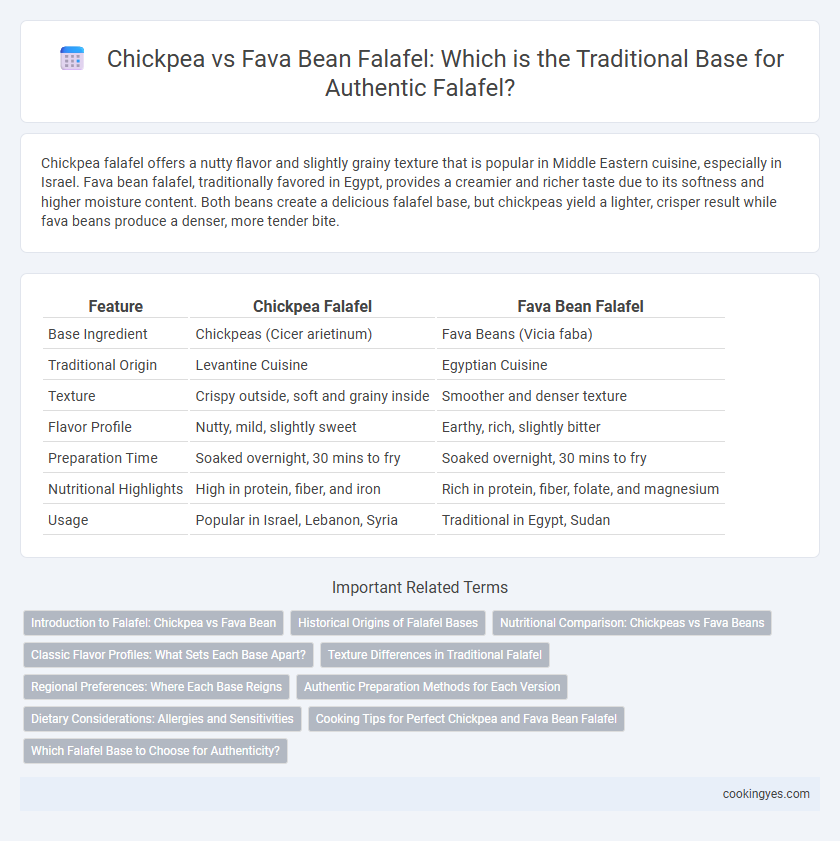
Chickpea falafel offers a nutty flavor and slightly grainy texture that is popular in Middle Eastern cuisine, especially in Israel. Fava bean falafel, traditionally favored in Egypt, provides a creamier and richer taste due to its softness and higher moisture content. Both beans create a delicious falafel base, but chickpeas yield a lighter, crisper result while fava beans produce a denser, more tender bite.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Chickpea Falafel | Fava Bean Falafel |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredient | Chickpeas (Cicer arietinum) | Fava Beans (Vicia faba) |
| Traditional Origin | Levantine Cuisine | Egyptian Cuisine |
| Texture | Crispy outside, soft and grainy inside | Smoother and denser texture |
| Flavor Profile | Nutty, mild, slightly sweet | Earthy, rich, slightly bitter |
| Preparation Time | Soaked overnight, 30 mins to fry | Soaked overnight, 30 mins to fry |
| Nutritional Highlights | High in protein, fiber, and iron | Rich in protein, fiber, folate, and magnesium |
| Usage | Popular in Israel, Lebanon, Syria | Traditional in Egypt, Sudan |
Introduction to Falafel: Chickpea vs Fava Bean
Chickpea falafel, made from ground chickpeas, offers a slightly nutty flavor and a crisp texture, popular in Levantine cuisine. Fava bean falafel, traditional to Egyptian recipes, features a creamy interior and earthier taste that highlights the bean's natural richness. Both bases provide high protein and fiber, making falafel a nutritious and satisfying street food staple.
Historical Origins of Falafel Bases
Chickpea falafel, traditionally favored in Middle Eastern countries like Israel and Lebanon, traces its origins to ancient Levantine cuisine, where chickpeas were abundant and central to early falafel recipes. In contrast, fava bean falafel holds a stronger historical presence in Egypt and Sudan, rooted in the use of local broad beans as the primary base for this iconic street food. Both bases reflect regional agricultural practices and cultural tastes, with chickpea falafel gaining prominence in the eastern Mediterranean and fava bean falafel deeply embedded in North African culinary traditions.
Nutritional Comparison: Chickpeas vs Fava Beans
Chickpea falafel is rich in protein, fiber, and essential minerals like iron and magnesium, making it a nutrient-dense choice for traditional falafel recipes. Fava bean falafel offers higher levels of folate and potassium, supporting heart health and energy metabolism, while providing a slightly lower calorie content. Both pulses deliver complex carbohydrates and plant-based protein, but chickpeas tend to have a slightly higher fat content from healthy unsaturated fats.
Classic Flavor Profiles: What Sets Each Base Apart?
Chickpea falafel offers a nutty, slightly sweet flavor with a dense, chewy texture that is popular in most Middle Eastern cuisines, while fava bean falafel provides a earthier, creamier taste favored in Egyptian recipes. The chickpea base tends to absorb spices like cumin and coriander more intensely, enhancing the aromatic profile, whereas fava beans bring a milder, buttery backdrop that highlights fresh herbs such as parsley and cilantro. These distinct flavor foundations create authentic variations that define traditional falafel experiences across different regions.
Texture Differences in Traditional Falafel
Chickpea falafel offers a denser, grainier texture with a slightly crumbly bite, while fava bean falafel produces a smoother, creamier interior with a more delicate crispness on the outside. The choice between chickpea and fava bean as the traditional base significantly influences the mouthfeel, where chickpea provides a heartier chew and fava bean delivers a softer, buttery experience. Texture variations in traditional falafel stem from the different starch and moisture content inherent in chickpeas versus fava beans.
Regional Preferences: Where Each Base Reigns
Chickpea falafel is predominantly favored in Levantine regions such as Lebanon, Syria, and Israel, where its nutty flavor and slightly grainy texture align with local culinary traditions. Fava bean falafel holds prominence in Egyptian cuisine, particularly in Alexandria and Cairo, offering a creamier and earthier taste preferred by regional palates. The choice between chickpea and fava bean bases reflects centuries-old cultural heritage and agricultural practices unique to each area.
Authentic Preparation Methods for Each Version
Chickpea falafel, rooted in Levantine cuisine, is traditionally made by soaking dried chickpeas overnight, then grinding them with herbs like parsley, cilantro, and spices such as cumin to achieve a coarse mixture before deep-frying. Fava bean falafel, typical in Egyptian recipes, involves soaking dried fava beans, blending them with garlic, coriander, and leeks for a distinct flavor profile, followed by frying to a golden crisp. Both versions emphasize the use of raw, soaked legumes rather than cooked beans, ensuring a texture that is crisp outside and tender inside, critical for authentic falafel preparation.
Dietary Considerations: Allergies and Sensitivities
Chickpea falafel is often preferred for its lower allergenic potential compared to fava bean falafel, which can trigger favism in individuals with G6PD deficiency. Chickpeas provide a gluten-free and nut-free option suitable for most dietary restrictions, whereas fava beans may cause allergic reactions or digestive sensitivities in some people. Choosing the base depends on specific health concerns, with chickpea falafel generally posing fewer risks related to allergies and enzymatic conditions.
Cooking Tips for Perfect Chickpea and Fava Bean Falafel
For perfect chickpea falafel, soak dried chickpeas overnight without cooking, then pulse with fresh herbs, onion, garlic, and spices to maintain a light, crispy texture. Fava bean falafel requires shelled and soaked fava beans, ensuring thorough rinsing to remove bitterness, and typically benefits from the addition of baking powder for a fluffier interior. Both types achieve ideal frying temperature between 350degF and 375degF to avoid greasiness while guaranteeing a golden, crunchy exterior.
Which Falafel Base to Choose for Authenticity?
Chickpea falafel, prevalent in Middle Eastern cuisine, offers a nutty flavor and a slightly grainy texture, making it the most recognized traditional base, especially in Lebanon and Israel. Fava bean falafel, rooted in Egyptian culinary tradition, provides a creamier consistency and earthier taste, often preferred in Nile Delta regions. Choosing between chickpea and fava bean falafel depends on the desired authenticity linked to regional heritage and flavor profile, with chickpeas favored for Levantine authenticity and fava beans for Egyptian tradition.
Chickpea falafel vs Fava bean falafel for traditional base Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com