Yogurt starter consists of live bacteria strains that initiate fermentation naturally, offering unique flavor profiles and probiotic benefits. Commercial cultures are standardized mixtures of selected bacteria, ensuring consistent texture, taste, and fermentation time for large-scale production. Choosing between yogurt starter and commercial culture depends on the desired control over fermentation, flavor complexity, and batch uniformity.
Table of Comparison
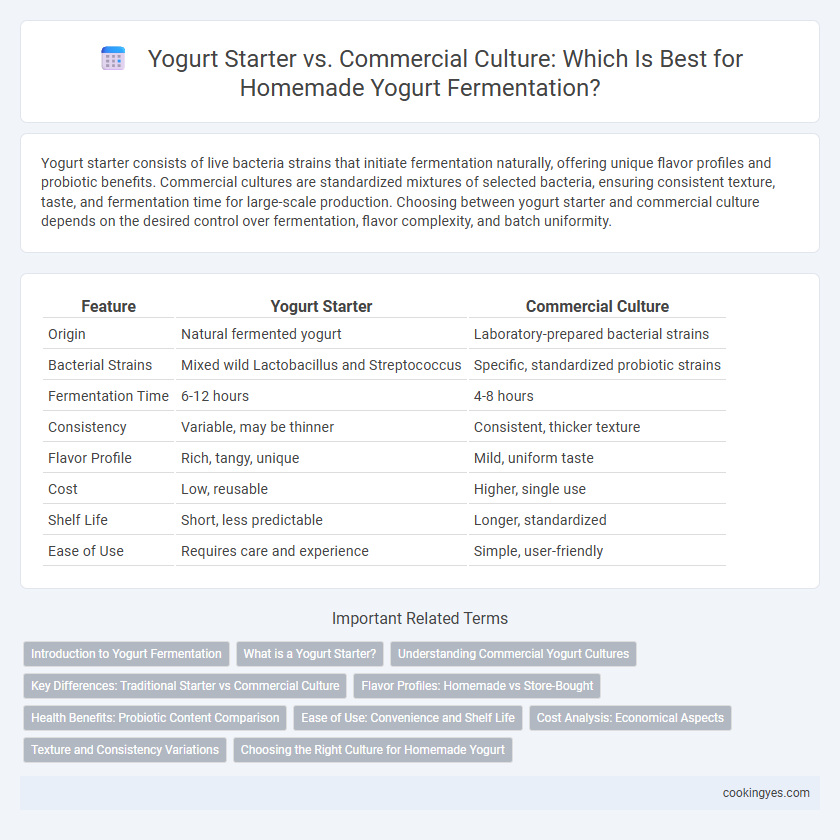
| Feature | Yogurt Starter | Commercial Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural fermented yogurt | Laboratory-prepared bacterial strains |
| Bacterial Strains | Mixed wild Lactobacillus and Streptococcus | Specific, standardized probiotic strains |
| Fermentation Time | 6-12 hours | 4-8 hours |
| Consistency | Variable, may be thinner | Consistent, thicker texture |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, tangy, unique | Mild, uniform taste |
| Cost | Low, reusable | Higher, single use |
| Shelf Life | Short, less predictable | Longer, standardized |
| Ease of Use | Requires care and experience | Simple, user-friendly |
Introduction to Yogurt Fermentation
Yogurt fermentation relies on the activity of specific bacterial cultures to convert lactose into lactic acid, resulting in a tangy texture and enhanced shelf life. Yogurt starters typically consist of live Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus strains, which ensure controlled fermentation and consistent flavor development. Commercial cultures offer standardized bacterial blends engineered for rapid acidification, improved probiotic content, and uniform product quality across large-scale production.
What is a Yogurt Starter?
A yogurt starter is a specific blend of live bacteria cultures, primarily Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, used to initiate the fermentation process. Unlike commercial cultures, yogurt starters are often natural and unprocessed, providing authentic probiotic benefits and distinct tangy flavor. These starters accelerate the transformation of milk into yogurt by producing lactic acid, which thickens the milk and creates the characteristic texture.
Understanding Commercial Yogurt Cultures
Commercial yogurt cultures consist of specific strains of bacteria such as Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, carefully selected to ensure consistent fermentation and flavor profiles. These cultures are standardized for predictable acidification rates and texture development, which is essential for large-scale yogurt production. Understanding the properties of commercial cultures enables manufacturers to control fermentation time, achieve optimal pH levels, and produce yogurt with desired creamy consistency and shelf stability.
Key Differences: Traditional Starter vs Commercial Culture
Yogurt starter typically contains live, natural bacteria strains such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which contribute to unique flavors and probiotic benefits, while commercial cultures are standardized blends formulated for consistency and faster fermentation. Traditional starters often originate from previous batches, preserving regional microbial diversity, whereas commercial cultures are mass-produced for precise fermentation control and longer shelf life. The choice between yogurt starter and commercial culture impacts texture, taste complexity, and microbial content in the final product.
Flavor Profiles: Homemade vs Store-Bought
Yogurt starters create a complex and tangy flavor profile due to diverse strains of live bacteria such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which develop slowly during fermentation. Commercial cultures often contain standardized bacterial blends designed for consistency and mild taste, resulting in less variation but reliable flavor. Homemade yogurt typically offers richer, more robust flavors influenced by fermentation time, temperature, and milk quality, while store-bought yogurt prioritizes uniform taste and shelf stability.
Health Benefits: Probiotic Content Comparison
Yogurt starters typically contain live, active probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which promote gut health and improve digestion. Commercial yogurt cultures often include additional probiotic strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium species, enhancing immune function and reducing inflammation. The diversity and concentration of probiotics in commercial cultures generally offer greater health benefits compared to traditional yogurt starters.
Ease of Use: Convenience and Shelf Life
Yogurt starters offer ease of use with pre-measured, single-use packets that simplify fermentation, requiring minimal preparation and consistent results. Commercial cultures provide a longer shelf life, often stored in a refrigerated form or freeze-dried powder, allowing extended storage without loss of potency. Convenience in yogurt production is enhanced by starters' quick activation, whereas commercial cultures offer flexibility and durability for multiple batches.
Cost Analysis: Economical Aspects
Using yogurt starter cultures is often more cost-effective than commercial cultures due to the ability to reuse and propagate the starter multiple times, significantly lowering ongoing expenses. Commercial cultures typically require frequent repurchasing and can be costly, especially for small-scale or home yogurt production. Analyzing the cost per batch reveals that yogurt starters provide better economic efficiency while maintaining consistent fermentation quality.
Texture and Consistency Variations
Yogurt starter cultures typically yield thicker, creamier yogurt with a more complex texture due to the presence of live, active bacteria like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which promote natural fermentation. Commercial cultures often include additional probiotic strains and stabilizers that enhance consistency, resulting in a smoother, more uniform texture but sometimes less tanginess compared to natural starters. Variations in fermentation time, temperature, and culture composition directly influence the yogurt's viscosity, firmness, and mouthfeel, making starter choice critical for desired texture outcomes.
Choosing the Right Culture for Homemade Yogurt
Selecting the right culture for homemade yogurt involves understanding the differences between yogurt starter and commercial cultures. Yogurt starter contains live active bacteria such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, providing a traditional, rich flavor with proven probiotic benefits. Commercial cultures offer diverse bacterial strains for specific textures and health benefits, allowing greater customization in fermentation time and yogurt consistency.
Yogurt starter vs commercial culture for fermentation Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com