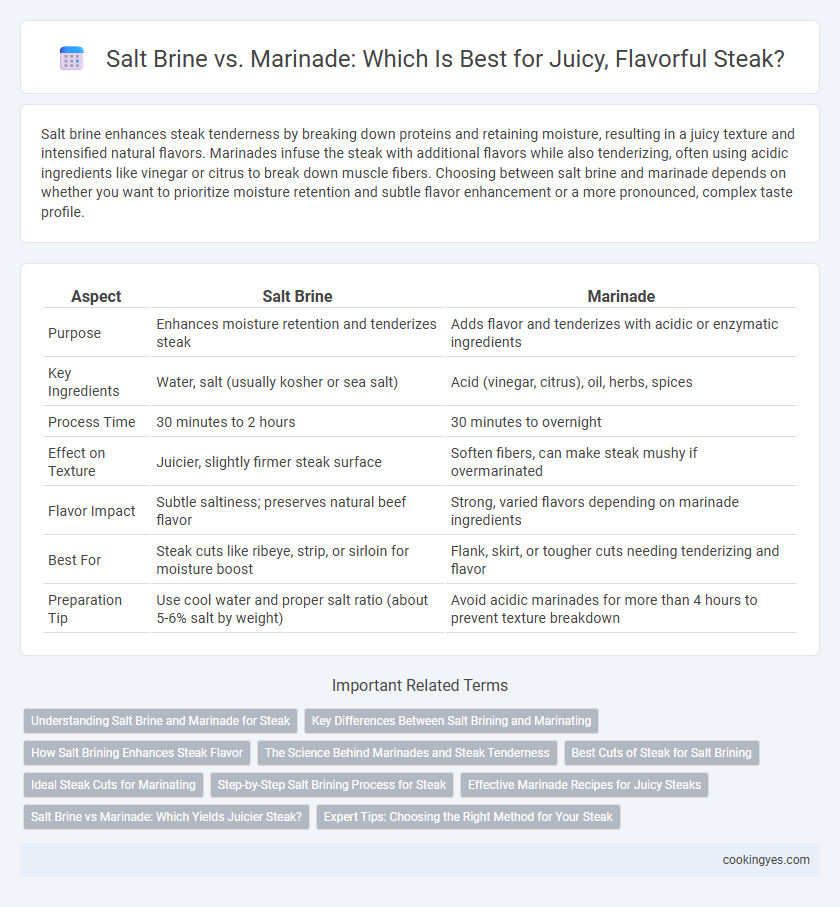
Salt brine enhances steak tenderness by breaking down proteins and retaining moisture, resulting in a juicy texture and intensified natural flavors. Marinades infuse the steak with additional flavors while also tenderizing, often using acidic ingredients like vinegar or citrus to break down muscle fibers. Choosing between salt brine and marinade depends on whether you want to prioritize moisture retention and subtle flavor enhancement or a more pronounced, complex taste profile.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Salt Brine | Marinade |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances moisture retention and tenderizes steak | Adds flavor and tenderizes with acidic or enzymatic ingredients |
| Key Ingredients | Water, salt (usually kosher or sea salt) | Acid (vinegar, citrus), oil, herbs, spices |
| Process Time | 30 minutes to 2 hours | 30 minutes to overnight |
| Effect on Texture | Juicier, slightly firmer steak surface | Soften fibers, can make steak mushy if overmarinated |
| Flavor Impact | Subtle saltiness; preserves natural beef flavor | Strong, varied flavors depending on marinade ingredients |
| Best For | Steak cuts like ribeye, strip, or sirloin for moisture boost | Flank, skirt, or tougher cuts needing tenderizing and flavor |
| Preparation Tip | Use cool water and proper salt ratio (about 5-6% salt by weight) | Avoid acidic marinades for more than 4 hours to prevent texture breakdown |
Understanding Salt Brine and Marinade for Steak
Salt brine enhances steak by penetrating the meat to retain moisture and improve tenderness through osmosis, using a solution of water and salt. Marinades combine acids, oils, herbs, and spices to flavor the steak surface and tenderize proteins, affecting both taste and texture. Choosing between salt brine and marinade depends on the desired outcome: salt brine primarily boosts juiciness and internal salt distribution, while marinade infuses complex flavors and tenderizes externally.
Key Differences Between Salt Brining and Marinating
Salt brining involves soaking steak in a saline solution to enhance moisture retention and improve texture by breaking down muscle proteins, while marinating uses acidic or enzymatic ingredients to infuse flavor and tenderize the meat. Brining primarily affects juiciness and tenderness through osmotic processes, whereas marinating focuses on flavor absorption and surface tenderization. Unlike marinades, salt brines do not significantly alter the steak's taste but provide a more consistent internal seasoning and moisture balance.
How Salt Brining Enhances Steak Flavor
Salt brining enhances steak flavor by penetrating the meat, improving moisture retention and seasoning it evenly throughout. The salt in the brine dissolves muscle proteins, resulting in a juicier, more tender texture and intensifying the natural beef taste. This process contrasts with marinades, which typically flavor only the surface, making brining a superior method for deep, flavorful steak preparation.
The Science Behind Marinades and Steak Tenderness
Salt brine enhances steak tenderness by penetrating muscle fibers, breaking down proteins, and increasing moisture retention for juicier meat. Marinades contain acids or enzymes that chemically alter connective tissues, further softening the steak and infusing complex flavors. The interplay between salt brine's osmotic effect and marinade's enzymatic action maximizes tenderness and taste in cooked steaks.
Best Cuts of Steak for Salt Brining
Salt brining enhances the juiciness and tenderness of tougher steak cuts like flank, skirt, and hanger steak by breaking down muscle fibers and promoting moisture retention. Unlike marinades, which often add flavor through acidic components, salt brines penetrate deeply to improve texture without overpowering the natural beef taste. Choosing cuts such as chuck or round steak for salt brining results in a more succulent and evenly cooked steak, making them ideal candidates for this method.
Ideal Steak Cuts for Marinating
Tender cuts like flank, skirt, and sirloin benefit most from marinating, as the acidic components in marinades break down muscle fibers, enhancing flavor and tenderness. In contrast, premium cuts such as ribeye and filet mignon are better suited for salt brine treatments that improve juiciness without overpowering their natural taste. Choosing the right method based on the cut ensures optimal texture and flavor balance for any steak preparation.
Step-by-Step Salt Brining Process for Steak
Salt brining steak involves submerging the meat in a solution of water and salt, typically using a ratio of 1/4 cup kosher salt per quart of water, for 1 to 2 hours to enhance moisture retention and flavor. After brining, rinse the steak under cold water, pat dry thoroughly, and let it rest at room temperature before cooking to ensure even seasoning and improved texture. This method differs from marinade by primarily focusing on moisture absorption rather than flavor infusion, resulting in a juicier, tender steak.
Effective Marinade Recipes for Juicy Steaks
Salt brine enhances steak juiciness by allowing salt to penetrate deeply, improving moisture retention and tenderness. Marinades combining acidic ingredients like lemon juice or vinegar with herbs, garlic, and olive oil break down muscle fibers, infusing rich flavors and further tenderizing the meat. Effective marinade recipes for juicy steaks often include soy sauce, Worcestershire sauce, brown sugar, and crushed black pepper to balance umami, sweetness, and spice while locking in moisture.
Salt Brine vs Marinade: Which Yields Juicier Steak?
Salt brining a steak involves soaking the meat in a saltwater solution that enhances moisture retention by breaking down muscle proteins, resulting in a juicier texture. Marinades, typically composed of acidic ingredients like vinegar or citrus combined with herbs and spices, tenderize the steak but may not penetrate as deeply or retain moisture as effectively as a salt brine. Scientific tests show that salt brining outperforms most marinades in preserving internal juiciness while providing balanced flavor absorption.
Expert Tips: Choosing the Right Method for Your Steak
Salt brining steak enhances moisture retention by allowing salt to penetrate the meat fibers, resulting in a juicier, more tender steak with improved seasoning. Marinades, typically acidic and oil-based, break down muscle proteins and infuse flavor profiles, ideal for tougher cuts requiring tenderization. Expert tips recommend salt brining for prime cuts like ribeye or strip steak, while marinades suit flank or skirt steaks that benefit from both flavor and tenderizing effects.
Salt Brine vs Marinade for Steak Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com