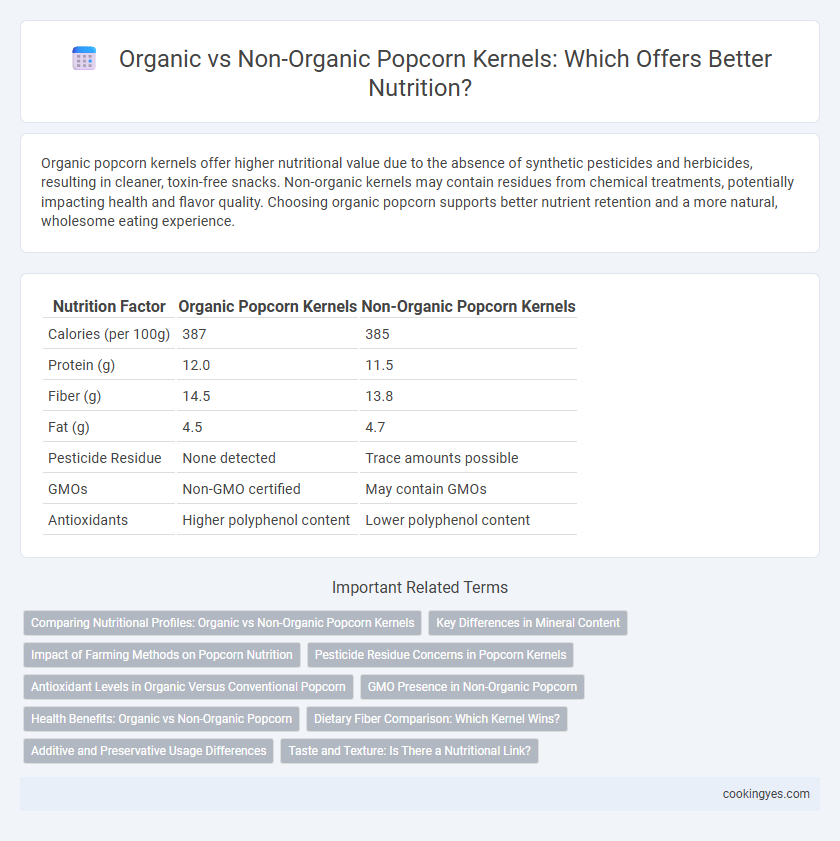
Organic popcorn kernels offer higher nutritional value due to the absence of synthetic pesticides and herbicides, resulting in cleaner, toxin-free snacks. Non-organic kernels may contain residues from chemical treatments, potentially impacting health and flavor quality. Choosing organic popcorn supports better nutrient retention and a more natural, wholesome eating experience.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrition Factor | Organic Popcorn Kernels | Non-Organic Popcorn Kernels |
|---|---|---|
| Calories (per 100g) | 387 | 385 |
| Protein (g) | 12.0 | 11.5 |
| Fiber (g) | 14.5 | 13.8 |
| Fat (g) | 4.5 | 4.7 |
| Pesticide Residue | None detected | Trace amounts possible |
| GMOs | Non-GMO certified | May contain GMOs |
| Antioxidants | Higher polyphenol content | Lower polyphenol content |
Comparing Nutritional Profiles: Organic vs Non-Organic Popcorn Kernels
Organic popcorn kernels typically contain fewer pesticide residues and higher antioxidant levels compared to non-organic kernels, contributing to a potentially healthier snack option. Both organic and non-organic popcorn kernels provide similar macronutrient profiles, including fiber, carbohydrates, and protein content. The nutritional differences mainly lie in micronutrient quality and exposure to synthetic chemicals rather than fundamental changes in basic nutrients.
Key Differences in Mineral Content
Organic popcorn kernels typically contain higher levels of essential minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc compared to non-organic kernels, which may be attributed to the nutrient-rich soil used in organic farming practices. Non-organic kernels often show increased residues of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides that can affect mineral absorption and overall nutritional quality. Choosing organic popcorn can enhance mineral intake while reducing exposure to chemical contaminants found more commonly in conventional popcorn varieties.
Impact of Farming Methods on Popcorn Nutrition
Organic popcorn kernels often contain higher levels of antioxidants and fewer pesticide residues compared to non-organic kernels, due to restrictions on synthetic chemicals in organic farming. Farming methods emphasizing soil health and biodiversity can enhance the nutritional profile of popcorn by promoting nutrient-dense kernels with improved fiber and micronutrient content. Non-organic popcorn may have slightly higher yields but can carry residual synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, potentially affecting long-term nutrient integrity.
Pesticide Residue Concerns in Popcorn Kernels
Organic popcorn kernels contain significantly lower pesticide residues compared to non-organic varieties, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals during consumption. Studies reveal that conventional popcorn often carries traces of synthetic pesticides linked to health risks such as endocrine disruption and neurotoxicity. Opting for organic kernels supports reduced pesticide intake, contributing to safer, cleaner nutrition in popcorn snacks.
Antioxidant Levels in Organic Versus Conventional Popcorn
Organic popcorn kernels contain higher levels of antioxidants compared to non-organic varieties due to the absence of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Studies indicate that organic popcorn has increased polyphenol content, which contributes to greater free radical neutralization and enhanced nutritional value. These elevated antioxidant levels may support better cellular health and reduce oxidative stress more effectively than conventional popcorn.
GMO Presence in Non-Organic Popcorn
Non-organic popcorn kernels often contain genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which can raise concerns about pesticide resistance and potential health effects. Organic popcorn is grown without synthetic pesticides or GMOs, ensuring a more natural product with fewer chemical residues. Choosing organic kernels supports non-GMO agriculture and may provide higher nutritional quality due to the absence of synthetic additives.
Health Benefits: Organic vs Non-Organic Popcorn
Organic popcorn kernels are grown without synthetic pesticides and herbicides, reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and potentially lowering health risks. Non-organic kernels may contain pesticide residues that could affect long-term health, although nutritional content such as fiber, protein, and antioxidants remains similar in both types. Choosing organic popcorn supports better overall health by minimizing toxin intake and promoting environmentally sustainable farming practices.
Dietary Fiber Comparison: Which Kernel Wins?
Organic popcorn kernels typically contain higher levels of dietary fiber compared to non-organic counterparts, enhancing digestive health and promoting satiety. Studies indicate that organic kernels have a fiber content of approximately 10-12 grams per 100 grams, whereas non-organic kernels average around 8-10 grams per 100 grams. Choosing organic popcorn can support a higher fiber intake, contributing to improved gut function and better weight management.
Additive and Preservative Usage Differences
Organic popcorn kernels are grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or chemical fertilizers, resulting in fewer chemical residues compared to non-organic kernels. Non-organic popcorn often contains additives and preservatives such as artificial flavorings, colorings, and chemical stabilizers to enhance shelf life and taste. Choosing organic kernels reduces exposure to these additives and preservatives, promoting a cleaner nutritional profile free from synthetic contaminants.
Taste and Texture: Is There a Nutritional Link?
Organic popcorn kernels often offer a richer flavor and crunchier texture due to the absence of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which can affect the growth environment and nutrient profile of the kernels. Non-organic kernels may contain residues that subtly impact taste, though their macronutrient content, such as carbohydrates and fiber, remains largely similar to organic varieties. Research indicates that organic kernels' enhanced nutrient density, including higher antioxidant levels, can influence overall flavor complexity and mouthfeel during popping.
Organic vs non-organic kernels for popcorn nutrition Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com