Sheep's milk yogurt tends to be tangier than cow's milk yogurt due to its higher concentration of fatty acids and natural sugars, which intensify the fermentation process. The increased protein content in sheep's milk also contributes to a creamier texture that balances the tartness. Cow's milk yogurt offers a milder tang, making it a versatile choice for those who prefer a less pronounced sour flavor.
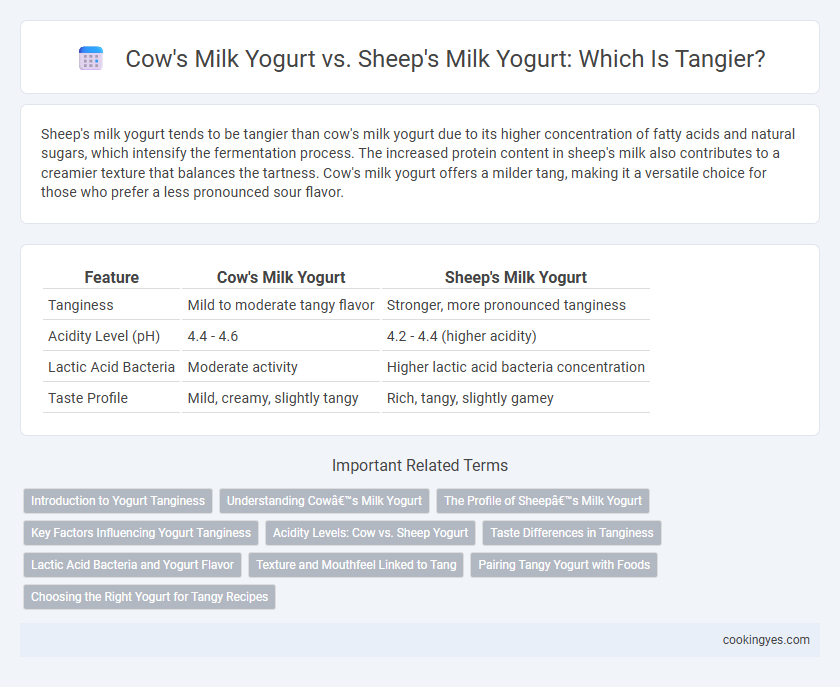
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cow's Milk Yogurt | Sheep's Milk Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Tanginess | Mild to moderate tangy flavor | Stronger, more pronounced tanginess |
| Acidity Level (pH) | 4.4 - 4.6 | 4.2 - 4.4 (higher acidity) |
| Lactic Acid Bacteria | Moderate activity | Higher lactic acid bacteria concentration |
| Taste Profile | Mild, creamy, slightly tangy | Rich, tangy, slightly gamey |
Introduction to Yogurt Tanginess
Cow's milk yogurt typically has a milder and slightly sweet tanginess due to its lower fat and protein content compared to sheep's milk yogurt. Sheep's milk yogurt offers a pronounced tangy flavor, attributed to its higher levels of lactic acid and richer composition of fats and proteins. This distinctive tanginess in sheep's milk yogurt gives it a creamier texture and more robust taste profile, preferred in many Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cuisines.
Understanding Cow’s Milk Yogurt
Cow's milk yogurt typically has a milder tanginess compared to the more pronounced and complex tartness found in sheep's milk yogurt, due to differences in fat and protein content. The higher lactose concentration in cow's milk promotes a moderate fermentation process, resulting in a smoother, less acidic flavor profile. Understanding these variations helps select the right yogurt based on desired tanginess and texture preferences.
The Profile of Sheep’s Milk Yogurt
Sheep's milk yogurt offers a richer and tangier flavor profile compared to cow's milk yogurt due to its higher fat and protein content, which enhances creaminess and intensifies acidity. The lactic acid bacteria in sheep's milk yogurt produce unique aromatic compounds, contributing to its distinctively sharp and robust tanginess. Its nutritional density includes elevated levels of calcium, vitamins B2 and B12, making it a flavorful and nutrient-rich alternative to traditional cow's milk yogurt.
Key Factors Influencing Yogurt Tanginess
Tanginess in cow's milk yogurt is primarily influenced by its lower fat content and higher lactose levels, which encourage lactic acid bacteria activity and result in a sharper flavor. Sheep's milk yogurt, richer in fat and proteins, tends to have a milder tang due to slower fermentation and increased creaminess that balances acidity. Key factors influencing yogurt tanginess include milk composition, bacterial strains used, fermentation time, and temperature control.
Acidity Levels: Cow vs. Sheep Yogurt
Sheep's milk yogurt generally has higher acidity levels compared to cow's milk yogurt, contributing to a tangier flavor profile. The increased lactic acid in sheep's milk yogurt enhances its sharpness and depth of taste, making it preferred for dishes requiring robust tartness. Cow's milk yogurt tends to be milder and less acidic, appealing to those who favor a creamy, subtle tang.
Taste Differences in Tanginess
Cow's milk yogurt typically offers a milder tanginess due to its lower fat and protein content compared to sheep's milk yogurt. Sheep's milk yogurt delivers a richer, more pronounced tangy flavor, enhanced by its higher concentration of natural sugars and lactic acid bacteria. The distinct fatty acid profile in sheep's milk contributes to a creamier texture that intensifies the perception of tanginess on the palate.
Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yogurt Flavor
Sheep's milk yogurt typically exhibits a more pronounced tanginess compared to cow's milk yogurt due to higher concentrations of lactic acid bacteria such as Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. These bacteria ferment lactose more efficiently in sheep's milk, producing greater lactic acid and enhancing yogurt flavor complexity. The rich protein and fat content in sheep's milk also contribute to a creamier texture and intensified aromatic compounds, elevating overall sensory experience.
Texture and Mouthfeel Linked to Tang
Cow's milk yogurt typically has a creamier texture with a mild tanginess, providing a smooth mouthfeel that appeals to those who prefer balanced acidity. Sheep's milk yogurt offers a denser, richer texture with a pronounced tang, delivering a more intense and lingering mouthfeel due to higher fat and protein content. The heightened tang in sheep's milk yogurt enhances its creamy texture, creating a distinct sensory experience compared to the lighter, silkier consistency of cow's milk yogurt.
Pairing Tangy Yogurt with Foods
Cow's milk yogurt typically offers a mild tanginess with a creamy texture, making it an excellent match for sweet fruits and crunchy granola. Sheep's milk yogurt has a richer, more tangy flavor due to higher fat and protein content, pairing well with savory dishes like roasted vegetables, herbs, and spicy spices. The unique acidity in sheep's milk yogurt complements bold flavors, enhancing dishes like Mediterranean mezze or spicy Indian curries.
Choosing the Right Yogurt for Tangy Recipes
Cow's milk yogurt typically offers a mild tanginess with a smooth texture, making it ideal for everyday tangy recipes and desserts. Sheep's milk yogurt has a richer, creamier consistency and a more pronounced tangy flavor due to higher protein and fat content, enhancing dishes that require a bold taste. Selecting sheep's milk yogurt elevates tangy sauces and marinades, while cow's milk yogurt maintains a balanced acidity perfect for lighter preparations.
Cow’s milk yogurt vs sheep’s milk yogurt for tanginess Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com