Candling is a method that uses a bright light to illuminate the egg's interior, revealing the air cell size and embryo development, which helps assess freshness and quality. Floating involves placing an egg in water to check its buoyancy; fresh eggs sink while older eggs float due to increased air pocket size. Both techniques provide quick, non-destructive ways to evaluate egg freshness, with candling offering more detailed internal insights compared to the simple float test.
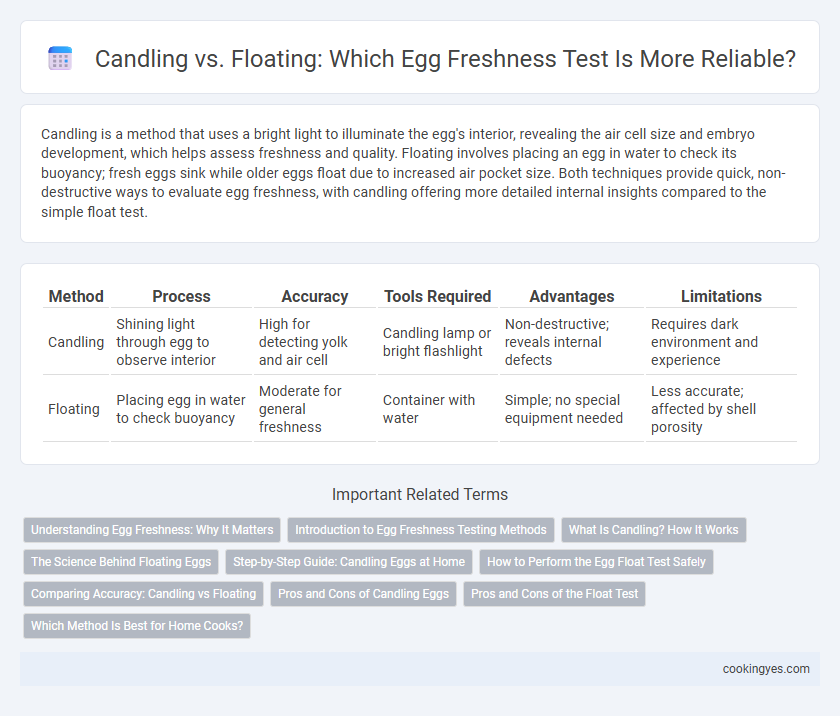
Table of Comparison
| Method | Process | Accuracy | Tools Required | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candling | Shining light through egg to observe interior | High for detecting yolk and air cell | Candling lamp or bright flashlight | Non-destructive; reveals internal defects | Requires dark environment and experience |
| Floating | Placing egg in water to check buoyancy | Moderate for general freshness | Container with water | Simple; no special equipment needed | Less accurate; affected by shell porosity |
Understanding Egg Freshness: Why It Matters
Egg freshness directly impacts taste, texture, and safety, making accurate testing methods like candling and floating essential for consumers and producers. Candling reveals internal egg quality by illuminating the air cell size and blood spots, while floating tests assess freshness based on the egg's buoyancy due to air cell growth. Understanding these methods ensures better selection of fresh eggs, reducing the risk of spoiled or contaminated products.
Introduction to Egg Freshness Testing Methods
Egg freshness testing methods include candling and floating, each offering unique insights into egg quality. Candling involves shining a bright light through the egg to inspect air cell size, yolk position, and potential defects, providing a detailed internal view. Floating tests egg buoyancy by placing it in water; fresher eggs sink due to smaller air cells, while older eggs float as air pockets enlarge.
What Is Candling? How It Works
Candling is a traditional egg freshness testing method that involves shining a bright light through the eggshell to observe the interior contents. By examining the size of the air cell, yolk position, and presence of any defects or cracks, candling reveals the egg's freshness and quality. This technique allows for non-destructive inspection, making it valuable for both commercial egg grading and home use.
The Science Behind Floating Eggs
Floating eggs indicate increased internal air cell size due to moisture loss and gas accumulation from decomposition, causing buoyancy. Candling reveals internal structures by shining light through the shell, allowing detection of embryonic development, cracks, or spoilage not evident from external observation. Floating eggs are typically older or spoiled, while candling provides a precise assessment of freshness and quality within the shell.
Step-by-Step Guide: Candling Eggs at Home
Candling eggs at home involves holding the egg up to a bright light source in a dark room, allowing you to observe the size of the air cell and the clarity of the egg white and yolk to determine freshness. Look for a small, well-defined air cell and a clear, firm yolk, which indicate a fresh egg, while a large air cell and hazy interior suggest an older egg. This method provides a non-invasive and immediate way to assess egg quality without cracking the shell, unlike floating tests that rely on water buoyancy to gauge egg age.
How to Perform the Egg Float Test Safely
To perform the egg float test safely, fill a bowl with cold water deep enough to fully submerge the egg. Gently place the egg in the water and observe its position: fresh eggs sink and lie flat, while older eggs float due to increased air pocket size. Avoid cracking the egg by lowering it carefully and use a clean container to prevent contamination.
Comparing Accuracy: Candling vs Floating
Candling provides higher accuracy in assessing egg freshness by revealing detailed internal features such as air cell size, yolk position, and blood spots, enabling precise evaluation of egg quality. Floating tests rely on the size of the air cell, where older eggs float due to increased buoyancy, but this method can yield false positives with varying egg sizes and shell porosity. Therefore, candling remains the preferred technique for reliable freshness testing in both commercial and home settings.
Pros and Cons of Candling Eggs
Candling eggs involves shining a bright light through the shell to observe the interior, allowing detection of cracks, yolk position, and embryo development, which ensures egg quality without breaking it. This method is quick, non-destructive, and provides detailed information about the egg's freshness and fertility but requires a dark environment and some expertise to interpret the results accurately. However, candling is less effective for very dark or thick shells and may fail to detect bacterial contamination or slight spoilage that floating tests can reveal.
Pros and Cons of the Float Test
The float test for egg freshness is a quick and simple method that involves placing an egg in water to observe its buoyancy, with fresh eggs sinking and older eggs floating due to air cell expansion. This test is advantageous for its ease of use and immediate results without special equipment, but it can be less accurate because factors like shell porosity and water temperature may affect buoyancy. While the float test effectively identifies very old eggs, it cannot precisely determine the exact freshness level or detect internal defects compared to the more detailed candling method.
Which Method Is Best for Home Cooks?
Candling offers a precise method for assessing egg freshness by illuminating the interior, allowing home cooks to spot air cell size and yolk movement, which indicate age. Floating tests eggs by submerging them in water; fresh eggs sink while older eggs float due to increased air pockets. For home cooks, candling provides more detailed insights but requires a light source, whereas floating is simpler and quick, making floating the best method for everyday freshness testing.
Candling vs Floating for egg freshness testing Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com