Tamagoyaki, a sweet and savory rolled omelet, showcases precise technique and layered flavors distinct from the fluffy, ingredient-filled Western omelet. In Japanese cuisine, tamagoyaki serves as a delicate balance of dashi, soy sauce, and sugar, highlighting subtle umami that contrasts with the Western omelet's emphasis on texture and variety of fillings. Both styles offer unique expressions of eggs, reflecting cultural preferences and culinary traditions.
Table of Comparison
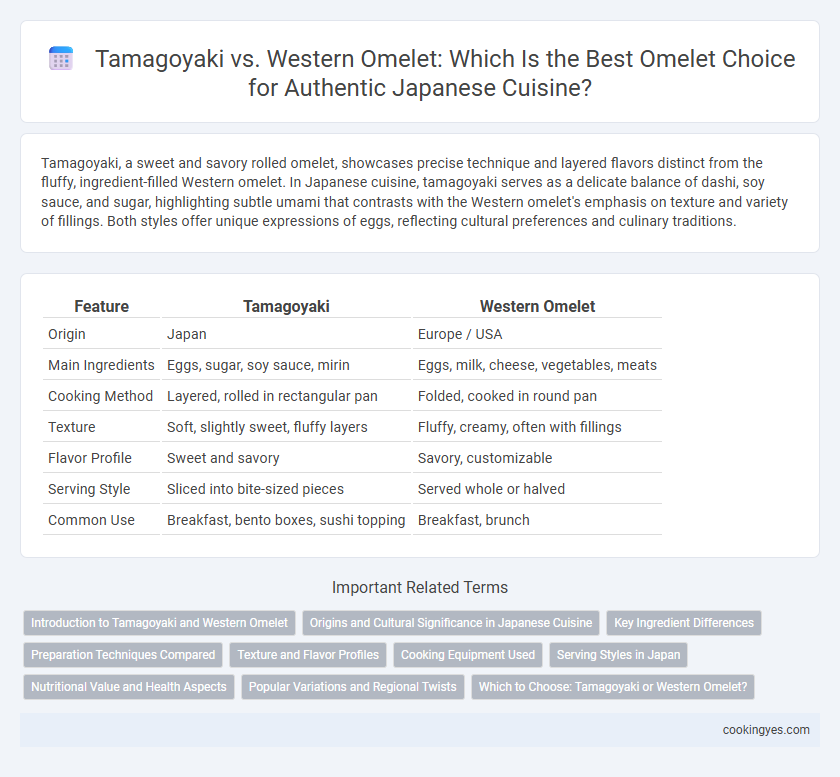
| Feature | Tamagoyaki | Western Omelet |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Japan | Europe / USA |
| Main Ingredients | Eggs, sugar, soy sauce, mirin | Eggs, milk, cheese, vegetables, meats |
| Cooking Method | Layered, rolled in rectangular pan | Folded, cooked in round pan |
| Texture | Soft, slightly sweet, fluffy layers | Fluffy, creamy, often with fillings |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet and savory | Savory, customizable |
| Serving Style | Sliced into bite-sized pieces | Served whole or halved |
| Common Use | Breakfast, bento boxes, sushi topping | Breakfast, brunch |
Introduction to Tamagoyaki and Western Omelet
Tamagoyaki is a Japanese rolled omelet made by layering seasoned egg mixture in a rectangular pan, resulting in a slightly sweet, fluffy texture. Western omelets are typically cooked in a round pan and folded over fillings like cheese, vegetables, or meats, offering a savory and customizable dish. Both forms highlight regional culinary traditions, with tamagoyaki emphasizing delicate flavors and presentation, while Western omelets prioritize heartier, diverse ingredients.
Origins and Cultural Significance in Japanese Cuisine
Tamagoyaki, a sweet, layered omelet originating from Japan's Edo period, embodies the delicate balance of flavors and meticulous technique central to Japanese cuisine. In contrast, the Western omelet, introduced through Western influence during the Meiji Restoration, represents a more robust, customizable approach emphasizing diverse fillings and textures. Tamagoyaki's cultural significance lies in its role as a staple in bento boxes and sushi, symbolizing tradition and precision, while the Western omelet highlights Japan's openness to culinary adaptation and innovation.
Key Ingredient Differences
Tamagoyaki, a traditional Japanese omelet, relies heavily on dashi, soy sauce, and mirin, creating a delicate balance of sweet and savory flavors that distinguish it from Western omelets. Western omelets typically emphasize eggs mixed with dairy such as milk or cream, resulting in a richer and fluffier texture. The distinct seasoning and cooking methods highlight the cultural culinary differences between Japanese Tamagoyaki and Western-style omelets.
Preparation Techniques Compared
Tamagoyaki features thin layers of seasoned egg cooked in a rectangular pan and rolled meticulously to create a delicate, slightly sweet texture. Western omelets are typically cooked as a single, thicker layer and folded over various fillings, resulting in a fluffier and more versatile dish. The key difference lies in tamagoyaki's layered rolling technique versus the Western method of folding a cooked egg base.
Texture and Flavor Profiles
Tamagoyaki features a delicate, slightly sweet flavor with a soft, layered texture achieved by rolling thin layers of seasoned egg, enhancing the umami experience in Japanese cuisine. In contrast, Western omelets have a fluffy, creamy texture with a savory, buttery taste often enriched by fillings like cheese, vegetables, or meat, creating a heartier flavor profile. Both variations emphasize unique textures and flavor balances that reflect their distinct culinary traditions.
Cooking Equipment Used
Tamagoyaki requires a rectangular tamagoyaki pan made from lightweight metal to achieve its distinctive layered shape, while a Western omelet is typically cooked in a round non-stick skillet or frying pan for easy flipping and folding. The tamagoyaki pan's design allows precise rolling of thin egg layers, essential for its texture and appearance. In contrast, Western omelets rely on even heat distribution in the skillet to cook fillings uniformly and create a fluffy texture.
Serving Styles in Japan
Tamagoyaki, a Japanese rolled omelet, is typically served sliced in rectangular pieces, often presented as part of a sushi platter or bento box, emphasizing its delicate texture and slightly sweet flavor. In contrast, Western-style omelets in Japan are usually served folded or rolled on a plate with fillings like cheese, vegetables, or ham, reflecting a more individual, hearty portion. Both styles showcase Japan's culinary adaptation by blending traditional presentation with diverse ingredient influences.
Nutritional Value and Health Aspects
Tamagoyaki, a Japanese rolled omelet, offers a lighter option with lower calories and sugar compared to the Western omelet, which often includes heavier fillings like cheese and meats that increase fat and calorie content. Rich in protein and essential amino acids, tamagoyaki also provides vitamins A and D, supporting eye and bone health, while its moderate sodium content aligns with heart-healthy diets. Western omelets, although nutrient-dense with diverse fillings, tend to have higher cholesterol and saturated fats, impacting cardiovascular health more than the traditionally balanced tamagoyaki.
Popular Variations and Regional Twists
Tamagoyaki, a sweet and savory layered omelet, is a staple in Japanese cuisine often flavored with soy sauce, mirin, and dashi, reflecting regional variations such as Kansai's lighter seasoning and Kanto's sweeter profile. In contrast, Western omelets in Japan incorporate local ingredients like mushrooms, seaweed, and seafood, showcasing the adaptation of Western culinary techniques to Japanese flavors. Both versions highlight Japan's culinary diversity, with tamagoyaki emphasizing traditional techniques and Western omelets offering versatile, ingredient-driven twists.
Which to Choose: Tamagoyaki or Western Omelet?
Tamagoyaki and Western omelets represent distinct approaches to egg preparation in Japanese cuisine, with tamagoyaki characterized by its sweet, layered texture and delicate flavor, while Western omelets offer a fluffier, savory option often filled with cheese, vegetables, or meats. Choosing between tamagoyaki and a Western omelet depends on the desired taste profile and occasion, as tamagoyaki is traditionally served in sushi, bento boxes, and breakfast sets, whereas Western omelets cater to a broader range of fillings and styles suited for casual breakfast or brunch. For an authentic Japanese culinary experience, tamagoyaki is preferred, whereas Western omelets provide versatility and customization for diverse palates.
Tamagoyaki vs Western Omelet for Japanese Cuisine Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com