Probiotic yogurt contains live, active cultures that enhance fermentation by boosting beneficial bacteria, improving digestion and gut health more effectively than regular yogurt. Regular yogurt undergoes fermentation but may lack the potent strains found in probiotic varieties, resulting in less impact on the microbiome. Choosing probiotic yogurt supports a stronger, healthier balance of gut flora through enhanced fermentation processes.
Table of Comparison
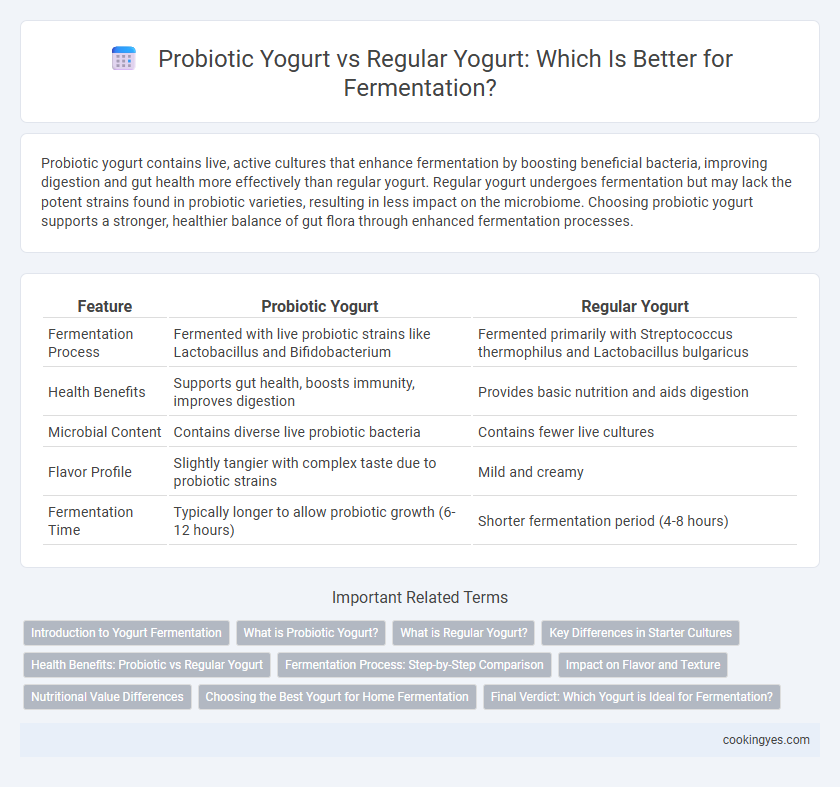
| Feature | Probiotic Yogurt | Regular Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Process | Fermented with live probiotic strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium | Fermented primarily with Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus |
| Health Benefits | Supports gut health, boosts immunity, improves digestion | Provides basic nutrition and aids digestion |
| Microbial Content | Contains diverse live probiotic bacteria | Contains fewer live cultures |
| Flavor Profile | Slightly tangier with complex taste due to probiotic strains | Mild and creamy |
| Fermentation Time | Typically longer to allow probiotic growth (6-12 hours) | Shorter fermentation period (4-8 hours) |
Introduction to Yogurt Fermentation
Probiotic yogurt contains live cultures such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance fermentation by promoting beneficial gut bacteria growth. Regular yogurt typically uses Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus strains to ferment lactose into lactic acid, giving yogurt its characteristic tangy flavor and thick texture. The presence of probiotic strains in fermented yogurt can improve digestion and boost the immune system more effectively than regular yogurt fermentation alone.
What is Probiotic Yogurt?
Probiotic yogurt contains live beneficial bacteria strains such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance gut health through improved digestion and immune support. Unlike regular yogurt, probiotic yogurt undergoes fermentation with these specific probiotics, ensuring higher concentrations of live cultures. This targeted fermentation process boosts the yogurt's function beyond basic nutrient provision, promoting a balanced microbiome and better nutrient absorption.
What is Regular Yogurt?
Regular yogurt is a dairy product fermented by lactic acid bacteria, primarily Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which convert lactose into lactic acid, giving yogurt its tangy flavor and thick texture. It typically contains live active cultures that contribute to gut health but may lack the diverse probiotic strains found in specialized probiotic yogurt. The fermentation process in regular yogurt enhances digestibility and provides essential nutrients like calcium, protein, and B vitamins.
Key Differences in Starter Cultures
Probiotic yogurt contains specific strains of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance gut health and improve digestion during fermentation. Regular yogurt primarily uses Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus as starter cultures, focusing on acidification and texture rather than probiotic benefits. The key difference lies in the inclusion of live probiotic strains in probiotic yogurt, offering added health advantages beyond basic fermentation.
Health Benefits: Probiotic vs Regular Yogurt
Probiotic yogurt contains live cultures such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance gut health by improving digestion and boosting the immune system, unlike regular yogurt that may lack these active strains. The fermentation process in probiotic yogurt produces beneficial enzymes and bioactive compounds that reduce inflammation and support nutrient absorption. Consuming probiotic yogurt regularly can aid in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for overall health, whereas regular yogurt offers limited probiotic effects.
Fermentation Process: Step-by-Step Comparison
Probiotic yogurt utilizes specific strains of live beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum, enhancing the fermentation process by producing higher levels of lactic acid and bioactive compounds compared to regular yogurt. The fermentation step for probiotic yogurt typically occurs at controlled temperatures around 40-45degC for 6-12 hours, promoting optimal bacterial growth and increasing gut-friendly microorganisms. In contrast, regular yogurt fermentation uses more generic starter cultures like Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, resulting in faster fermentation but lower probiotic content and microbial diversity.
Impact on Flavor and Texture
Probiotic yogurt contains live cultures such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance fermentation, resulting in a tangier flavor and creamier texture compared to regular yogurt that typically uses Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. The extended fermentation process in probiotic yogurt increases lactic acid production, contributing to a richer taste and thicker consistency. Texture is further influenced by the presence of exopolysaccharides produced by probiotic strains, which improve mouthfeel and viscosity.
Nutritional Value Differences
Probiotic yogurt contains live beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium, enhancing gut health and improving digestion compared to regular yogurt. It often has higher levels of active cultures and may provide additional vitamins like B12 and K2 due to fermentation by probiotics. Regular yogurt typically contains fewer live cultures and may lack these enhanced nutritional benefits, making probiotic yogurt a superior choice for supporting immune and digestive functions.
Choosing the Best Yogurt for Home Fermentation
Probiotic yogurt contains live, active cultures such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium, which enhance the fermentation process and promote gut health more effectively than regular yogurt. Regular yogurt may lack these specific strains or contain fewer live cultures, resulting in slower fermentation and less potent probiotic benefits. For home fermentation, selecting yogurt labeled with live and active cultures ensures optimal bacterial growth and a successful fermentation outcome.
Final Verdict: Which Yogurt is Ideal for Fermentation?
Probiotic yogurt contains live, active cultures such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains that enhance fermentation by promoting beneficial bacterial growth and improving gut health. Regular yogurt may lack these concentrated probiotics, resulting in slower or less efficient fermentation processes. For optimal fermentation, probiotic yogurt is ideal due to its higher microbial diversity and activity.
Probiotic yogurt vs regular yogurt for fermentation Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com