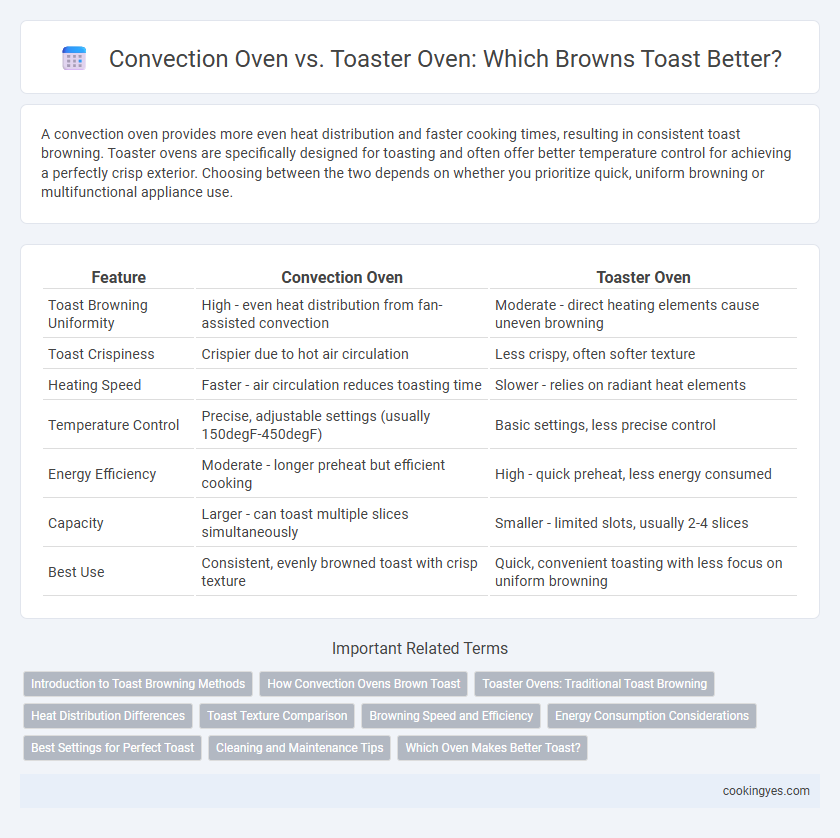
A convection oven provides more even heat distribution and faster cooking times, resulting in consistent toast browning. Toaster ovens are specifically designed for toasting and often offer better temperature control for achieving a perfectly crisp exterior. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize quick, uniform browning or multifunctional appliance use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Convection Oven | Toaster Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Toast Browning Uniformity | High - even heat distribution from fan-assisted convection | Moderate - direct heating elements cause uneven browning |
| Toast Crispiness | Crispier due to hot air circulation | Less crispy, often softer texture |
| Heating Speed | Faster - air circulation reduces toasting time | Slower - relies on radiant heat elements |
| Temperature Control | Precise, adjustable settings (usually 150degF-450degF) | Basic settings, less precise control |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate - longer preheat but efficient cooking | High - quick preheat, less energy consumed |
| Capacity | Larger - can toast multiple slices simultaneously | Smaller - limited slots, usually 2-4 slices |
| Best Use | Consistent, evenly browned toast with crisp texture | Quick, convenient toasting with less focus on uniform browning |
Introduction to Toast Browning Methods
Toast browning methods primarily rely on heat distribution to achieve the desired crispness and color. Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air evenly, resulting in consistent toasting across the bread's surface. Toaster ovens, while smaller, provide direct radiant heating elements that can produce quicker browning but may sometimes create uneven results due to localized heat zones.
How Convection Ovens Brown Toast
Convection ovens brown toast by circulating hot air evenly around the bread, creating a consistent toasting surface and reducing cooking time. The fan-driven air distribution ensures Maillard reaction occurs uniformly, resulting in crispier and evenly browned toast. Unlike toaster ovens, convection ovens offer precise temperature control and moisture reduction for optimal toast browning.
Toaster Ovens: Traditional Toast Browning
Toaster ovens provide consistent and evenly distributed heat, making them ideal for traditional toast browning with a crisp exterior and a warm, soft interior. Their compact size and adjustable browning settings enable precise control over toast color and texture, outperforming convection ovens in energy efficiency for small batches. The use of quartz or halogen elements in many toaster ovens ensures rapid and uniform toasting, preserving flavor without drying out the bread.
Heat Distribution Differences
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air evenly around the bread, ensuring uniform toast browning on all sides. Toaster ovens rely on heating elements positioned closer to the bread, which can result in uneven heat distribution and patchy browning. The consistent airflow in convection ovens reduces hot spots, producing a more evenly toasted slice compared to the direct but uneven heat of toaster ovens.
Toast Texture Comparison
Convection ovens produce toast with a more even texture due to their circulating hot air, resulting in a consistently crisp exterior and soft interior. Toaster ovens may create uneven browning with slightly chewier edges, as heat distribution is less uniform. Choosing a convection oven enhances toast texture by balancing crunch and moisture retention more effectively.
Browning Speed and Efficiency
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in faster and more even browning of toast compared to toaster ovens, which rely on radiant heat without air circulation. The efficient heat distribution in convection ovens reduces toasting time while achieving consistent browning on all sides. Toaster ovens may offer convenience for small batches but generally take longer and produce less uniform browning than convection ovens.
Energy Consumption Considerations
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, distributing heat more evenly and reducing cooking time, which often results in lower energy consumption compared to toaster ovens. Toaster ovens typically consume less energy per use due to their smaller size but may take longer to achieve desired toast browning, potentially offsetting energy savings. Evaluating energy consumption for toast browning depends on balancing cooking time, oven size, and heat distribution efficiency.
Best Settings for Perfect Toast
Achieving the perfect toast browning requires understanding the differences between convection ovens and toaster ovens, with convection ovens providing more even heat distribution due to their fan-assisted air circulation. Setting the temperature between 350degF to 400degF in a convection oven ensures consistent browning without burning, while toaster ovens often perform best at 375degF using the toast or bake setting for quick, evenly browned results. Monitoring toasting time closely, typically 3 to 5 minutes depending on bread type, prevents overcooking and allows customization of toast crispness.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Convection ovens distribute heat evenly, reducing burnt residue and making cleaning easier with removable trays and self-cleaning options, while toaster ovens often require frequent crumb tray emptying to prevent buildup. To maintain optimal toast browning, regularly wipe interior surfaces with a damp cloth and avoid using abrasive cleaners that could damage heating elements. Ensuring proper maintenance extends appliance lifespan and preserves consistent browning performance.
Which Oven Makes Better Toast?
A convection oven offers more even heat distribution and faster cooking times, resulting in consistently browned toast with a crispy exterior and soft interior. In contrast, a toaster oven provides convenience and quicker preheating but may produce uneven browning due to less efficient heat circulation. For achieving superior toast browning, especially in larger batches, convection ovens generally outperform toaster ovens.
Convection Oven vs Toaster Oven for Toast Browning Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com