Dairy milk provides a creamy texture and rich flavor that make traditional ice cream smooth and indulgent, while plant-based milk offers a lighter, dairy-free alternative often favored for its lower environmental impact and suitability for lactose intolerance. Almond, coconut, and oat milks are popular plant-based bases, each contributing unique flavors and varying levels of creaminess. Choosing between dairy and plant-based milk affects not only taste and texture but also nutritional content and dietary preferences.
Table of Comparison
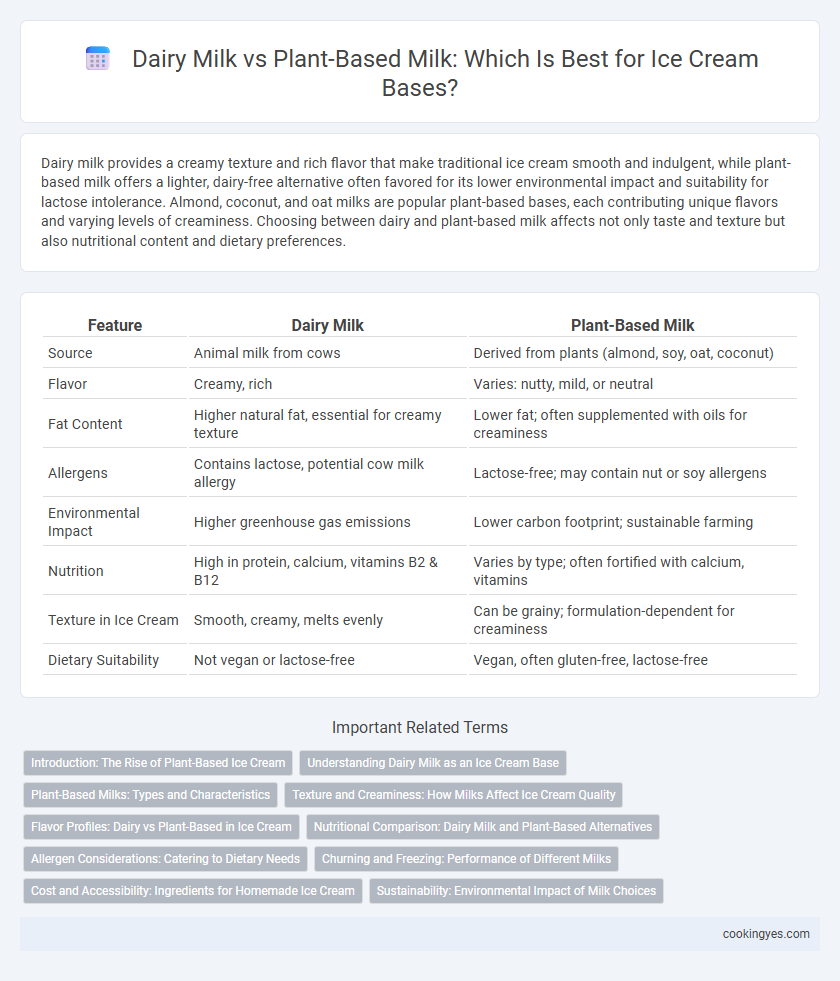
| Feature | Dairy Milk | Plant-Based Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal milk from cows | Derived from plants (almond, soy, oat, coconut) |
| Flavor | Creamy, rich | Varies: nutty, mild, or neutral |
| Fat Content | Higher natural fat, essential for creamy texture | Lower fat; often supplemented with oils for creaminess |
| Allergens | Contains lactose, potential cow milk allergy | Lactose-free; may contain nut or soy allergens |
| Environmental Impact | Higher greenhouse gas emissions | Lower carbon footprint; sustainable farming |
| Nutrition | High in protein, calcium, vitamins B2 & B12 | Varies by type; often fortified with calcium, vitamins |
| Texture in Ice Cream | Smooth, creamy, melts evenly | Can be grainy; formulation-dependent for creaminess |
| Dietary Suitability | Not vegan or lactose-free | Vegan, often gluten-free, lactose-free |
Introduction: The Rise of Plant-Based Ice Cream
Plant-based milk, derived from sources such as almonds, oats, and soy, has surged in popularity as an alternative ice cream base due to its environmental benefits and appeal to lactose-intolerant consumers. Dairy milk remains favored for its creamy texture and rich flavor, but innovations in plant-based formulations increasingly match these qualities. Market trends indicate that plant-based ice cream growth is outpacing traditional dairy, driven by consumer demand for sustainable and health-conscious options.
Understanding Dairy Milk as an Ice Cream Base
Dairy milk serves as a traditional ice cream base due to its balanced fat content and natural proteins, which contribute to a creamy texture and rich flavor. The lactose in dairy milk aids in caramelization during freezing, enhancing sweetness and mouthfeel. Its emulsifying properties help stabilize air incorporation, resulting in a smooth, consistent ice cream texture.
Plant-Based Milks: Types and Characteristics
Plant-based milks for ice cream bases include almond, coconut, oat, and soy, each offering unique characteristics that influence texture and flavor. Coconut milk provides creaminess and a rich mouthfeel due to its high fat content, while oat milk offers natural sweetness and a smooth consistency with moderate protein. Almond milk delivers a light, nutty flavor with lower fat, and soy milk contributes a creamy texture and higher protein content, making it a versatile choice for dairy-free ice cream formulations.
Texture and Creaminess: How Milks Affect Ice Cream Quality
Dairy milk provides a rich, creamy texture with higher fat content that enhances ice cream's smoothness and mouthfeel, contributing to classic creaminess. Plant-based milks such as almond, oat, or coconut often have lower protein and fat levels, which can result in a lighter texture and may require additional ingredients like stabilizers or fats to mimic traditional creaminess. The choice between dairy and plant-based milks significantly influences ice cream quality, where dairy milk excels in richness while plant-based options offer varied textures supported by formulation adjustments.
Flavor Profiles: Dairy vs Plant-Based in Ice Cream
Dairy milk provides a rich, creamy texture with naturally sweet and buttery flavor notes that enhance the traditional ice cream experience. Plant-based milks, such as almond, coconut, or oat, introduce unique nutty, fruity, or earthy undertones that create diverse and often lighter flavor profiles. The choice between dairy and plant-based milk significantly influences the ice cream's mouthfeel, sweetness, and overall taste complexity.
Nutritional Comparison: Dairy Milk and Plant-Based Alternatives
Dairy milk provides a rich source of complete proteins, calcium, and vitamin B12, essential for bone health and muscle function, while plant-based milk alternatives like almond, soy, and oat milk often have lower protein content but may be fortified with calcium and vitamins D and B12 to match nutritional profiles. Plant-based milks tend to have lower saturated fat and cholesterol levels, making them suitable for heart health, but the bioavailability of certain nutrients like calcium can vary compared to dairy milk. Choosing between dairy and plant-based milk for ice cream influences not only texture and flavor but also the balance of macronutrients and micronutrients essential for a health-conscious diet.
Allergen Considerations: Catering to Dietary Needs
Dairy milk ice cream contains common allergens like lactose and casein, posing challenges for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Plant-based milk alternatives such as almond, soy, oat, or coconut milk reduce allergen risks, making ice cream accessible to those with dietary restrictions or vegan preferences. Careful selection of plant-based bases ensures catering to diverse allergen sensitivities while maintaining creamy texture and flavor.
Churning and Freezing: Performance of Different Milks
Dairy milk creates a smoother and creamier ice cream texture due to its higher fat content, which enhances the churning process by promoting better fat crystallization and air incorporation. Plant-based milks, such as almond or oat milk, typically have lower fat and different protein compositions, often resulting in icier textures and less stable freeze-thaw cycles. Adjusting stabilizers and emulsifiers in plant-based recipes can improve freezing performance and texture to more closely mimic traditional dairy-based ice cream.
Cost and Accessibility: Ingredients for Homemade Ice Cream
Dairy milk remains a cost-effective and widely accessible option for homemade ice cream, with consistent availability in most grocery stores and a lower price point compared to many plant-based milks. Plant-based milks, such as almond, oat, and coconut, often come at a higher cost and may be less readily available in some regions, impacting overall affordability and convenience. The choice between these bases depends on dietary preferences, but dairy typically offers more economical and accessible ingredients for crafting ice cream at home.
Sustainability: Environmental Impact of Milk Choices
Dairy milk production generates significantly higher greenhouse gas emissions and requires more water and land resources compared to plant-based milk alternatives, making it less sustainable for ice cream bases. Plant-based milk options, such as almond, oat, and coconut milk, generally have a lower carbon footprint and contribute to reduced deforestation and water pollution. Choosing plant-based milk for ice cream bases supports environmental conservation and aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly food products.
Dairy milk vs Plant-based milk for ice cream base Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com