Gluten-free toast provides a safe alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, preventing adverse reactions commonly triggered by wheat gluten. Wheat toast contains essential nutrients like fiber and vitamins but can cause digestive discomfort or immune responses in those with gluten intolerance. Choosing gluten-free options ensures dietary needs are met without sacrificing taste or texture in everyday meals.
Table of Comparison
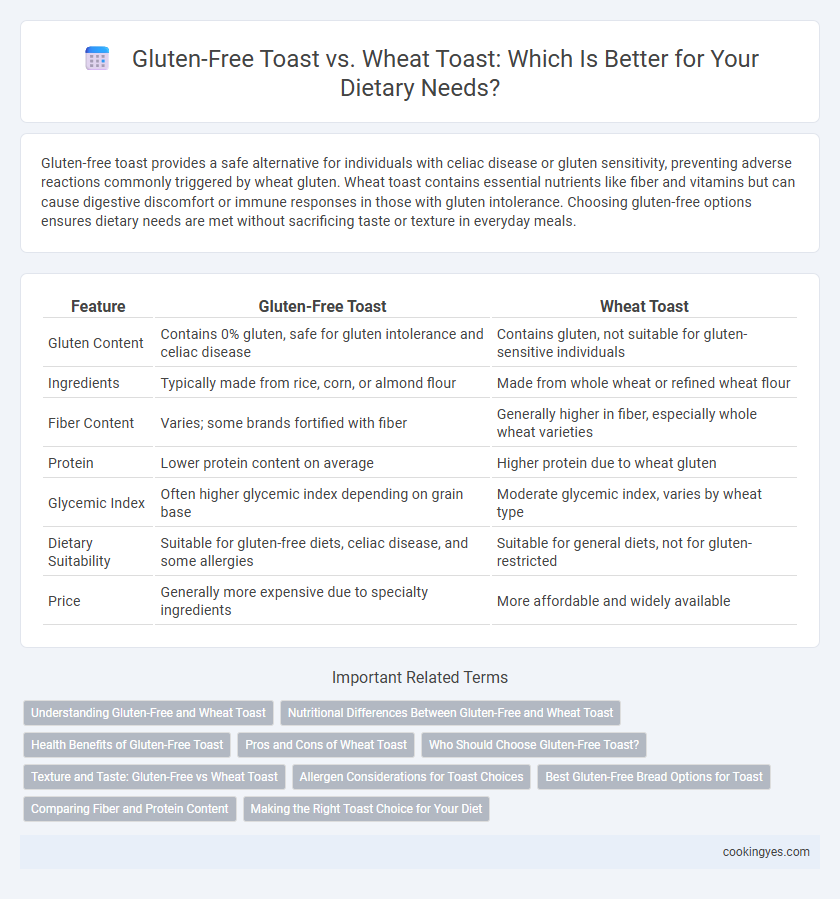
| Feature | Gluten-Free Toast | Wheat Toast |
|---|---|---|
| Gluten Content | Contains 0% gluten, safe for gluten intolerance and celiac disease | Contains gluten, not suitable for gluten-sensitive individuals |
| Ingredients | Typically made from rice, corn, or almond flour | Made from whole wheat or refined wheat flour |
| Fiber Content | Varies; some brands fortified with fiber | Generally higher in fiber, especially whole wheat varieties |
| Protein | Lower protein content on average | Higher protein due to wheat gluten |
| Glycemic Index | Often higher glycemic index depending on grain base | Moderate glycemic index, varies by wheat type |
| Dietary Suitability | Suitable for gluten-free diets, celiac disease, and some allergies | Suitable for general diets, not for gluten-restricted |
| Price | Generally more expensive due to specialty ingredients | More affordable and widely available |
Understanding Gluten-Free and Wheat Toast
Gluten-free toast is made from alternative flours such as rice, almond, or sorghum, specifically designed for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, ensuring no gluten exposure. Wheat toast contains gluten, a protein that provides elasticity and chewiness but can trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals. Choosing gluten-free toast supports digestive health and prevents inflammation for those with gluten intolerance or wheat allergy.
Nutritional Differences Between Gluten-Free and Wheat Toast
Gluten-free toast often contains alternative flours like rice, almond, or tapioca, which can result in lower protein and fiber content compared to wheat toast that is rich in gluten and bran. Wheat toast typically provides higher amounts of essential nutrients such as B vitamins, iron, and dietary fiber, supporting digestive health and sustained energy levels. For individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, gluten-free toast offers a safe alternative but may require careful selection to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Health Benefits of Gluten-Free Toast
Gluten-free toast offers significant health benefits for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity by reducing inflammation and preventing digestive discomfort. It is typically made from alternative grains like rice, almond, or oat flour, which can provide higher levels of fiber and essential nutrients compared to traditional wheat toast. Choosing gluten-free toast supports better gut health and enhances nutrient absorption for those with dietary restrictions related to gluten.
Pros and Cons of Wheat Toast
Wheat toast provides essential nutrients like fiber, B vitamins, and iron, supporting digestive health and energy metabolism. However, it contains gluten, which can trigger adverse reactions in individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. While wheat toast offers more protein and minerals than gluten-free alternatives, it may cause digestive discomfort or inflammation for those with gluten-related disorders.
Who Should Choose Gluten-Free Toast?
Gluten-free toast is essential for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, as it prevents adverse reactions like digestive distress and inflammation. Those with wheat allergies or autoimmune disorders also benefit from choosing gluten-free options to avoid immune system triggers. People aiming to reduce gluten intake for digestive health or personal dietary preferences may find gluten-free toast a suitable alternative to traditional wheat toast.
Texture and Taste: Gluten-Free vs Wheat Toast
Gluten-free toast often has a denser, chewier texture compared to the light, airy crumb of traditional wheat toast due to the absence of gluten, which provides elasticity and structure. The taste of gluten-free toast can vary significantly depending on the blend of alternative flours used, often lending a nuttier or earthier flavor, while wheat toast maintains a familiar, mild, and slightly sweet flavor profile. Consumers with dietary needs frequently choose gluten-free toast for gluten intolerance or celiac disease, accepting the trade-off in texture and taste for health benefits.
Allergen Considerations for Toast Choices
Gluten-free toast offers a safe alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, eliminating the risk of gluten-related allergic reactions common in wheat toast. Wheat toast contains gluten proteins such as gliadin, which can trigger immune responses ranging from mild digestive discomfort to severe anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals. Selecting gluten-free toast ensures adherence to strict allergen avoidance protocols, reducing potential exposure to wheat allergens and cross-contamination in dietary plans.
Best Gluten-Free Bread Options for Toast
Best gluten-free bread options for toast include varieties made from almond flour, rice flour, and tapioca starch, which provide a satisfying texture and flavor while avoiding gluten. These breads often contain added fiber and protein to enhance nutritional value and help maintain stable blood sugar levels, making them suitable for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Brands like Udi's, Canyon Bakehouse, and Schar are known for producing high-quality gluten-free toast breads that perform well in toasters without crumbling.
Comparing Fiber and Protein Content
Gluten-free toast often contains less fiber and protein compared to traditional wheat toast, which is naturally rich in these nutrients due to its whole grain content. Wheat toast provides higher levels of dietary fiber, essential for digestive health, and more protein, critical for muscle repair and growth. For individuals prioritizing fiber and protein intake, wheat toast generally offers more nutritional benefits than gluten-free alternatives.
Making the Right Toast Choice for Your Diet
Gluten-free toast provides a safe and nutritious option for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, as it eliminates harmful gluten proteins found in wheat toast. Wheat toast contains essential nutrients like fiber and B vitamins but can trigger adverse reactions in those with gluten intolerance. Choosing the right toast depends on dietary restrictions and nutritional needs, prioritizing gluten-free options for those requiring strict gluten avoidance.
Gluten-free toast vs wheat toast for dietary needs Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com