Veloute and potage represent two distinct styles of French soups, with veloute characterized by its smooth, creamy texture created through a roux-based sauce enriched with stock and cream. Potage, on the other hand, refers to a broader category of soups ranging from thick purees to clear broths, often featuring a variety of vegetables and meats simmered together for a heartier flavor. Choosing between veloute and potage depends on the desired consistency and richness, with veloute offering a velvety mouthfeel and potage providing a more rustic, diverse taste experience.
Table of Comparison
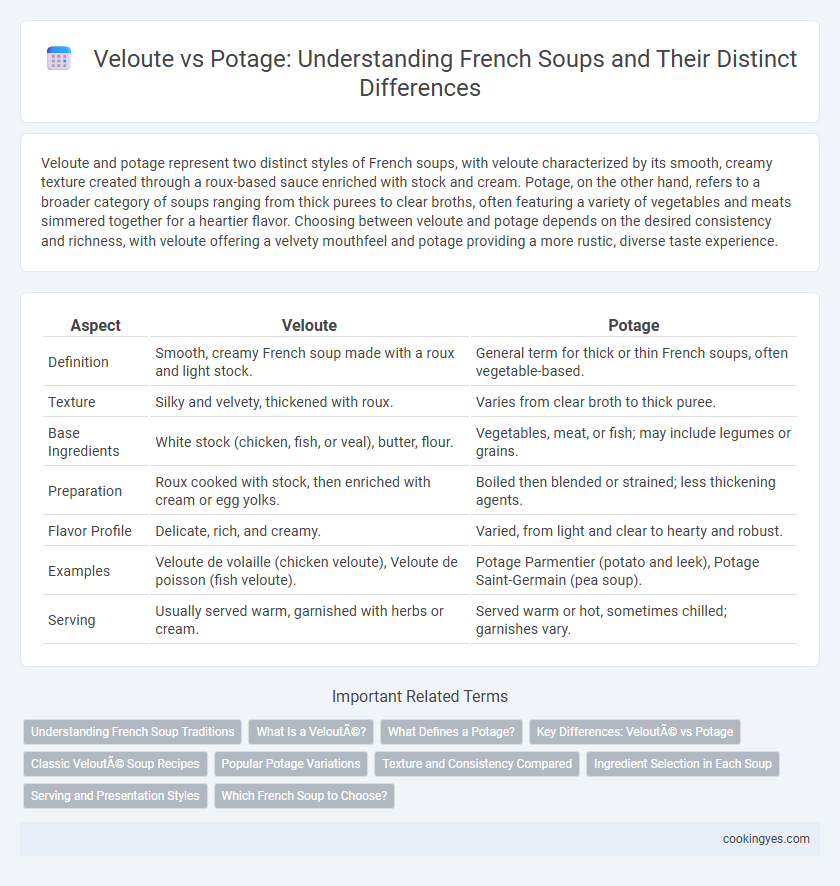
| Aspect | Veloute | Potage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smooth, creamy French soup made with a roux and light stock. | General term for thick or thin French soups, often vegetable-based. |
| Texture | Silky and velvety, thickened with roux. | Varies from clear broth to thick puree. |
| Base Ingredients | White stock (chicken, fish, or veal), butter, flour. | Vegetables, meat, or fish; may include legumes or grains. |
| Preparation | Roux cooked with stock, then enriched with cream or egg yolks. | Boiled then blended or strained; less thickening agents. |
| Flavor Profile | Delicate, rich, and creamy. | Varied, from light and clear to hearty and robust. |
| Examples | Veloute de volaille (chicken veloute), Veloute de poisson (fish veloute). | Potage Parmentier (potato and leek), Potage Saint-Germain (pea soup). |
| Serving | Usually served warm, garnished with herbs or cream. | Served warm or hot, sometimes chilled; garnishes vary. |
Understanding French Soup Traditions
Veloute and potage represent two fundamental categories in French soup traditions, each with distinct characteristics. Veloute is a smooth, creamy soup made from a white stock thickened with a roux, offering a velvety texture and subtle flavor profile. Potage refers to a broader range of soups, often chunky or pureed, incorporating a variety of vegetables, meats, or grains, highlighting the rustic and diverse nature of French culinary heritage.
What Is a Velouté?
A veloute is a classic French soup characterized by its smooth, creamy texture achieved through a base of light stock thickened with a roux, typically made from butter and flour. Unlike potage, which is more general and can include chunky vegetables or purees, veloute emphasizes a velvety consistency without visible solid ingredients. This soup is often enriched with cream or egg yolks to enhance its rich, silky mouthfeel.
What Defines a Potage?
Potage is a traditional French soup characterized by its thick, hearty consistency, typically made by boiling vegetables, legumes, or meat in a broth until soft and then blending or mashing them to create a smooth or chunky texture. Unlike veloute, which is a velvety sauce-based soup thickened with a roux and enriched with cream, potage emphasizes the natural flavors and textures of the primary ingredients without relying on a velvety base. Classic examples of potage include potage parmentier (potato and leek soup) and potage aux legumes (vegetable soup), showcasing its versatility and rustic appeal.
Key Differences: Velouté vs Potage
Veloute is a classic French soup characterized by a smooth, velvety texture achieved through a base of roux and clear stock, often enriched with cream, making it lighter and silkier. Potage, in contrast, refers broadly to thick, hearty soups that are typically pureed and may include a variety of vegetables, legumes, or meats, emphasizing rustic and robust flavors. The key difference lies in veloute's delicate, creamy consistency versus potage's more substantial, chunky or blended nature reflecting traditional comfort food.
Classic Velouté Soup Recipes
Classic veloute soup recipes are distinguished by their rich, smooth texture achieved through a veloute sauce base made from light stock and a blond roux. Unlike potage, which is a more general term for thick, pureed soups, veloute emphasizes a silky consistency and delicate flavor, often incorporating cream or egg yolks for added richness. Traditional varieties include chicken veloute and seafood veloute, prized in French cuisine for their refined taste and elegant presentation.
Popular Potage Variations
Potage represents a broad category of French soups, typically thick and hearty, with popular variations including Potage Parmentier (leek and potato) and Potage Saint-Germain (pea soup). Veloute, contrasted with potage, is a smooth, velvety soup made from a light stock such as chicken, fish, or veal and thickened with a roux, often enriched with cream. While veloute emphasizes a silky texture and delicate flavor, potage showcases a diverse range of vegetables and purees, reflecting rustic and regional culinary traditions.
Texture and Consistency Compared
Veloute soups exhibit a smooth, velvety texture achieved by thickening light stock with a roux, creating a rich yet delicate consistency. Potage soups offer a thicker, heartier texture, often pureed or containing chunky vegetables, providing a more substantial mouthfeel. The key difference lies in veloute's refined silkiness contrasted with potage's robust, dense consistency.
Ingredient Selection in Each Soup
Veloute soup relies on a light stock, typically chicken or fish, and is thickened with a roux made from butter and flour, emphasizing smooth, creamy textures. Potage incorporates a broader range of ingredients including vegetables, meats, and grains, often pureed or left chunky, creating a heartier and more diverse flavor profile. Ingredient selection for veloute centers on delicate, refined elements, while potage embraces rustic, robust components for varied consistency.
Serving and Presentation Styles
Veloute soups are typically served as smooth, creamy courses in elegant bowls, often garnished with a dollop of cream or finely chopped herbs to enhance their velvety texture. Potage, on the other hand, is presented more rustic and hearty, frequently featuring chunky vegetables or meat, served in deeper dishes to accommodate its thicker consistency. Both styles emphasize visual appeal, but veloute aims for a refined, polished finish while potage embraces a comforting, robust presentation.
Which French Soup to Choose?
Veloute and potage are two classic French soup styles distinguished by their texture and preparation; veloute features a smooth, velvety base made from a light stock thickened with a roux, while potage is a broader category that includes chunky, brothy, and pureed soups. Choosing between veloute and potage depends on the desired mouthfeel and ingredient presentation, with veloute ideal for rich, creamy soups like chicken veloute or seafood bisque, and potage offering more variety with rustic vegetable or meat-based broths. For a refined dining experience, veloute is preferred, whereas potage suits casual meals or when highlighting fresh, rustic ingredients.
Velouté vs Potage for French soups Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com