Choosing between bulgur and no bulgur for falafel fillers affects texture and flavor; bulgur adds a nutty taste and a slightly chewy consistency, enhancing authenticity. Without bulgur, falafel tends to be lighter and smoother, appealing to those seeking a gluten-free or softer option. Both versions can be delicious, but the choice depends on desired texture and dietary preferences.
Table of Comparison
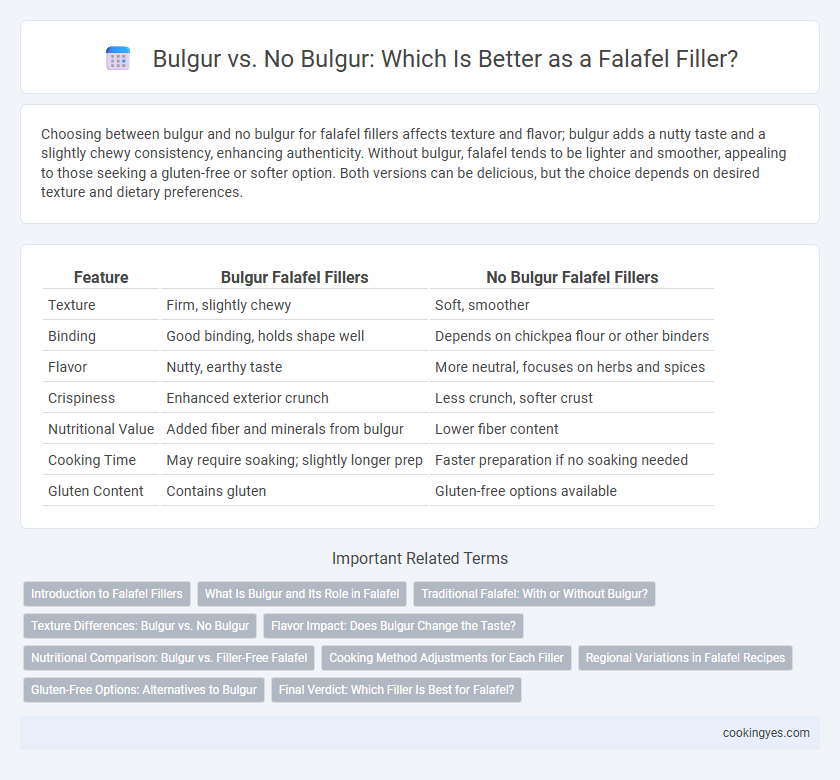
| Feature | Bulgur Falafel Fillers | No Bulgur Falafel Fillers |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Firm, slightly chewy | Soft, smoother |
| Binding | Good binding, holds shape well | Depends on chickpea flour or other binders |
| Flavor | Nutty, earthy taste | More neutral, focuses on herbs and spices |
| Crispiness | Enhanced exterior crunch | Less crunch, softer crust |
| Nutritional Value | Added fiber and minerals from bulgur | Lower fiber content |
| Cooking Time | May require soaking; slightly longer prep | Faster preparation if no soaking needed |
| Gluten Content | Contains gluten | Gluten-free options available |
Introduction to Falafel Fillers
Falafel fillers play a crucial role in achieving the desired texture and flavor of traditional Middle Eastern falafel. Bulgur, a cracked wheat grain, offers a nutty taste and slightly chewy texture while enhancing binding properties, making the falafel more cohesive and less prone to crumbling. In contrast, no bulgur fillers rely primarily on chickpeas or fava beans combined with herbs and spices, resulting in a lighter and more crumbly falafel that emphasizes the legume's natural flavor profiles.
What Is Bulgur and Its Role in Falafel
Bulgur, a cracked wheat grain, serves as a traditional filler in falafel, providing a chewy texture and nutty flavor that enhances the overall bite. Its high fiber content aids in binding the chickpea mixture while maintaining moisture, preventing the falafel from becoming too dense or crumbly. Using no bulgur results in a lighter, often more delicate falafel but may require alternative binders like flour or breadcrumbs to achieve the desired consistency.
Traditional Falafel: With or Without Bulgur?
Traditional falafel recipes often call for bulgur to add texture and absorb moisture, enhancing the overall consistency of the falafel mixture. Using bulgur creates a slightly denser, more crumbly falafel, while recipes without bulgur tend to be lighter and crispier due to the reliance on soaked chickpeas alone. The choice between bulgur or no bulgur depends on desired texture and regional preferences, with Middle Eastern falafel commonly including bulgur for authentic flavor and mouthfeel.
Texture Differences: Bulgur vs. No Bulgur
Bulgur in falafel fillers creates a coarse, chewy texture that provides a satisfying bite and helps bind the mixture for structural integrity. In contrast, falafel made without bulgur tends to have a smoother, softer interior that can result in a lighter, less dense patty. The choice between bulgur and no bulgur directly impacts the mouthfeel and how well the falafel holds together during frying or baking.
Flavor Impact: Does Bulgur Change the Taste?
Bulgur adds a nutty and slightly earthy flavor to falafel, enriching its traditional taste profile compared to fillers without bulgur. Using no bulgur results in a smoother texture and allows the distinct chickpea and herb flavors to dominate more prominently. The choice between bulgur and no bulgur significantly influences the falafel's overall flavor, balancing texture and taste according to preference.
Nutritional Comparison: Bulgur vs. Filler-Free Falafel
Bulgur in falafel fillers enhances fiber and protein content, contributing to better digestion and sustained energy release compared to filler-free falafel, which relies solely on chickpeas for nutrients. Bulgur adds essential minerals such as iron and magnesium, increasing the nutritional density of falafel without significantly altering calorie count. Filler-free falafel, while simpler, may have a lower glycemic index but lacks the complex carbohydrates and micronutrients found in bulgur-enriched recipes.
Cooking Method Adjustments for Each Filler
Bulgur falafel requires soaking or partial cooking of the bulgur grain to achieve the right texture, while no bulgur falafel relies entirely on soaked or sprouted chickpeas for moisture and binding. When using bulgur, adjust frying time to ensure the grain cooks through without burning the exterior, typically reducing the temperature slightly to allow thorough cooking. Conversely, no bulgur falafel may need a shorter frying time with higher heat to achieve a crispy outside and tender inside, as there is no grain requiring extended cooking.
Regional Variations in Falafel Recipes
Falafel fillers often vary regionally, with bulgur commonly used in Levantine recipes to add texture and a nutty flavor, while Egyptian versions typically omit bulgur, relying solely on chickpeas or fava beans for a smoother consistency. The use of bulgur enhances the structural integrity of falafel, preventing crumbling during frying, which is preferred in Middle Eastern countries like Lebanon and Syria. In contrast, falafel without bulgur, popular in Egypt and parts of Israel, emphasizes a denser, creamier interior that highlights the legume's natural taste.
Gluten-Free Options: Alternatives to Bulgur
Bulgur is a traditional falafel filler that provides a nutty texture but contains gluten, making it unsuitable for gluten-free diets. Alternatives such as chickpea flour, quinoa, or ground nuts offer gluten-free options that maintain the falafel's binding properties and enhance flavor. These substitutes ensure that gluten-sensitive individuals can enjoy authentic falafel without compromising texture or taste.
Final Verdict: Which Filler Is Best for Falafel?
Bulgur adds a nutty flavor and slightly chewy texture to falafel, enhancing moisture retention and nutritional value with extra fiber and protein. Traditional no-bulgur falafel relies solely on ground chickpeas or fava beans for a denser, crunchier bite and a purer legume taste. For a balanced blend of texture, taste, and nutrition, bulgur-based fillers are often favored, but purists seeking authentic falafel prefer no bulgur for its straightforward, classic flavor profile.
Bulgur vs No Bulgur for Falafel Fillers Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com