Radicchio offers a deep, robust bitterness with a slightly spicy undertone, ideal for adding bold flavor and vibrant color to salads. Endive delivers a milder bitterness with a crisp texture, providing a refreshing contrast without overpowering other ingredients. Selecting between radicchio and endive depends on the desired intensity of bitter notes and the overall balance of the salad.
Table of Comparison
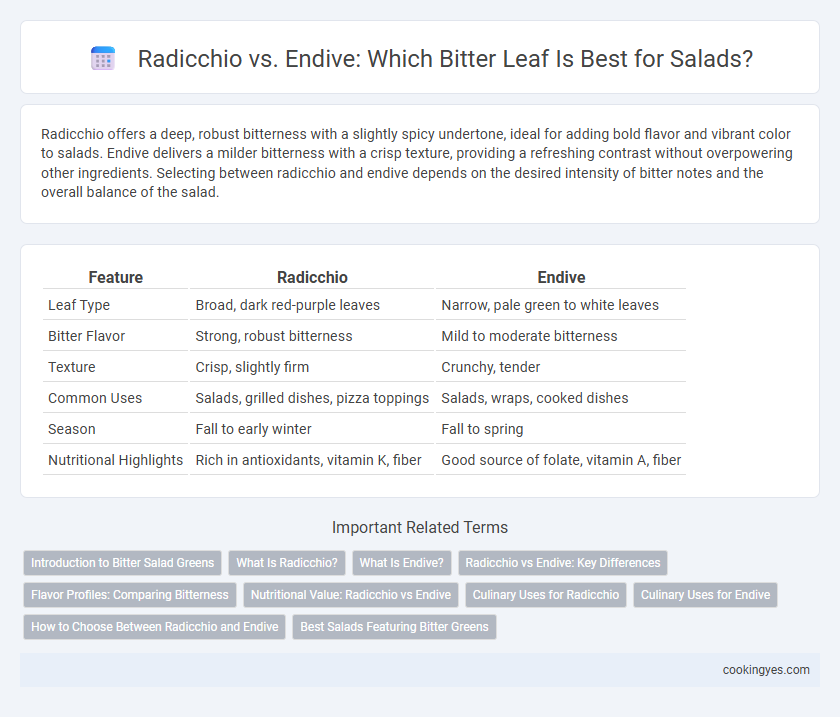
| Feature | Radicchio | Endive |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Type | Broad, dark red-purple leaves | Narrow, pale green to white leaves |
| Bitter Flavor | Strong, robust bitterness | Mild to moderate bitterness |
| Texture | Crisp, slightly firm | Crunchy, tender |
| Common Uses | Salads, grilled dishes, pizza toppings | Salads, wraps, cooked dishes |
| Season | Fall to early winter | Fall to spring |
| Nutritional Highlights | Rich in antioxidants, vitamin K, fiber | Good source of folate, vitamin A, fiber |
Introduction to Bitter Salad Greens
Radicchio and endive are popular bitter salad greens known for their distinct flavors and nutritional benefits. Radicchio features deep red leaves with a slightly spicy bitterness, rich in antioxidants and vitamins A and K. Endive offers pale, crisp leaves with a milder bitterness and is a great source of fiber and folate, making both ideal for adding complexity to salads.
What Is Radicchio?
Radicchio is a type of leafy vegetable known for its vibrant red-purple leaves and distinctive bitter flavor, often used to add contrast in salads. It belongs to the chicory family and is rich in antioxidants, vitamins K and C, and dietary fiber. Compared to endive, radicchio offers a more robust bitterness and a slightly crunchy texture, making it a popular choice for bold culinary applications.
What Is Endive?
Endive is a leafy vegetable belonging to the chicory family, known for its slightly bitter taste and crisp texture, often used in salads to add complexity and balance. It comes in two main varieties: curly endive (frisee) with frilly leaves and Belgian endive, which has pale yellow, tightly packed leaves. Unlike radicchio, which has a more robust bitterness and deep red color, endive offers a milder bitterness and a lighter, more tender leaf, making it versatile in both raw and cooked dishes.
Radicchio vs Endive: Key Differences
Radicchio and endive both belong to the chicory family but differ significantly in flavor and appearance; radicchio displays deep red-purple leaves with white veins and offers a robust, slightly spicy bitterness, while endive features pale green-yellow leaves with a more delicate, mild bitterness. Nutritionally, radicchio is rich in antioxidants such as anthocyanins, which contribute to its vibrant color and health benefits, whereas endive provides higher amounts of dietary fiber and vitamins A and K. Culinary uses vary as radicchio is often grilled or roasted to mellow its bitterness, contrasting with endive's popular raw use in salads or as a crisp edible scoop for appetizers.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Bitterness
Radicchio exhibits a robust, sharp bitterness with spicy and slightly sweet undertones, ideal for adding depth to salads. Endive delivers a milder, more delicate bitterness characterized by subtle nutty and slightly citrusy notes, making it versatile for balanced dishes. Both leafy greens offer distinct bitter profiles that complement a variety of salad ingredients depending on the desired intensity.
Nutritional Value: Radicchio vs Endive
Radicchio provides higher levels of antioxidants, including vitamin K and anthocyanins, which contribute to heart health and anti-inflammatory benefits. Endive offers a richer source of vitamin A, essential for eye health and immune function, alongside a slightly higher fiber content supporting digestion. Both leafy greens are low in calories and deliver important nutrients, but radicchio's potent antioxidant profile often makes it the preferred choice for maximizing nutrient density in bitter leaf salads.
Culinary Uses for Radicchio
Radicchio offers a distinct bitter flavor that enhances grilled salads, pasta dishes, and risottos with its vibrant color and crisp texture. Its sturdy leaves hold up well to high-heat cooking methods, making it ideal for roasting, sauteing, or adding a smoky depth to pizzas and sandwiches. Chefs often pair radicchio with sweet ingredients like balsamic vinegar or honey to balance its natural bitterness while enriching savory dishes.
Culinary Uses for Endive
Endive offers a mild bitterness and crisp texture, making it ideal for fresh salads, where it complements sweeter ingredients like fruits or nuts. Its sturdy leaves also hold up well when grilled or braised, enhancing dishes with a slightly nutty, mellow flavor. Chefs often use endive as an edible vessel for appetizers, stuffing the leaves with cheeses, seafood, or spreads to balance its nuanced bitterness.
How to Choose Between Radicchio and Endive
Radicchio and endive both offer distinct bitter flavors but differ in texture and culinary uses, making choice dependent on recipe needs. Radicchio features a denser, slightly spicy leaf ideal for grilling or roasting, while endive provides a crisp, moderately bitter taste perfect for raw salads or as a scoop for dips. Consider the desired bitterness level and preparation method, as radicchio's robust flavor suits cooked dishes, whereas endive's mild bitterness enhances fresh, crunchy salads.
Best Salads Featuring Bitter Greens
Radicchio and endive offer distinct bitter profiles that elevate salads with complex, sharp flavors. Radicchio's vibrant purple leaves bring a robust bitterness and a slightly spicy finish, making it ideal for grilled salads or balanced with sweet ingredients like oranges. Endive's crisp, pale leaves provide a milder bitterness and a crunchy texture, perfect for fresh, light salads combined with creamy dressings or nuts to enhance the taste balance.
Radicchio vs Endive for bitter leaves Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com