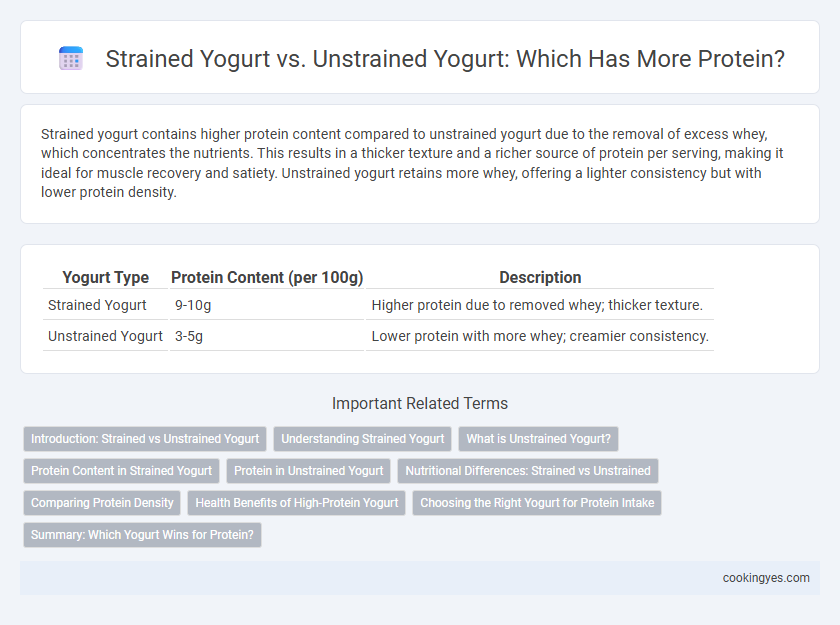
Strained yogurt contains higher protein content compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of excess whey, which concentrates the nutrients. This results in a thicker texture and a richer source of protein per serving, making it ideal for muscle recovery and satiety. Unstrained yogurt retains more whey, offering a lighter consistency but with lower protein density.
Table of Comparison
| Yogurt Type | Protein Content (per 100g) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Strained Yogurt | 9-10g | Higher protein due to removed whey; thicker texture. |
| Unstrained Yogurt | 3-5g | Lower protein with more whey; creamier consistency. |
Introduction: Strained vs Unstrained Yogurt
Strained yogurt, also known as Greek yogurt, contains significantly higher protein content compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey, resulting in a thicker texture and concentrated nutrients. Unstrained yogurt retains more whey, offering a creamier consistency but with lower protein concentration per serving. Choosing strained yogurt supports higher protein intake essential for muscle repair and satiety, while unstrained yogurt provides a softer texture with moderate protein levels.
Understanding Strained Yogurt
Strained yogurt, also known as Greek yogurt, contains significantly higher protein content than unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey during the straining process. This results in a thicker texture and concentrated nutrients, providing approximately 10 grams of protein per 100 grams compared to around 5 grams in regular yogurt. The increased protein in strained yogurt supports muscle repair and satiety, making it a preferred choice for individuals seeking higher protein intake.
What is Unstrained Yogurt?
Unstrained yogurt, also known as regular or traditional yogurt, contains whey, making it thinner and less concentrated in protein compared to strained yogurt. It typically has around 5 grams of protein per 100 grams, as the liquid whey retains some nutrients but dilutes the protein density. Unstrained yogurt is often creamier and provides more calcium due to the preserved whey content.
Protein Content in Strained Yogurt
Strained yogurt, also known as Greek yogurt, contains significantly higher protein content compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey during straining. On average, strained yogurt provides around 10 grams of protein per 100 grams, while unstrained yogurt contains approximately 4 to 5 grams per 100 grams. The concentrated protein in strained yogurt supports muscle repair and satiety, making it a popular choice for high-protein diets.
Protein in Unstrained Yogurt
Unstrained yogurt typically contains less protein compared to strained yogurt because it retains more whey, the liquid part of milk that contains fewer proteins. On average, unstrained yogurt provides around 5 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a moderate source of this essential macronutrient. Its protein content supports muscle repair and growth but is less concentrated than strained varieties like Greek yogurt, which can have nearly double the protein content.
Nutritional Differences: Strained vs Unstrained
Strained yogurt contains higher protein content compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey during straining, which concentrates the protein and reduces water content. Unstrained yogurt has a thinner consistency and lower protein density but retains more lactose and minerals. Choosing strained yogurt enhances protein intake, beneficial for muscle repair and satiety.
Comparing Protein Density
Strained yogurt contains a higher protein density compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey and excess liquid, which concentrates the protein content. Typically, strained yogurt like Greek yogurt offers about 10 grams of protein per 100 grams, whereas unstrained yogurt has around 5 grams per 100 grams. This concentration makes strained yogurt a preferred choice for those seeking a protein-rich diet.
Health Benefits of High-Protein Yogurt
Strained yogurt contains significantly higher protein levels than unstrained yogurt due to the removal of excess whey, making it an excellent choice for muscle repair and satiety. High-protein yogurt supports metabolic health by promoting sustained energy release and improving appetite control. Incorporating strained yogurt into the diet enhances bone strength and aids weight management through its rich nutrient profile and probiotic content.
Choosing the Right Yogurt for Protein Intake
Strained yogurt, often known as Greek yogurt, contains significantly higher protein content per serving compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey, resulting in a thicker texture and concentrated nutrients. Choosing Greek yogurt supports muscle repair and satiety more effectively, making it ideal for individuals seeking increased protein intake. Unstrained yogurt offers a lighter option with lower protein but retains more calcium and probiotics, suitable for those prioritizing digestion and calcium needs over protein density.
Summary: Which Yogurt Wins for Protein?
Strained yogurt contains significantly higher protein content compared to unstrained yogurt due to the removal of whey, concentrating its nutrients. Greek yogurt, a common type of strained yogurt, typically offers around 10-15 grams of protein per 100 grams serving, while unstrained yogurt contains about 3-5 grams per the same amount. For those prioritizing protein intake, strained yogurt is the superior choice for promoting muscle repair and satiety.
Strained yogurt vs unstrained yogurt for protein content Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com