Bone broth offers a rich source of collagen, amino acids, and minerals like calcium and magnesium, which support joint health and boost the immune system. Vegetable broth provides essential vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber from various vegetables, promoting digestion and overall wellness. Choosing between bone broth and vegetable broth depends on dietary preferences and nutritional goals, with bone broth excelling in protein content and vegetable broth offering plant-based nutrients.
Table of Comparison
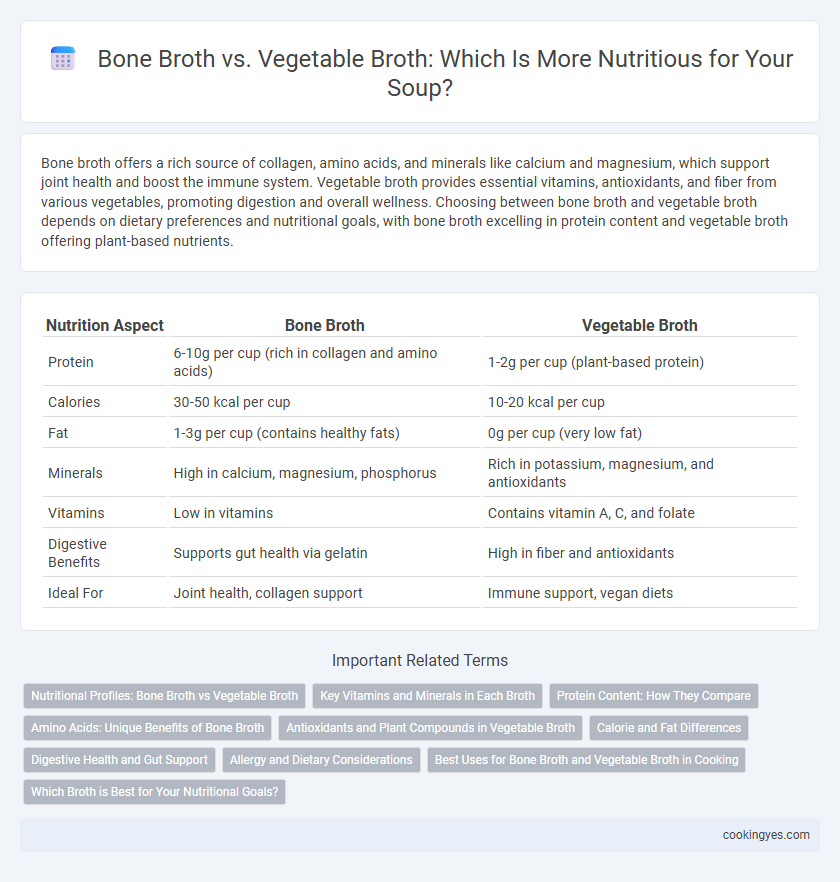
| Nutrition Aspect | Bone Broth | Vegetable Broth |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 6-10g per cup (rich in collagen and amino acids) | 1-2g per cup (plant-based protein) |
| Calories | 30-50 kcal per cup | 10-20 kcal per cup |
| Fat | 1-3g per cup (contains healthy fats) | 0g per cup (very low fat) |
| Minerals | High in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus | Rich in potassium, magnesium, and antioxidants |
| Vitamins | Low in vitamins | Contains vitamin A, C, and folate |
| Digestive Benefits | Supports gut health via gelatin | High in fiber and antioxidants |
| Ideal For | Joint health, collagen support | Immune support, vegan diets |
Nutritional Profiles: Bone Broth vs Vegetable Broth
Bone broth is rich in collagen, amino acids, and minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, supporting joint health and skin elasticity. Vegetable broth provides antioxidants, vitamins such as A, C, and K, and dietary fiber, promoting immune function and digestion. Comparing nutritional profiles, bone broth excels in protein and mineral content, while vegetable broth offers higher levels of vitamins and plant-based nutrients.
Key Vitamins and Minerals in Each Broth
Bone broth is rich in minerals such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium, which support bone health and muscle function, along with collagen and amino acids like glycine and proline that aid in joint and skin health. Vegetable broth provides essential vitamins such as vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate, derived from nutrient-dense vegetables, contributing to immune support, antioxidant protection, and blood clotting. Both broths offer unique nutritional benefits: bone broth excels in mineral content and connective tissue support, while vegetable broth delivers higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants.
Protein Content: How They Compare
Bone broth contains significantly higher protein levels, typically around 6-10 grams per cup, due to collagen and amino acids released from simmered animal bones. Vegetable broth usually provides minimal protein, often less than 1 gram per cup, as it is made primarily from simmered vegetables and herbs. For individuals seeking a protein-rich option for muscle repair or satiety, bone broth is the superior choice compared to vegetable broth.
Amino Acids: Unique Benefits of Bone Broth
Bone broth contains a rich profile of essential amino acids, including glycine, proline, and glutamine, which support joint health, gut integrity, and muscle repair. Vegetable broth provides some amino acids but lacks the collagen-derived peptides found in bone broth that promote skin elasticity and reduce inflammation. Consuming bone broth offers unique nutritional advantages by delivering bioavailable amino acids critical for recovery and immune function.
Antioxidants and Plant Compounds in Vegetable Broth
Vegetable broth is rich in antioxidants and plant compounds such as flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols, which help reduce inflammation and combat oxidative stress. Unlike bone broth, which primarily provides collagen and minerals, vegetable broth offers a higher concentration of vitamins C and E, enhancing immune function and skin health. These plant-derived nutrients promote cellular repair and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases linked to free radical damage.
Calorie and Fat Differences
Bone broth typically contains higher calories and fat due to collagen and marrow content, offering essential amino acids and healthy fats that support joint health. Vegetable broth is lower in calories and fat, making it a lighter option rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants from various vegetables. Choosing between the two depends on dietary goals; bone broth benefits those seeking protein and fat, while vegetable broth suits low-calorie, plant-based nutrition.
Digestive Health and Gut Support
Bone broth is rich in collagen, gelatin, and amino acids like glutamine, which support gut lining repair and improve digestive health. Vegetable broth provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote overall gut balance and reduce inflammation. For optimal digestive support, bone broth offers targeted gut-healing properties, while vegetable broth enhances nutrient diversity and microbial health.
Allergy and Dietary Considerations
Bone broth offers rich collagen and minerals beneficial for joint health but may trigger allergies in individuals sensitive to animal proteins or histamines. Vegetable broth, free from common allergens like dairy, gluten, and animal products, suits vegan diets and those with food sensitivities, providing antioxidants and vitamins from diverse vegetables. Choosing between bone and vegetable broth depends on dietary restrictions, allergy profiles, and nutritional goals such as collagen intake versus plant-based nutrients.
Best Uses for Bone Broth and Vegetable Broth in Cooking
Bone broth, rich in collagen, amino acids, and minerals, is ideal for enhancing the nutritional profile of soups, stews, and sauces, providing a deep, savory flavor and health benefits like improved joint and gut health. Vegetable broth offers a lighter, nutrient-dense base packed with vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber, perfect for vegan or vegetarian recipes, soups, and light sauces that require a fresh, clean taste. Using bone broth suits hearty dishes requiring rich umami notes, while vegetable broth excels in delicate, plant-based meals needing a subtle, aromatic foundation.
Which Broth is Best for Your Nutritional Goals?
Bone broth is rich in collagen, amino acids, and minerals like calcium and magnesium, making it ideal for those seeking joint health and skin benefits. Vegetable broth provides antioxidants, vitamins A and C, and fiber, supporting immune function and digestion, suitable for plant-based or lower-calorie diets. Choose bone broth for protein and mineral density or vegetable broth for antioxidant intake and dietary fiber aligned with your nutritional goals.
Bone broth vs Vegetable broth for nutrition Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com