Spanish Tortilla and frittata are both egg-based dishes, but the Spanish Tortilla typically features thinly sliced potatoes and onions cooked slowly in olive oil, creating a dense, hearty texture. Frittatas often include a variety of vegetables, cheeses, and meats mixed into beaten eggs and cooked more quickly, resulting in a lighter, fluffier consistency. While both dishes are versatile and can be served hot or cold, the Spanish Tortilla emphasizes simplicity and rustic flavors, whereas frittatas highlight a more flexible mix of ingredients and textures.
Table of Comparison
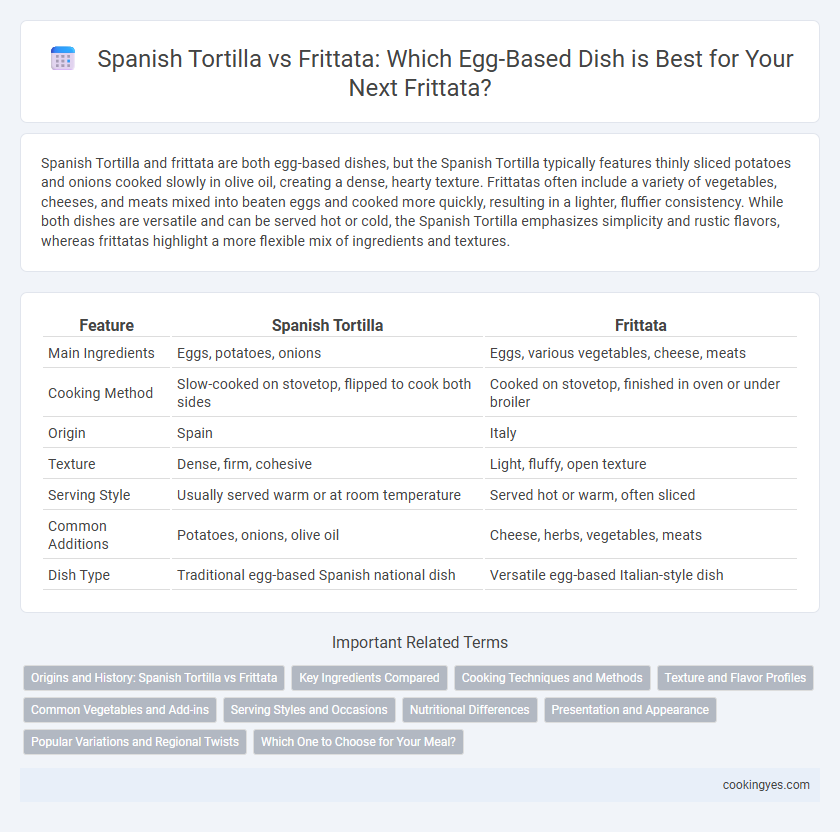
| Feature | Spanish Tortilla | Frittata |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Eggs, potatoes, onions | Eggs, various vegetables, cheese, meats |
| Cooking Method | Slow-cooked on stovetop, flipped to cook both sides | Cooked on stovetop, finished in oven or under broiler |
| Origin | Spain | Italy |
| Texture | Dense, firm, cohesive | Light, fluffy, open texture |
| Serving Style | Usually served warm or at room temperature | Served hot or warm, often sliced |
| Common Additions | Potatoes, onions, olive oil | Cheese, herbs, vegetables, meats |
| Dish Type | Traditional egg-based Spanish national dish | Versatile egg-based Italian-style dish |
Origins and History: Spanish Tortilla vs Frittata
The Spanish Tortilla originated in Spain during the early 19th century as a simple, hearty dish made with eggs, potatoes, and onions. In contrast, the Italian Frittata dates back to Ancient Rome, evolving from a versatile egg-based dish incorporating various vegetables, meats, and cheeses depending on regional availability. Both dishes reflect their cultural heritage, with the Spanish Tortilla emphasizing rustic simplicity and the Frittata showcasing culinary adaptability.
Key Ingredients Compared
Spanish tortilla primarily uses potatoes, onions, and eggs, creating a dense, hearty texture, while frittata incorporates a broader variety of vegetables, cheeses, and meats, offering more flavor flexibility. Both dishes rely on eggs as the base, but the tortilla's slow cooking technique emphasizes caramelized onions and tender potatoes, whereas the frittata is often finished under a broiler or stovetop for a lighter, fluffier consistency. The key difference lies in ingredient composition and cooking methods, where tortilla is simpler and starch-focused, and frittata includes diverse ingredients for a more complex taste profile.
Cooking Techniques and Methods
Spanish Tortilla involves slow cooking sliced potatoes and onions in olive oil before combining with eggs and gently frying the mixture, resulting in a thick, tender omelet with a slightly caramelized exterior. Frittata cooking starts by lightly sauteing vegetables or meats, then pouring beaten eggs over the fillings, finishing the dish by baking or broiling to create a fluffy, open-faced egg casserole. The Spanish Tortilla's key technique lies in the stewing of potatoes within the egg mixture, while the Frittata emphasizes layering ingredients and using oven heat to set the eggs evenly.
Texture and Flavor Profiles
Spanish Tortilla features a dense, custard-like texture achieved through slow cooking potatoes and eggs, delivering a rich, earthy flavor complemented by caramelized onions. Frittata offers a lighter, fluffier consistency with a more pronounced egg flavor, often enhanced by diverse vegetables, cheeses, and herbs folded in before baking. While both are egg-based, Spanish Tortilla emphasizes heartiness and mild sweetness, whereas Frittata prioritizes airy texture and layered, vibrant taste.
Common Vegetables and Add-ins
Spanish Tortilla traditionally features potatoes and onions as its primary vegetables, creating a dense and hearty texture, while frittatas offer a versatile base often incorporating a wider variety of vegetables such as spinach, bell peppers, mushrooms, and tomatoes. Common add-ins for frittatas also include cheeses like feta, cheddar, or goat cheese, and proteins like ham or bacon, enhancing flavor complexity. In contrast, Spanish Tortilla tends to maintain simplicity with fewer ingredients, emphasizing the harmony of eggs, potatoes, and onions.
Serving Styles and Occasions
Spanish Tortilla features thick potato layers and is often served warm or at room temperature, making it ideal for tapas bars or family gatherings. Frittata, with its flexible mix of vegetables, cheeses, and meats, is typically sliced and served hot or cold for brunches, casual dinners, or picnics. Both dishes adapt well to sharing but differ in serving styles: Tortilla's rustic presentation contrasts with the frittata's versatile and colorful portions.
Nutritional Differences
Spanish tortilla and frittata both are egg-based dishes but differ nutritionally due to ingredients and cooking methods. Spanish tortilla traditionally contains potatoes and olive oil, resulting in higher carbohydrate and fat content, while frittata incorporates various vegetables, cheeses, and meats, offering more protein and micronutrients. The caloric profile varies accordingly, with Spanish tortilla typically providing a denser energy source, whereas frittata offers a more balanced mix of macronutrients and is often lower in calories per serving.
Presentation and Appearance
Spanish Tortilla features a thick, round shape with a golden-brown crust and visible layers of potatoes and onions, offering a rustic, homestyle appearance. Frittata, by contrast, appears lighter and fluffier with a more colorful presentation due to the inclusion of a variety of vegetables and herbs, often finished under a broiler for a slightly browned top. Both dishes emphasize visual appeal through their texture and layering but differ in density and ingredient distribution impacting their overall presentation.
Popular Variations and Regional Twists
Spanish Tortilla features a thick omelette made with potatoes and onions, often cooked slowly to develop a tender texture, while the Italian Frittata incorporates a wider range of ingredients like cheeses, vegetables, and meats, mixed into beaten eggs and finished under a broiler or in the oven. Popular variations of the Spanish Tortilla include the addition of chorizo in regions of Spain such as Castilla, whereas the Frittata embraces regional twists like the inclusion of sun-dried tomatoes and basil in Southern Italy or spinach and goat cheese in Northern Italian recipes. Both dishes showcase local produce and culinary traditions, reflecting their respective Mediterranean origins and cultural influences.
Which One to Choose for Your Meal?
Spanish tortilla features thick slices of potato cooked in olive oil, creating a dense, hearty texture ideal for a filling meal, while frittata incorporates a variety of vegetables, meats, and cheeses, resulting in a lighter, more versatile dish. Choosing between the two depends on your preference for texture and flavor intensity: opt for Spanish tortilla if you want a rich, rustic experience or a frittata for a customizable, nutrient-packed option. Both dishes offer satisfying protein content and can be adapted to suit different dietary needs, making them excellent choices for any egg-based meal.
Spanish Tortilla vs Frittata for Egg-Based Dish Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com