Heavy cream adds a velvety richness and a creamy texture to omelets, making them more indulgent and flavorful. Milk creates a lighter, fluffier omelet while still providing moisture and tenderness without overwhelming the eggs. Choosing between heavy cream and milk depends on whether you prefer a richer, denser omelet or a soft and airy consistency.
Table of Comparison
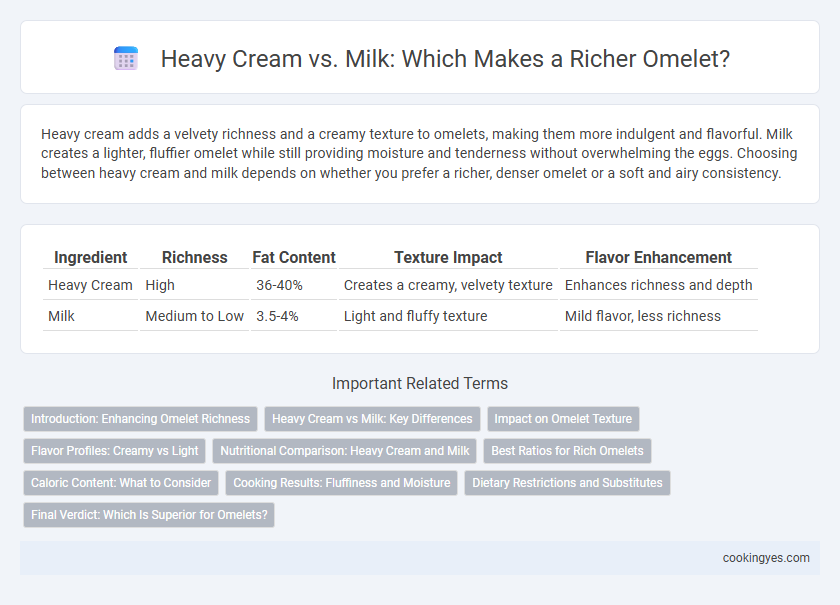
| Ingredient | Richness | Fat Content | Texture Impact | Flavor Enhancement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Cream | High | 36-40% | Creates a creamy, velvety texture | Enhances richness and depth |
| Milk | Medium to Low | 3.5-4% | Light and fluffy texture | Mild flavor, less richness |
Introduction: Enhancing Omelet Richness
Heavy cream significantly boosts omelet richness due to its high fat content, creating a creamier and more luxurious texture. Milk, while lighter in fat, still enhances moisture and fluffiness but yields a subtler, less decadent flavor. Choosing heavy cream over milk intensifies the omelet's richness, appealing to those seeking a velvety mouthfeel and robust taste.
Heavy Cream vs Milk: Key Differences
Heavy cream contains approximately 36-40% fat, significantly higher than milk's 3-4%, which enhances omelet richness and creaminess by providing a denser texture and fuller flavor. Milk adds moisture and a lighter consistency, while heavy cream yields a fluffier, more luxurious omelet due to its fat content supporting better air incorporation. Choosing heavy cream over milk results in richer taste and smoother mouthfeel, ideal for gourmet-style omelets.
Impact on Omelet Texture
Heavy cream enhances omelet richness by adding a higher fat content, resulting in a creamier, denser texture and a more luxurious mouthfeel. Milk produces a lighter, fluffier omelet with a less rich taste due to its lower fat and higher water content. Choosing heavy cream over milk significantly impacts the omelet's texture by increasing moisture retention and smoothness.
Flavor Profiles: Creamy vs Light
Using heavy cream in an omelet creates a rich, velvety texture that enhances the creaminess and depth of flavor, making each bite more indulgent. Milk produces a lighter, airier omelet with a subtle dairy flavor that lets other ingredients shine without overpowering them. Choosing between heavy cream and milk affects the overall mouthfeel and richness, tailoring the omelet experience to personal taste preferences.
Nutritional Comparison: Heavy Cream and Milk
Heavy cream contains higher fat content, typically around 36-40%, which significantly increases the richness and caloric density of an omelet compared to milk, which usually contains 1-2% fat. Milk provides more protein and fewer calories, making it a lighter option while still adding moisture and some creaminess. Choosing heavy cream enhances flavor and texture with a smooth, velvety consistency but results in a higher intake of saturated fat and calories.
Best Ratios for Rich Omelets
Using heavy cream instead of milk in omelets significantly enhances richness due to its higher fat content, typically around 36-40%, compared to milk's 2-3%. The best ratio for a rich, creamy omelet is about one tablespoon of heavy cream per two large eggs, which balances texture without overpowering the egg flavor. This ratio creates a velvety consistency and fluffy texture, making each bite luxurious and satisfying.
Caloric Content: What to Consider
Heavy cream contains significantly more calories than milk, with approximately 50 calories per tablespoon compared to milk's 9-12 calories per tablespoon, making it a richer choice for omelets. Using heavy cream increases the omelet's caloric content substantially, which benefits those seeking a higher-energy meal but may not suit calorie-conscious individuals. Milk provides a lighter alternative, contributing to omelet fluffiness with fewer calories and less fat.
Cooking Results: Fluffiness and Moisture
Heavy cream enhances an omelet's fluffiness by increasing fat content, which traps air and creates a light, tender texture. Milk adds moisture without as much fat, resulting in a slightly less rich but still creamy omelet. Using heavy cream leads to a richer, moister omelet with pronounced softness, while milk yields a lighter, more delicate outcome.
Dietary Restrictions and Substitutes
Heavy cream enhances omelet richness with a higher fat content, ideal for keto or low-carb diets but unsuitable for those lactose intolerant or seeking lower calories. Milk offers a lighter texture and fewer calories, fitting well in low-fat diets but may cause issues for dairy-sensitive individuals. For dietary restrictions, alternatives like almond milk or coconut cream provide lactose-free options while maintaining creamy consistency.
Final Verdict: Which Is Superior for Omelets?
Heavy cream delivers a richer, creamier texture to omelets due to its higher fat content, enhancing flavor and moisture retention. Milk provides a lighter consistency but may result in a less fluffy and less decadent omelet. For those seeking maximum richness and a velvety mouthfeel, heavy cream is superior for omelet preparation.
Heavy cream vs Milk for omelet richness Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com