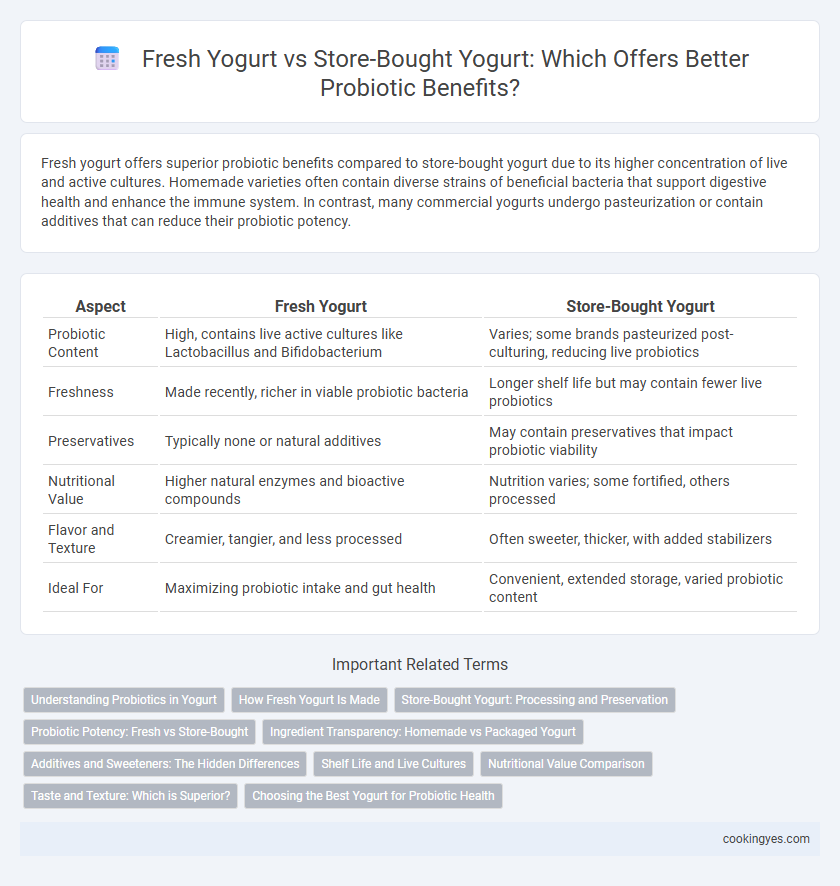
Fresh yogurt offers superior probiotic benefits compared to store-bought yogurt due to its higher concentration of live and active cultures. Homemade varieties often contain diverse strains of beneficial bacteria that support digestive health and enhance the immune system. In contrast, many commercial yogurts undergo pasteurization or contain additives that can reduce their probiotic potency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fresh Yogurt | Store-Bought Yogurt |
|---|---|---|
| Probiotic Content | High, contains live active cultures like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium | Varies; some brands pasteurized post-culturing, reducing live probiotics |
| Freshness | Made recently, richer in viable probiotic bacteria | Longer shelf life but may contain fewer live probiotics |
| Preservatives | Typically none or natural additives | May contain preservatives that impact probiotic viability |
| Nutritional Value | Higher natural enzymes and bioactive compounds | Nutrition varies; some fortified, others processed |
| Flavor and Texture | Creamier, tangier, and less processed | Often sweeter, thicker, with added stabilizers |
| Ideal For | Maximizing probiotic intake and gut health | Convenient, extended storage, varied probiotic content |
Understanding Probiotics in Yogurt
Fresh yogurt contains live cultures such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which are essential probiotics that support gut health and digestion. Store-bought yogurt often undergoes pasteurization, which can reduce the number of viable probiotics, diminishing their effectiveness. To maximize probiotic benefits, selecting yogurt labeled with "live and active cultures" is crucial for maintaining a healthy microbiome.
How Fresh Yogurt Is Made
Fresh yogurt is made by fermenting milk with live bacterial cultures, primarily Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, under controlled temperature conditions that promote the growth of beneficial probiotics. Unlike store-bought yogurt, fresh yogurt often contains higher levels of active probiotics because it is consumed shortly after preparation without extensive processing or refrigeration delays. This natural fermentation process enhances the probiotic content, supporting gut health more effectively than many commercial yogurts with added preservatives or heat treatments.
Store-Bought Yogurt: Processing and Preservation
Store-bought yogurt undergoes pasteurization and homogenization processes that can reduce the number of live probiotic cultures compared to fresh yogurt. Commercial brands often include added preservatives and stabilizers to extend shelf life, which may impact the viability of beneficial bacteria. Despite these factors, many store-bought yogurts are fortified with specific probiotic strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium to enhance gut health benefits.
Probiotic Potency: Fresh vs Store-Bought
Fresh yogurt typically contains a higher concentration of live probiotic cultures such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum compared to many store-bought varieties, which often undergo pasteurization that reduces probiotic potency. Store-bought yogurts may include added preservatives and undergo processing methods that degrade beneficial bacteria, resulting in lower colony-forming units (CFUs) per serving. For maximum probiotic benefits, consuming fresh yogurt with active and diverse microbial strains ensures enhanced gut health and improved digestion.
Ingredient Transparency: Homemade vs Packaged Yogurt
Fresh yogurt offers greater ingredient transparency as it often contains only milk and live cultures without added preservatives, sweeteners, or artificial flavors commonly found in store-bought yogurt. Packaged yogurts frequently include stabilizers, sugar, and artificial additives that may reduce the probiotic efficacy and alter the natural fermentation process. Choosing homemade yogurt ensures control over fermentation time and culture strains, maximizing probiotic potency and health benefits.
Additives and Sweeteners: The Hidden Differences
Fresh yogurt contains live probiotic cultures without artificial additives or sweeteners, preserving its natural health benefits. Store-bought yogurt often includes preservatives, stabilizers, and added sugars that can diminish probiotic efficacy and introduce unnecessary calories. Choosing fresh yogurt ensures a purer source of probiotics, supporting digestive health more effectively.
Shelf Life and Live Cultures
Fresh yogurt typically contains a higher concentration of live probiotic cultures due to minimal processing, supporting gut health more effectively than many store-bought yogurts. Store-bought yogurt often has a longer shelf life but may undergo pasteurization or contain preservatives that reduce viable probiotics. Consumers seeking maximum probiotic benefits should prioritize fresh yogurt with active live cultures labeled on the packaging for optimal gut flora support.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Fresh yogurt contains higher levels of live probiotics and fewer additives compared to store-bought yogurt, enhancing its digestive health benefits. Store-bought yogurts often include added sugars and preservatives, which can diminish their nutritional value and probiotic potency. The natural fermentation process in fresh yogurt promotes richer concentrations of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, crucial for gut health.
Taste and Texture: Which is Superior?
Fresh yogurt contains live active cultures that provide rich probiotic benefits, offering a creamy texture and tangy taste that many find superior to store-bought alternatives. Store-bought yogurt often undergoes pasteurization and may include preservatives or added sugars, which can diminish natural probiotic potency and alter flavor profiles. The taste of fresh yogurt is typically more vibrant and the texture smoother, enhancing the overall sensory experience while maximizing probiotic effectiveness.
Choosing the Best Yogurt for Probiotic Health
Fresh yogurt contains live, active cultures that provide higher probiotic benefits compared to many store-bought yogurts, which may be pasteurized or contain fewer live strains. Choosing yogurt with labels indicating "live and active cultures" ensures the presence of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, crucial for gut health. Greek yogurt and homemade varieties often have denser probiotic content, enhancing digestion and immune function more effectively than conventional processed options.
Fresh Yogurt vs Store-Bought Yogurt for Probiotic Benefits Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com