Falafel and Tamiya are both popular Middle Eastern patties, but Tamiya is specifically the Egyptian version made primarily from fava beans, offering a softer texture and earthier flavor compared to the chickpea-based falafel. Egyptian Tamiya often includes fresh herbs like parsley and dill, enhancing its vibrant taste and making it distinctly different from the spicier, crunchier falafel found in other regions. Choosing between the two depends on personal preference for texture and regional flavor profiles, with Tamiya being a staple of Egyptian street food culture.
Table of Comparison
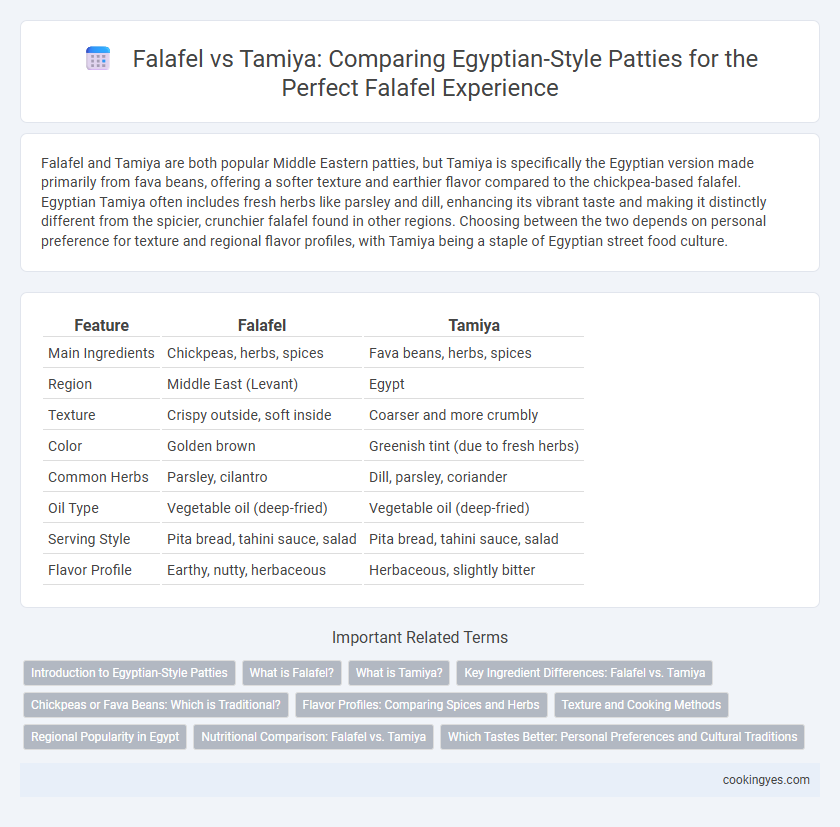
| Feature | Falafel | Tamiya |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Chickpeas, herbs, spices | Fava beans, herbs, spices |
| Region | Middle East (Levant) | Egypt |
| Texture | Crispy outside, soft inside | Coarser and more crumbly |
| Color | Golden brown | Greenish tint (due to fresh herbs) |
| Common Herbs | Parsley, cilantro | Dill, parsley, coriander |
| Oil Type | Vegetable oil (deep-fried) | Vegetable oil (deep-fried) |
| Serving Style | Pita bread, tahini sauce, salad | Pita bread, tahini sauce, salad |
| Flavor Profile | Earthy, nutty, herbaceous | Herbaceous, slightly bitter |
Introduction to Egyptian-Style Patties
Egyptian-style patties, commonly known as tamiya, are distinct from traditional falafel due to their main ingredient of crushed fava beans instead of chickpeas, which provides a unique texture and flavor profile. Tamiya incorporates fresh herbs like parsley and cilantro alongside spices such as cumin and coriander, creating a more herbaceous and aromatic taste typical to Egyptian cuisine. These patties are often fried until crisp and golden, offering a hearty and nutritious option that highlights Egypt's culinary heritage.
What is Falafel?
Falafel is a deep-fried ball or patty made from ground chickpeas, fava beans, or a combination, seasoned with herbs, garlic, and spices typical of Middle Eastern cuisine. In Egypt, falafel is often synonymous with Tamiya, which specifically uses fava beans as the primary ingredient, giving it a distinct texture and flavor compared to chickpea-based falafel. The Egyptian-style Tamiya is known for its vibrant green interior due to fresh herbs like parsley and cilantro, differentiating it from other regional falafel varieties.
What is Tamiya?
Tamiya is the Egyptian variation of falafel, traditionally made from fava beans rather than chickpeas, giving it a distinct flavor and texture unique to Egyptian cuisine. Unlike typical Middle Eastern falafel, Tamiya incorporates fresh herbs like parsley, cilantro, and dill, enhancing its vibrant green interior and aromatic profile. Its preparation often includes coarse grinding, which results in a coarser, crunchier patty that differentiates it from the smoother chickpea-based falafel found elsewhere.
Key Ingredient Differences: Falafel vs. Tamiya
Falafel and Tamiya differ primarily in their key ingredients, with falafel traditionally made from soaked chickpeas, while Tamiya uses fava beans as its base. The chickpeas in falafel contribute to a denser texture and nuttier flavor, whereas the fava beans in Tamiya result in a softer and earthier taste. These ingredient choices significantly influence the patties' texture, taste, and nutritional profiles, highlighting regional preferences in Egyptian cuisine.
Chickpeas or Fava Beans: Which is Traditional?
Egyptian-style patties traditionally use fava beans, known locally as tamiya, which offer a distinct texture and earthy flavor unique to the region. Falafel, made primarily from chickpeas, is more common in Levantine cuisine. The choice between chickpeas and fava beans fundamentally defines the authentic taste and cultural roots of Egyptian falafel.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Spices and Herbs
Egyptian-style falafel, also called tamiya, features a distinct flavor profile characterized by the use of fresh parsley, cilantro, and dill, delivering a vibrant herbal freshness. The spice blend often includes cumin, coriander, and a hint of chili, creating a warm and mildly spicy taste that differs from falafel made with chickpeas, which tends to be earthier with a stronger garlic and onion presence. The unique combination of fava beans and herbs in tamiya results in a lighter, greener flavor compared to the denser, nuttier taste of traditional chickpea falafel.
Texture and Cooking Methods
Egyptian-style falafel, also known as tamiya, is traditionally made from crushed fava beans, resulting in a coarser, grainier texture compared to chickpea-based falafel. Tamiya patties are typically deep-fried in oil, which creates a crisp outer layer while maintaining a moist interior, whereas falafel often involves frying chickpea mixtures that yield a denser and smoother consistency. The difference in legume base and frying technique significantly influences both the texture and cooking process, making tamiya uniquely distinct in Egyptian cuisine.
Regional Popularity in Egypt
Falafel and Tamiya are staple Egyptian-style patties with distinct regional popularity, where Tamiya, made primarily from fava beans, dominates in Egypt's Nile Delta and Cairo regions due to its traditional roots. Falafel, typically made from chickpeas, is more common in Middle Eastern countries but has a growing presence in southern Egypt and urban centers seeking diverse flavors. Both patties reflect Egypt's culinary heritage, with Tamiya firmly embedded in local street food culture and falafel expanding as an alternative across various regions.
Nutritional Comparison: Falafel vs. Tamiya
Falafel and Tamiya, both popular Egyptian-style patties, differ notably in nutritional content, with Falafel typically made from chickpeas and Tamiya from fava beans. Falafel offers higher protein and fiber per serving, supporting muscle health and digestion, while Tamiya tends to have slightly fewer calories and lower fat levels, making it a lighter option. Both are rich in essential vitamins and minerals like iron and folate, but Tamiya's fava bean base provides a unique antioxidant profile beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Which Tastes Better: Personal Preferences and Cultural Traditions
Falafel and Tamiya are both popular Egyptian-style patties made primarily from fava beans, yet they differ in texture and seasoning, influencing their taste profiles. Falafel tends to have a crispier exterior with a blend of herbs and spices like cumin and coriander, while Tamiya often includes fresh parsley and dill, offering a greener and more herbaceous flavor. Taste preferences vary widely, with many Egyptians favoring Tamiya for its authentic, fresh taste reflecting cultural traditions, while others prefer falafel's sharper, spiced flavor.
Falafel vs Tamiya for Egyptian-style patties Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com