Yogurt offers a smooth texture and consistent tanginess that enhances Indian curries and marinades, providing a creamy base that curd sometimes lacks due to its uneven fermentation. Unlike curd, which can have a variable taste and thickness depending on the starter culture and preparation, yogurt is homogenized and strained, ensuring a stable quality ideal for dishes like raita, lassi, and kadhi. Using yogurt in Indian cooking not only improves flavor but also aids in tenderizing meats and balancing spices effectively.
Table of Comparison
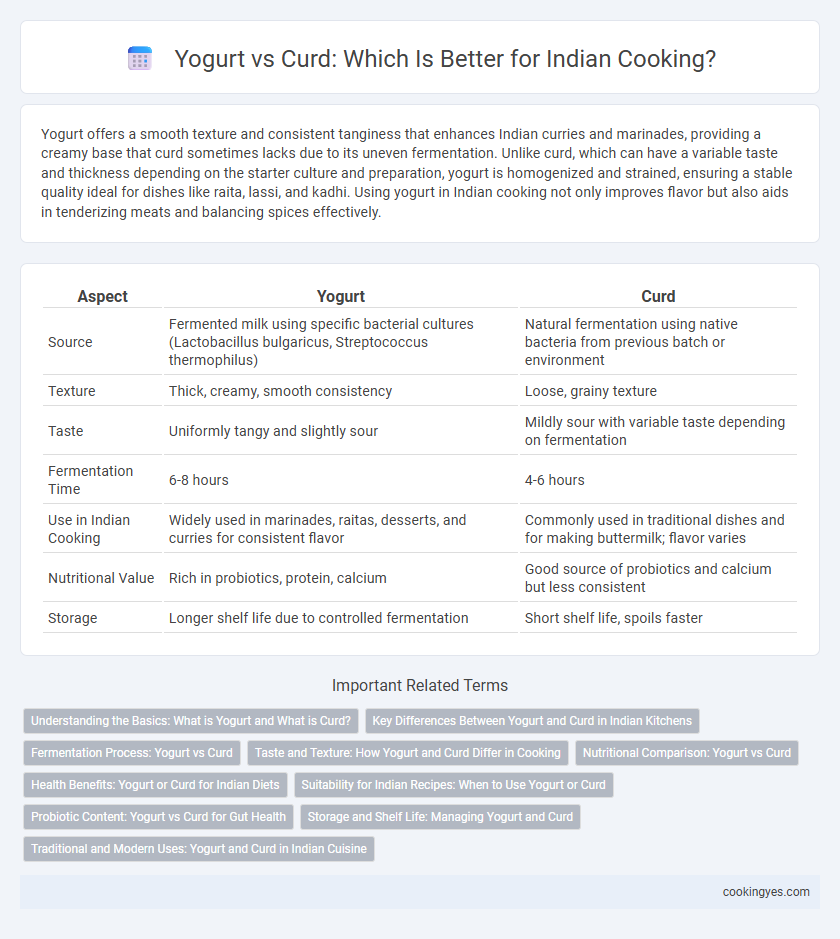
| Aspect | Yogurt | Curd |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fermented milk using specific bacterial cultures (Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus) | Natural fermentation using native bacteria from previous batch or environment |
| Texture | Thick, creamy, smooth consistency | Loose, grainy texture |
| Taste | Uniformly tangy and slightly sour | Mildly sour with variable taste depending on fermentation |
| Fermentation Time | 6-8 hours | 4-6 hours |
| Use in Indian Cooking | Widely used in marinades, raitas, desserts, and curries for consistent flavor | Commonly used in traditional dishes and for making buttermilk; flavor varies |
| Nutritional Value | Rich in probiotics, protein, calcium | Good source of probiotics and calcium but less consistent |
| Storage | Longer shelf life due to controlled fermentation | Short shelf life, spoils faster |
Understanding the Basics: What is Yogurt and What is Curd?
Yogurt is a fermented dairy product made by adding specific bacterial cultures like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus to milk, resulting in a creamy texture and slightly tangy taste. Curd, commonly prepared in Indian households, is formed by naturally fermenting milk with naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria without standardized cultures, leading to variability in texture and flavor. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for Indian cooking, as yogurt offers consistent probiotic benefits and taste, while curd provides a traditional, locally influenced fermentation process.
Key Differences Between Yogurt and Curd in Indian Kitchens
Yogurt in Indian kitchens is a cultured dairy product made using specific bacterial strains like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, resulting in a consistent texture and tangy flavor. Curd, often homemade, involves fermenting milk with naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria, which can lead to variations in taste and texture depending on the starter used. Yogurt is preferred for recipes requiring uniform fermentation and probiotic benefits, while curd is commonly used for traditional dishes due to its ease of preparation and localized microbial content.
Fermentation Process: Yogurt vs Curd
Yogurt and curd differ significantly in their fermentation processes, which impacts their taste and texture in Indian cooking. Yogurt is made using specific bacterial strains like Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, ensuring consistent fermentation and a tangy flavor. Curd is traditionally prepared by fermenting boiled milk with a small amount of previous batch curd, involving a diverse mix of naturally occurring bacteria, resulting in variable taste and texture.
Taste and Texture: How Yogurt and Curd Differ in Cooking
Yogurt offers a creamy, smooth texture with a consistent tangy flavor that enhances Indian dishes like raita and marinades, while curd tends to have a coarser texture and a slightly variable taste due to traditional fermentation methods. The uniform consistency of yogurt ensures better emulsification in dishes such as kadhi and lassi, whereas curd's uneven curdling can affect the mouthfeel and overall balance of flavors. In Indian cooking, yogurt is preferred for its stability and refined texture, making it essential for recipes requiring precise taste and smoothness.
Nutritional Comparison: Yogurt vs Curd
Yogurt contains higher probiotic cultures than curd, enhancing digestive health and immunity. Curd, often homemade, varies in nutritional content but generally has less protein and calcium compared to commercially prepared yogurt. Both provide essential vitamins like B12 and minerals, yet yogurt's consistent fermentation process makes it a more reliable source of gut-friendly bacteria in Indian cooking.
Health Benefits: Yogurt or Curd for Indian Diets
Yogurt contains live probiotic cultures like Lactobacillus, which improve gut health and boost immunity, making it a valuable inclusion in Indian diets. Curd, often homemade and less standardized, may vary in probiotic content but still provides essential nutrients like calcium and protein. Regular consumption of yogurt offers more consistent digestive benefits and supports a balanced Indian diet rich in fermented dairy.
Suitability for Indian Recipes: When to Use Yogurt or Curd
Yogurt and curd differ in texture and fermentation methods, influencing their use in Indian cooking; yogurt offers a consistent, tangy flavor ideal for marinades, raita, and desserts, while homemade curd provides a softer, milder taste often preferred in traditional dishes like kadhi and certain dals. Yogurt's uniformity and probiotic benefits make it suitable for recipes requiring precise acidity control and creamy consistency, whereas curd's natural fermentation suits rustic preparations and quick meals. Selecting between yogurt and curd depends on recipe requirements, desired taste profiles, and fermentation time for optimal results in Indian cuisine.
Probiotic Content: Yogurt vs Curd for Gut Health
Yogurt contains live bacterial cultures such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, which are proven probiotics promoting gut health by enhancing digestion and boosting immunity. In contrast, traditional Indian curd may have variable probiotic content depending on preparation methods and starter cultures used, often lacking consistent probiotic strains. For optimal gut health benefits in Indian cooking, choosing commercially prepared yogurt with standardized probiotic strains ensures more effective and reliable probiotic intake.
Storage and Shelf Life: Managing Yogurt and Curd
Yogurt typically has a longer shelf life than curd due to its controlled fermentation process and presence of specific probiotic strains, making it more suitable for longer storage in refrigeration at 4degC for up to two weeks. Curd, often homemade using spontaneous fermentation, has a shorter shelf life of about 3 to 4 days when stored at similar temperatures, requiring faster consumption to avoid spoilage. Proper airtight containers and consistent cold storage are essential to maintain the freshness and prevent bacterial contamination in both yogurt and curd for Indian cooking.
Traditional and Modern Uses: Yogurt and Curd in Indian Cuisine
Yogurt and curd both play essential roles in Indian cooking, with yogurt often preferred in modern recipes for its consistent texture and probiotic benefits. Traditional Indian cuisine relies heavily on curd, especially homemade versions, for marination, tempering, and fermentation processes that enhance flavor and digestion. The distinction lies in yogurt's controlled bacterial culture compared to curd's spontaneous fermentation, making yogurt a staple in contemporary dishes like raita and lassi, while curd remains integral in rustic, regional preparations.
Yogurt vs Curd for Indian Cooking Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com