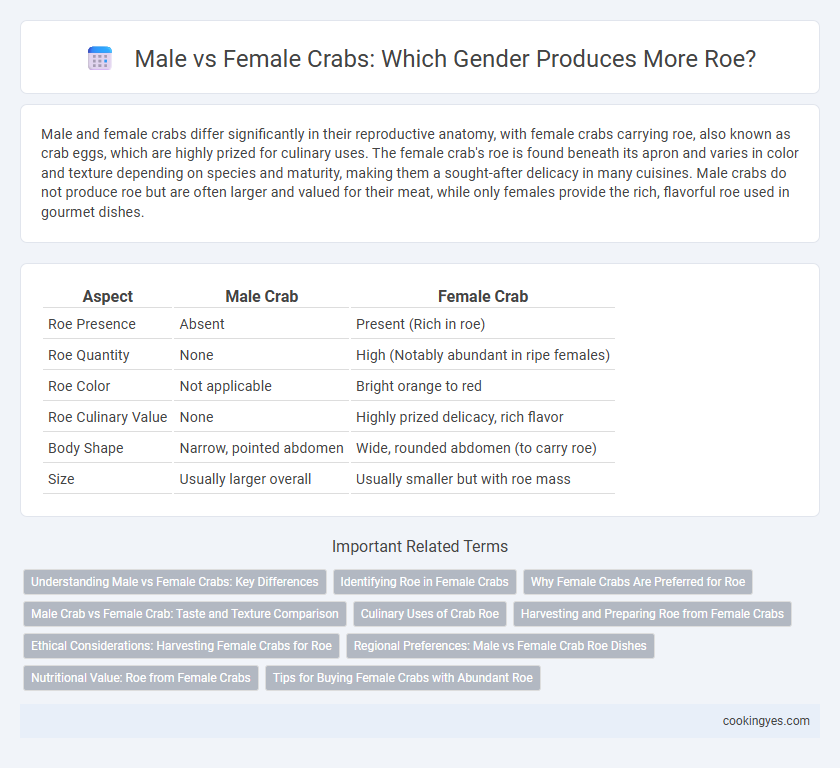
Male and female crabs differ significantly in their reproductive anatomy, with female crabs carrying roe, also known as crab eggs, which are highly prized for culinary uses. The female crab's roe is found beneath its apron and varies in color and texture depending on species and maturity, making them a sought-after delicacy in many cuisines. Male crabs do not produce roe but are often larger and valued for their meat, while only females provide the rich, flavorful roe used in gourmet dishes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Male Crab | Female Crab |
|---|---|---|
| Roe Presence | Absent | Present (Rich in roe) |
| Roe Quantity | None | High (Notably abundant in ripe females) |
| Roe Color | Not applicable | Bright orange to red |
| Roe Culinary Value | None | Highly prized delicacy, rich flavor |
| Body Shape | Narrow, pointed abdomen | Wide, rounded abdomen (to carry roe) |
| Size | Usually larger overall | Usually smaller but with roe mass |
Understanding Male vs Female Crabs: Key Differences
Male and female crabs exhibit distinct physical differences, with females typically possessing a wider, rounded apron on their abdomen for holding roe, while males have a narrow, pointed apron. Female crabs are the primary source of roe, prized for its rich flavor and texture, making them highly sought after in seafood markets. Identifying these key differences is crucial for harvesting practices, ensuring sustainability and optimal roe yield.
Identifying Roe in Female Crabs
Female crabs are easily identified by their broad, rounded abdominal flap, which houses the bright orange roe, a prized delicacy in culinary markets. In contrast, male crabs have a narrow, pointed apron and lack roe entirely, making the presence of the wide apron a key indicator of female crab. The vivid coloration and texture of roe inside the female crab's shell serve as the primary markers for distinguishing female crabs for harvesting purposes.
Why Female Crabs Are Preferred for Roe
Female crabs are preferred for roe because they contain rich, creamy, and flavorful eggs that are highly prized in culinary dishes. The roe, also known as crab caviar, is exclusively found in females during spawning season, offering a unique texture and taste that male crabs lack. This distinct reproductive characteristic makes female crabs the primary choice for harvesting roe in seafood cuisine.
Male Crab vs Female Crab: Taste and Texture Comparison
Female crab roe is prized for its rich, creamy texture and sweet, briny flavor, making it a delicacy in many culinary traditions. Male crab meat tends to be firmer and less abundant in roe, offering a milder taste and a denser texture compared to the female's roe-filled body. The contrast between female roe's delicate, buttery consistency and male crab's meatier bite highlights distinct culinary uses and preparation methods.
Culinary Uses of Crab Roe
Female crabs are prized in culinary applications for their rich, flavorful roe, which is often used in sushi, sauces, and as a delicacy in Asian cuisine. Male crabs lack roe but offer firm, sweet meat preferred for crab cakes and soups. The vibrant orange roe from females provides a nutrient-rich ingredient that enhances the texture and taste of many gourmet dishes.
Harvesting and Preparing Roe from Female Crabs
Female crabs are prized for their roe, which is harvested by carefully removing the crab's apron to access the bright orange eggs inside. Proper preparation of roe involves gently rinsing it to remove impurities without damaging the delicate texture, followed by steaming or sauteing to enhance its rich, briny flavor. Male crabs, lacking roe, are primarily harvested for their meat, making female crabs the exclusive source for this sought-after delicacy.
Ethical Considerations: Harvesting Female Crabs for Roe
Harvesting female crabs for roe raises significant ethical concerns due to their critical role in reproduction and population sustainability. Removing egg-bearing females disrupts breeding cycles, leading to potential declines in crab populations and ecosystem imbalance. Sustainable practices prioritize protecting female crabs with roe to ensure long-term marine biodiversity and fisheries health.
Regional Preferences: Male vs Female Crab Roe Dishes
Regional preferences for crab roe dishes often highlight female crabs, prized for their rich, flavorful eggs, especially in East Asian cuisines where female crab roe is a delicacy. In contrast, some Western regions favor male crab roe, known for its creamier texture and milder taste, used in gourmet seafood recipes. The distinction between male and female crab roe influences culinary traditions and market demand across different coastal cultures.
Nutritional Value: Roe from Female Crabs
Roe from female crabs is highly valued for its rich nutritional profile, providing essential omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality protein, and vital vitamins such as B12 and D. Compared to male crabs, female crab roe contains higher concentrations of antioxidants and crucial minerals like zinc and copper, which support immune health and cellular repair. The unique composition of female crab roe contributes to its superior benefits in promoting brain function and cardiovascular health.
Tips for Buying Female Crabs with Abundant Roe
Choose female crabs with a well-rounded, brightly colored apron for maximum roe content, typically found in mature specimens during the spawning season. Look for crabs with firm, intact shells and avoid those with damaged limbs or discoloration to ensure freshness and quality. Purchasing from reputable seafood markets specializing in seasonal female crabs increases the likelihood of obtaining roe-rich specimens.
Male vs Female Crab for roe Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com