Tahini provides a rich, nutty flavor and creamy texture that defines traditional hummus, adding depth and a slightly bitter undertone. Yogurt offers a lighter, tangier alternative that creates a smoother, fresher taste while enhancing creaminess with probiotics. Choosing between tahini and yogurt impacts the hummus's flavor profile and nutritional benefits, catering to different dietary preferences.
Table of Comparison
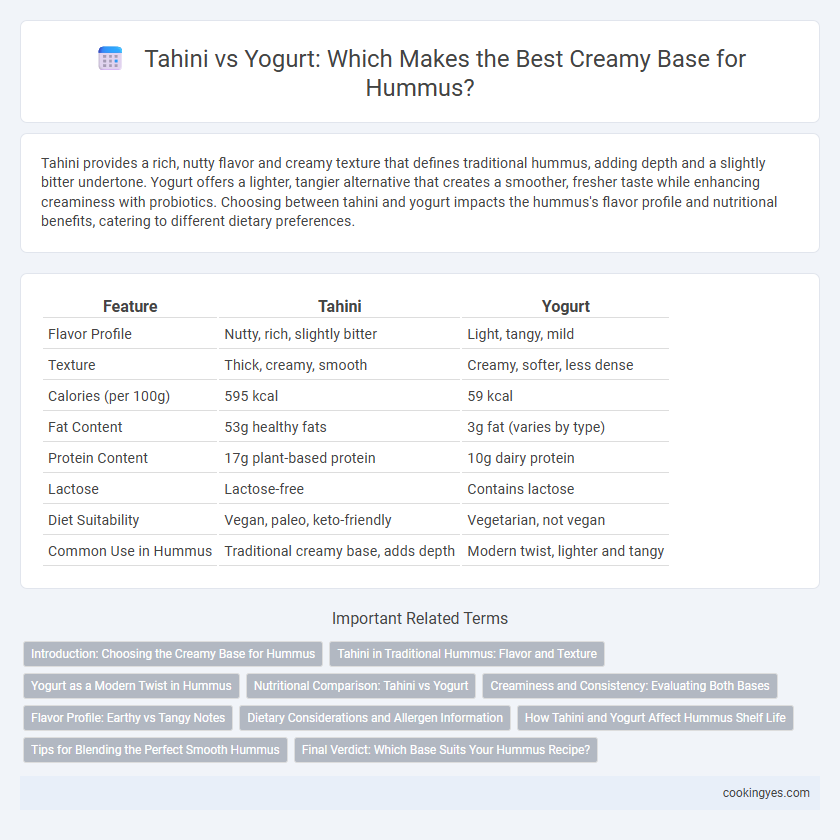
| Feature | Tahini | Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor Profile | Nutty, rich, slightly bitter | Light, tangy, mild |
| Texture | Thick, creamy, smooth | Creamy, softer, less dense |
| Calories (per 100g) | 595 kcal | 59 kcal |
| Fat Content | 53g healthy fats | 3g fat (varies by type) |
| Protein Content | 17g plant-based protein | 10g dairy protein |
| Lactose | Lactose-free | Contains lactose |
| Diet Suitability | Vegan, paleo, keto-friendly | Vegetarian, not vegan |
| Common Use in Hummus | Traditional creamy base, adds depth | Modern twist, lighter and tangy |
Introduction: Choosing the Creamy Base for Hummus
Tahini, made from ground sesame seeds, offers a rich, nutty flavor and smooth texture that enhances the traditional hummus experience. Yogurt provides a lighter, tangy creaminess that can create a refreshing variation while adding probiotics and a subtle acidity. Selecting between tahini and yogurt depends on the desired taste profile and nutritional benefits in the hummus recipe.
Tahini in Traditional Hummus: Flavor and Texture
Tahini, made from ground sesame seeds, provides traditional hummus with its rich, nutty flavor and creamy texture that is essential for authentic taste. This sesame paste enhances the smoothness without overpowering the chickpeas, creating a balanced blend characteristic of classic Middle Eastern recipes. The natural oil content in tahini contributes to a luxurious mouthfeel that yogurt-based hummus, which offers tanginess and lighter consistency, cannot replicate.
Yogurt as a Modern Twist in Hummus
Yogurt introduces a tangy, creamy texture that enhances hummus with a modern twist, offering a lighter alternative to traditional tahini. Its probiotic benefits and delicate flavor profile create a refreshing balance to the earthiness of chickpeas. Using yogurt as a creamy base redefines classic hummus while maintaining its rich nutritional value and smooth consistency.
Nutritional Comparison: Tahini vs Yogurt
Tahini, made from ground sesame seeds, is rich in healthy fats, protein, calcium, and iron, offering a nutrient-dense creamy base for hummus. Yogurt provides a lower-calorie alternative with a high content of probiotics, calcium, and protein, promoting digestive health and a lighter texture. Choosing between tahini and yogurt impacts hummus nutrition: tahini enhances heart-healthy fats and minerals, while yogurt adds beneficial bacteria and reduces calorie density.
Creaminess and Consistency: Evaluating Both Bases
Tahini provides a rich, nutty creaminess with a dense, smooth consistency that enhances the classic hummus texture. Yogurt offers a lighter, tangier creaminess, making the hummus less thick but more refreshing and slightly looser in body. Both bases affect the overall mouthfeel, with tahini delivering a more traditional, indulgent creaminess and yogurt introducing a mild, airy softness.
Flavor Profile: Earthy vs Tangy Notes
Tahini provides an earthy, nutty flavor that deepens the traditional hummus profile, offering a rich and creamy texture. Yogurt introduces a tangy, slightly acidic note that brightens and lightens the dip, giving it a fresh, vibrant taste. Choosing between tahini and yogurt affects the hummus' flavor balance, with tahini emphasizing depth and yogurt highlighting brightness.
Dietary Considerations and Allergen Information
Tahini, made from ground sesame seeds, is a rich source of healthy fats and protein but poses allergen risks for individuals with sesame allergies. Yogurt offers a dairy-based alternative that provides probiotics and calcium but may not be suitable for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Choosing between tahini and yogurt as a creamy base in hummus depends on dietary restrictions, allergen sensitivity, and nutritional preferences.
How Tahini and Yogurt Affect Hummus Shelf Life
Tahini, rich in natural oils and antioxidants, helps extend hummus shelf life by preventing oxidation and spoilage, making it a stable creamy base. Yogurt introduces moisture and active cultures, which can shorten shelf life due to increased potential for fermentation and bacterial growth. Choosing tahini over yogurt significantly enhances hummus preservation while maintaining creamy texture.
Tips for Blending the Perfect Smooth Hummus
Tahini creates a rich, nutty flavor and creamy texture in hummus, while yogurt adds a tangy, lighter consistency that can balance bold flavors. For a perfectly smooth blend, use well-cooked chickpeas soaked overnight and peel the skins to reduce graininess. Blend slowly with cold water or chickpea liquid, adding tahini or yogurt gradually to achieve the desired creaminess without over-thinning.
Final Verdict: Which Base Suits Your Hummus Recipe?
Tahini provides a rich, nutty flavor and creamy texture that enhances traditional hummus authenticity, while yogurt offers a tangy, lighter alternative that suits those seeking a fresher taste and lower fat content. Choosing between tahini and yogurt depends on desired taste profile, dietary preferences, and texture consistency in the final hummus. For a classic, velvety hummus, tahini is ideal, whereas yogurt works well for a smoother, subtly tangy variation.
Tahini vs Yogurt for creamy base in hummus Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com