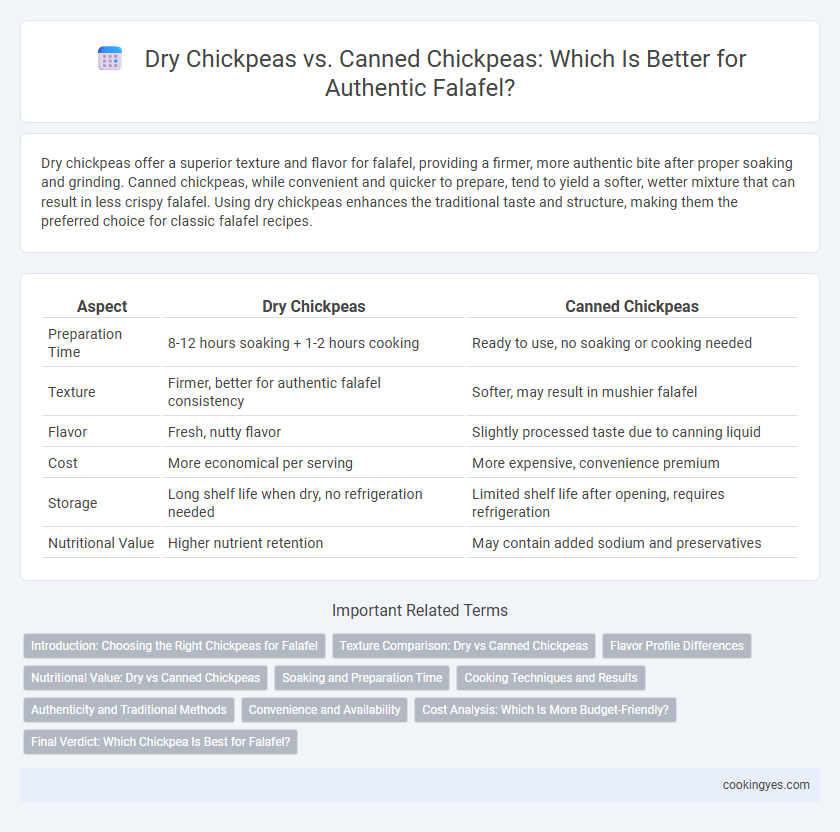
Dry chickpeas offer a superior texture and flavor for falafel, providing a firmer, more authentic bite after proper soaking and grinding. Canned chickpeas, while convenient and quicker to prepare, tend to yield a softer, wetter mixture that can result in less crispy falafel. Using dry chickpeas enhances the traditional taste and structure, making them the preferred choice for classic falafel recipes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dry Chickpeas | Canned Chickpeas |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | 8-12 hours soaking + 1-2 hours cooking | Ready to use, no soaking or cooking needed |
| Texture | Firmer, better for authentic falafel consistency | Softer, may result in mushier falafel |
| Flavor | Fresh, nutty flavor | Slightly processed taste due to canning liquid |
| Cost | More economical per serving | More expensive, convenience premium |
| Storage | Long shelf life when dry, no refrigeration needed | Limited shelf life after opening, requires refrigeration |
| Nutritional Value | Higher nutrient retention | May contain added sodium and preservatives |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Chickpeas for Falafel
Dry chickpeas offer a superior texture and flavor for authentic falafel, requiring soaking and thorough cooking to achieve the ideal consistency for forming patties. Canned chickpeas provide convenience and reduced preparation time but may result in a wetter mixture that affects the falafel's crispness. Selecting dry chickpeas ensures control over moisture levels and enhances the traditional taste and firmness essential for quality falafel.
Texture Comparison: Dry vs Canned Chickpeas
Dry chickpeas yield a firmer, more textured falafel due to their denser composition and lower moisture content after soaking and cooking. Canned chickpeas, pre-cooked and higher in moisture, produce a softer, creamier falafel that may lack the desired crispiness. For optimal texture, dry chickpeas allow better control over consistency and yield a traditional, crunchy exterior with a tender interior.
Flavor Profile Differences
Dry chickpeas offer a nuttier, earthier flavor and a firmer texture when soaked and cooked properly, enhancing the authentic taste of falafel. Canned chickpeas tend to have a softer texture and a slightly milder, less complex flavor due to the preservation process and added sodium. Choosing dry chickpeas allows for better control over seasoning and consistency, resulting in a more vibrant and traditional falafel flavor profile.
Nutritional Value: Dry vs Canned Chickpeas
Dry chickpeas offer higher nutritional value compared to canned chickpeas due to their lower sodium content and absence of preservatives, providing more controlled nutrient intake. Canned chickpeas, while convenient, often contain added salt and may lose some water-soluble vitamins during the canning process, impacting their overall nutrient density. For optimal falafel health benefits, soaking and cooking dry chickpeas retains more protein, fiber, and essential minerals like iron and magnesium.
Soaking and Preparation Time
Dry chickpeas require soaking for 8 to 12 hours before cooking, allowing them to soften and reduce cooking time significantly, which results in a better texture ideal for falafel. Canned chickpeas offer convenience by eliminating soaking time, but their softer texture can affect the traditional crispness and consistency of falafel. Preparing falafel from dry chickpeas demands more advance planning, while canned chickpeas provide a quicker, though slightly different, preparation process.
Cooking Techniques and Results
Dry chickpeas require soaking for 8-12 hours followed by boiling for 1-2 hours, resulting in a firmer texture that enhances falafel's structural integrity and crispiness when fried. Canned chickpeas offer convenience with no soaking or long cooking time but tend to produce a softer, slightly more crumbly falafel due to higher moisture content. The choice between dry and canned chickpeas significantly affects the falafel's texture, flavor depth, and frying performance, with dry chickpeas preferred for traditional recipes demanding a denser, more cohesive patty.
Authenticity and Traditional Methods
Dry chickpeas are the preferred base ingredient for authentic falafel, as traditional recipes emphasize soaking and grinding them fresh to achieve the proper texture and flavor. Using canned chickpeas often results in a softer, less crumbly mixture that deviates from traditional methods passed down through Middle Eastern culinary heritage. The meticulous preparation of dry chickpeas preserves the original taste profile and maintains the cultural authenticity of homemade falafel.
Convenience and Availability
Dry chickpeas offer a cost-effective and shelf-stable option for preparing falafel but require soaking and longer cooking times, which can impact convenience. Canned chickpeas provide immediate usability without the need for soaking, making them highly accessible and time-saving for quick falafel preparation. Availability of canned chickpeas is widespread in supermarkets, while dry chickpeas are often found in bulk sections, catering to both casual cooks and culinary enthusiasts.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Budget-Friendly?
Dry chickpeas are significantly more budget-friendly than canned chickpeas, costing approximately half per serving when purchased in bulk. While canned chickpeas save preparation time, their higher price offsets convenience for large-scale cooking or frequent falafel production. Considering long-term use, dry chickpeas offer better value with extended shelf life and lower per-unit cost.
Final Verdict: Which Chickpea Is Best for Falafel?
Dry chickpeas yield a superior falafel texture with a firmer, more authentic bite and enhanced flavor due to their lower moisture content compared to canned chickpeas. Soaking and cooking dry chickpeas from scratch preserves essential starches that ensure crispiness and proper binding, crucial for traditional falafel quality. Canned chickpeas offer convenience but often result in softer, less cohesive falafel, making dry chickpeas the preferred choice for optimal taste and texture.
Dry chickpeas vs Canned chickpeas for base ingredient Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com