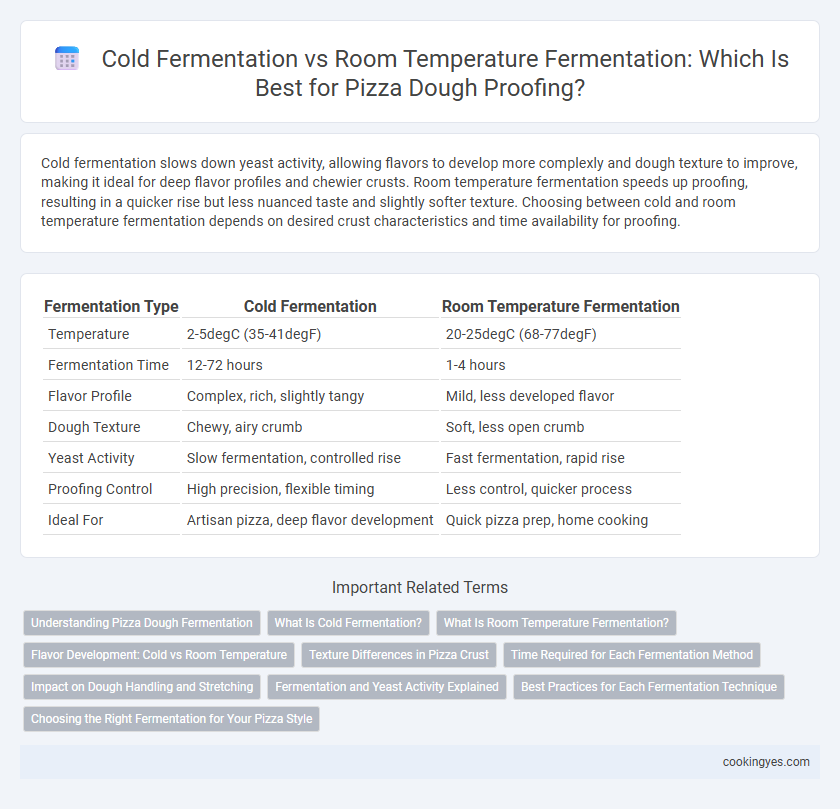
Cold fermentation slows down yeast activity, allowing flavors to develop more complexly and dough texture to improve, making it ideal for deep flavor profiles and chewier crusts. Room temperature fermentation speeds up proofing, resulting in a quicker rise but less nuanced taste and slightly softer texture. Choosing between cold and room temperature fermentation depends on desired crust characteristics and time availability for proofing.
Table of Comparison
| Fermentation Type | Cold Fermentation | Room Temperature Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 2-5degC (35-41degF) | 20-25degC (68-77degF) |
| Fermentation Time | 12-72 hours | 1-4 hours |
| Flavor Profile | Complex, rich, slightly tangy | Mild, less developed flavor |
| Dough Texture | Chewy, airy crumb | Soft, less open crumb |
| Yeast Activity | Slow fermentation, controlled rise | Fast fermentation, rapid rise |
| Proofing Control | High precision, flexible timing | Less control, quicker process |
| Ideal For | Artisan pizza, deep flavor development | Quick pizza prep, home cooking |
Understanding Pizza Dough Fermentation
Cold fermentation of pizza dough enhances flavor development and texture by slowing yeast activity at temperatures around 35-40degF over 24 to 72 hours. Room temperature fermentation accelerates proofing, typically completing in 1 to 3 hours at 70-75degF, yielding a lighter crust but less complex flavors. Balancing fermentation temperature and time is key to achieving the desired dough elasticity, airiness, and crust taste in artisanal pizza baking.
What Is Cold Fermentation?
Cold fermentation is a pizza dough proofing method that involves slowing down yeast activity by refrigerating the dough, typically between 4degC to 8degC (39degF to 46degF). This process enhances flavor development through extended fermentation, allowing complex organic acids and alcohols to form, resulting in a richer, more nuanced taste. Cold fermentation usually lasts from 24 to 72 hours, creating a dough with better texture, improved elasticity, and optimal gluten strength for a crisp yet chewy crust.
What Is Room Temperature Fermentation?
Room temperature fermentation for pizza proofing involves letting the dough rise at ambient temperatures, typically between 68degF and 75degF (20degC to 24degC), to promote yeast activity and gluten development. This method generally takes 1 to 3 hours, allowing the dough to expand quickly and develop a light, airy texture suitable for same-day baking. It contrasts with cold fermentation by fostering faster fermentation, resulting in a more pronounced yeast flavor but less complex dough depth.
Flavor Development: Cold vs Room Temperature
Cold fermentation enhances flavor complexity in pizza dough by allowing slow enzymatic activity over 24 to 72 hours, resulting in a richer, more nuanced taste with subtle tanginess. Room temperature fermentation accelerates yeast activity, producing a quicker rise but often yields a simpler, yeast-forward flavor within 1 to 2 hours. Choosing cold fermentation maximizes flavor depth, while room temperature fermentation prioritizes speed and mild taste.
Texture Differences in Pizza Crust
Cold fermentation enhances the pizza crust's texture by allowing slow enzyme activity, resulting in a chewier, more complex flavor profile with a crisp, blistered exterior. Room temperature fermentation speeds up yeast activity, producing a softer, lighter crust with a tender crumb but less depth in flavor. Bakers often prefer cold fermentation for artisan-style pizzas due to the desirable balance of elasticity and crunch it imparts.
Time Required for Each Fermentation Method
Cold fermentation typically requires 24 to 72 hours to develop complex flavors and a chewy texture, as the dough ferments slowly in the refrigerator. Room temperature fermentation, on the other hand, completes in 1 to 4 hours, providing quicker proofing but resulting in a milder flavor profile. Choosing between the two depends on desired flavor depth and available preparation time.
Impact on Dough Handling and Stretching
Cold fermentation slows yeast activity, resulting in a dough with increased gluten strength that is easier to handle and stretch without tearing. Room temperature fermentation accelerates fermentation, producing a softer, more extensible dough that can be prone to stickiness and over-proofing, making it more challenging to shape. The choice between cold and room temperature fermentation directly affects dough elasticity, extensibility, and ease of stretching for optimal pizza crust texture.
Fermentation and Yeast Activity Explained
Cold fermentation slows yeast activity by maintaining dough at temperatures between 35degF and 50degF, allowing complex flavor development over 24 to 72 hours. Room temperature fermentation accelerates yeast metabolism, typically completing proofing within 1 to 3 hours, resulting in a lighter crust but less pronounced flavor. Yeast produces carbon dioxide and alcohol during fermentation, with temperature directly influencing the rate of these biochemical reactions and the resulting dough texture and taste.
Best Practices for Each Fermentation Technique
Cold fermentation involves proofing pizza dough at temperatures between 35degF and 40degF for 24 to 72 hours, enhancing flavor development and dough elasticity by allowing slow yeast activity. Room temperature fermentation occurs at approximately 70degF to 75degF and typically takes 1 to 3 hours, promoting faster rise but with less complex flavor profiles. Best practices include tightly covering the dough during cold fermentation to prevent drying and monitoring dough rise carefully at room temperature to avoid overproofing and loss of structure.
Choosing the Right Fermentation for Your Pizza Style
Cold fermentation enhances dough flavor and texture by allowing enzymes to break down starches slowly at temperatures around 4degC, ideal for Neapolitan and artisan-style pizzas. Room temperature fermentation, typically between 20-25degC, accelerates yeast activity, producing a lighter, airier crust suited for quick-rising doughs like Sicilian or classic American pizza styles. Selecting the right fermentation method depends on your desired crust characteristics, proofing time constraints, and flavor complexity preferences.
Cold Fermentation vs Room Temperature Fermentation for Pizza Proofing Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com