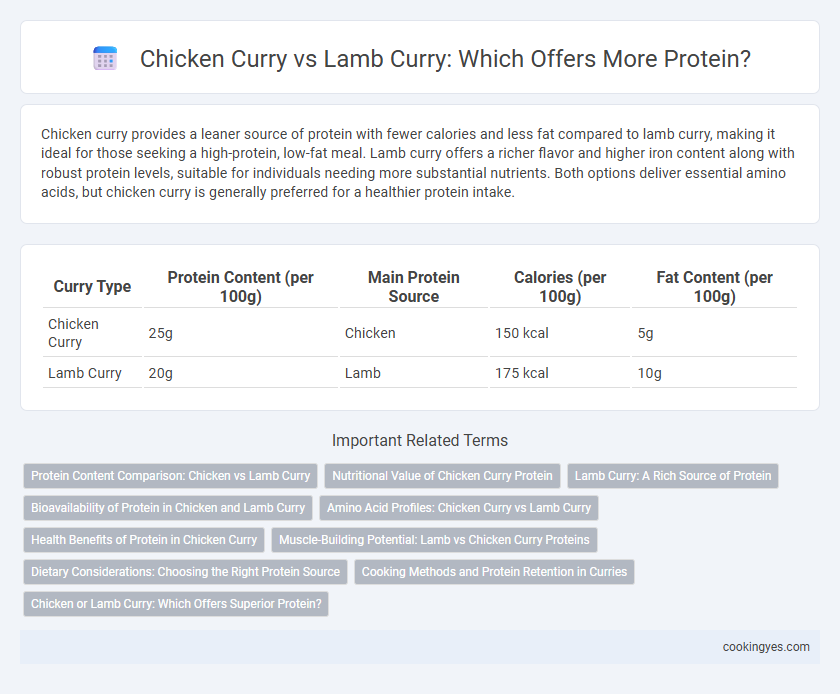
Chicken curry provides a leaner source of protein with fewer calories and less fat compared to lamb curry, making it ideal for those seeking a high-protein, low-fat meal. Lamb curry offers a richer flavor and higher iron content along with robust protein levels, suitable for individuals needing more substantial nutrients. Both options deliver essential amino acids, but chicken curry is generally preferred for a healthier protein intake.
Table of Comparison
| Curry Type | Protein Content (per 100g) | Main Protein Source | Calories (per 100g) | Fat Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken Curry | 25g | Chicken | 150 kcal | 5g |
| Lamb Curry | 20g | Lamb | 175 kcal | 10g |
Protein Content Comparison: Chicken vs Lamb Curry
Chicken curry typically contains around 25 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a lean protein option. Lamb curry provides approximately 20 to 23 grams of protein per 100 grams and includes more fat, which can affect overall calorie content. Comparing protein density, chicken curry is generally preferred for higher protein intake with lower fat levels, supporting muscle growth and maintenance.
Nutritional Value of Chicken Curry Protein
Chicken curry contains approximately 27 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a rich source of lean protein essential for muscle repair and growth. Compared to lamb curry, which provides about 25 grams of protein per 100 grams but is higher in saturated fats, chicken curry offers a healthier protein profile with lower fat content. The high protein content and lower calorie count in chicken curry make it an ideal choice for individuals seeking nutritious, high-protein meals.
Lamb Curry: A Rich Source of Protein
Lamb curry provides a rich source of high-quality protein, essential for muscle growth and repair, containing approximately 25 grams of protein per 100 grams of cooked meat. Compared to chicken curry, lamb curry offers a higher concentration of essential amino acids and vital nutrients like iron and zinc, which support immune function and overall health. The robust flavor and nutrient density of lamb curry make it a superior choice for those seeking a protein-rich meal.
Bioavailability of Protein in Chicken and Lamb Curry
Chicken curry offers highly bioavailable protein with essential amino acids that are easily absorbed and utilized by the body, making it an excellent choice for muscle repair and growth. Lamb curry provides protein with slightly lower bioavailability due to its higher fat content, which can slow digestion, but it still supplies vital nutrients like iron and zinc. Choosing chicken curry supports more efficient protein synthesis, while lamb curry delivers additional micronutrients beneficial for overall health.
Amino Acid Profiles: Chicken Curry vs Lamb Curry
Chicken curry offers a leaner source of protein with a higher concentration of essential amino acids like leucine, valine, and isoleucine, which support muscle repair and growth. Lamb curry provides a richer profile of sulfur-containing amino acids such as methionine and cysteine, important for antioxidant production and immune function. Both options deliver complete protein sources but vary slightly in their amino acid balance, affecting their suitability for different dietary needs.
Health Benefits of Protein in Chicken Curry
Chicken curry provides a high-quality source of lean protein essential for muscle growth, tissue repair, and immune system support. Compared to lamb curry, chicken curry generally contains less saturated fat, making it a heart-healthier option while still delivering complete amino acids necessary for optimal body function. Incorporating chicken curry into a balanced diet can help maintain healthy metabolism and promote sustained energy levels.
Muscle-Building Potential: Lamb vs Chicken Curry Proteins
Chicken curry contains approximately 27 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a lean source ideal for muscle repair and growth. Lamb curry provides about 25 grams of protein per 100 grams, offering slightly less protein but with a higher fat content that supports sustained energy release for intense workouts. For muscle-building potential, chicken curry's higher protein-to-fat ratio favors lean muscle development, while lamb curry delivers a richer amino acid profile beneficial for overall recovery.
Dietary Considerations: Choosing the Right Protein Source
Chicken curry typically offers a leaner protein option with lower fat content and fewer calories compared to lamb curry, making it preferable for those seeking weight management or heart-healthy diets. Lamb curry provides higher levels of essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin B12, benefiting individuals with increased micronutrient needs. Dietary considerations such as fat intake, caloric goals, and nutrient requirements should guide the choice between chicken and lamb curry as protein sources.
Cooking Methods and Protein Retention in Curries
Chicken curry typically retains more protein after cooking due to shorter cooking times and gentler methods like sauteing or simmering, which minimize protein breakdown. Lamb curry often requires longer, slow-cooking techniques such as braising or stewing to tenderize the meat, potentially leading to slight protein loss but enhancing flavor complexity. The choice of cooking method significantly impacts protein retention, with quicker methods preserving more of the original protein content found in chicken and lamb.
Chicken or Lamb Curry: Which Offers Superior Protein?
Chicken curry provides a higher protein content per serving compared to lamb curry, making it a preferred choice for those seeking lean protein sources. A typical 100g portion of cooked chicken curry offers approximately 27 grams of protein, whereas lamb curry delivers around 25 grams. In addition to protein, chicken curry tends to be lower in saturated fat, enhancing its appeal for health-conscious individuals aiming to maximize muscle growth and recovery.
Chicken curry vs Lamb curry for protein Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com