries, making it less favored in cultural culinary practices. The use of paneer symbolizes a connection to Indian heritage, reflecting regional culinary customs and religious dietary preferences, especially among vegetarian communities.
Which Is Better for Authentic Indian Curries?
Paneer offers a firm texture and mild flavor that holds well in authentic Indian curries, absorbing spices without breaking apart, unlike cottage cheese, which tends to be softer and crumbly. Traditional recipes favor paneer due to its ability to maintain structure during extended cooking, enhancing the curry's richness. Nutritionally, paneer also provides a higher fat content ideal for creamy sauces typical in Indian cuisine.
Paneer vs Cottage Cheese for curry Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com