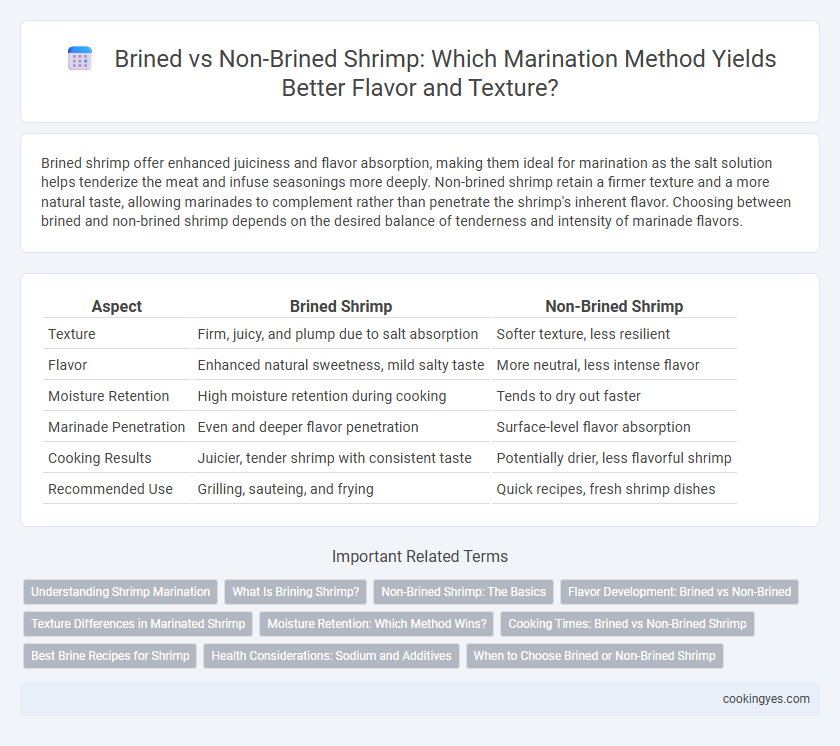
Brined shrimp offer enhanced juiciness and flavor absorption, making them ideal for marination as the salt solution helps tenderize the meat and infuse seasonings more deeply. Non-brined shrimp retain a firmer texture and a more natural taste, allowing marinades to complement rather than penetrate the shrimp's inherent flavor. Choosing between brined and non-brined shrimp depends on the desired balance of tenderness and intensity of marinade flavors.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Brined Shrimp | Non-Brined Shrimp |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Firm, juicy, and plump due to salt absorption | Softer texture, less resilient |
| Flavor | Enhanced natural sweetness, mild salty taste | More neutral, less intense flavor |
| Moisture Retention | High moisture retention during cooking | Tends to dry out faster |
| Marinade Penetration | Even and deeper flavor penetration | Surface-level flavor absorption |
| Cooking Results | Juicier, tender shrimp with consistent taste | Potentially drier, less flavorful shrimp |
| Recommended Use | Grilling, sauteing, and frying | Quick recipes, fresh shrimp dishes |
Understanding Shrimp Marination
Brined shrimp absorb moisture and salt through osmosis, resulting in juicier, more flavorful seafood with enhanced texture. Non-brined shrimp marinate more slowly, relying primarily on surface absorption of seasonings, which can lead to less tender results. Understanding the difference in shrimp marination techniques is essential for optimizing taste and texture in seafood dishes.
What Is Brining Shrimp?
Brining shrimp involves soaking the seafood in a saltwater solution, which enhances moisture retention and intensifies natural flavors during cooking. The process typically uses a mixture of water, salt, and sometimes sugar or spices, creating a balance that prevents the shrimp from drying out and improving texture. Non-brined shrimp marination skips this step, resulting in a less juicy and less flavorful final dish.
Non-Brined Shrimp: The Basics
Non-brined shrimp marination involves soaking the shrimp directly in flavorful liquids without a prior saltwater soak, preserving the natural texture and delivering a more intense marinade absorption. Skipping the brine process results in shrimp that tend to cook firmer and maintain a slightly sweeter, ocean-fresh taste. This method suits recipes emphasizing bold, acidic, or spicy marinades designed to penetrate the shrimp's surface quickly.
Flavor Development: Brined vs Non-Brined
Brined shrimp absorbs salt and aromatics, enhancing natural sweetness and resulting in juicier, more flavorful meat with improved texture. Non-brined shrimp may lack depth, sometimes tasting bland or rubbery after cooking due to moisture loss. The brining process promotes even seasoning and intensifies umami, making it the preferred method for robust flavor development in shrimp dishes.
Texture Differences in Marinated Shrimp
Brined shrimp exhibit a firmer, juicier texture due to the salt solution penetrating the muscle fibers and enhancing water retention. Non-brined shrimp tend to be softer and less resilient, often resulting in a more delicate bite but less structural integrity. The brining process preserves the shrimp's natural succulence, preventing it from becoming rubbery during cooking.
Moisture Retention: Which Method Wins?
Brined shrimp retain significantly more moisture during cooking compared to non-brined shrimp, resulting in juicier and more tender texture. The salt solution in brining enhances water absorption and helps prevent moisture loss, leading to better flavor and succulence. Non-brined shrimp tend to lose natural juices quickly, often producing a drier final product.
Cooking Times: Brined vs Non-Brined Shrimp
Brined shrimp absorb moisture and seasoning faster, resulting in shorter cooking times, typically 2 to 3 minutes compared to 3 to 4 minutes for non-brined shrimp. The salt in the brine helps to firm the shrimp's texture, preventing overcooking and ensuring even heat penetration. Non-brined shrimp require more careful timing to avoid rubberiness and dryness during cooking.
Best Brine Recipes for Shrimp
Brined shrimp retain optimal moisture and absorb flavors more deeply, enhancing texture and taste compared to non-brined counterparts. Best brine recipes for shrimp typically include a balanced mix of water, kosher salt, sugar, and aromatics like garlic, lemon zest, and bay leaves for maximum flavor infusion. Using a 20-minute soak in these brines ensures shrimp remain juicy and flavorful, perfect for grilling or sauteing.
Health Considerations: Sodium and Additives
Brined shrimp contain higher sodium levels due to the saltwater solution used in the process, which can impact those monitoring their sodium intake for health reasons such as hypertension. Non-brined shrimp generally have fewer additives and lower sodium content, making them a preferable option for a cleaner, more natural choice in seafood consumption. Choosing non-brined shrimp helps reduce the risk of excessive sodium intake and exposure to preservatives commonly found in commercial brining solutions.
When to Choose Brined or Non-Brined Shrimp
Brined shrimp absorb salt and moisture, resulting in juicier, more flavorful seafood ideal for grilling or frying. Non-brined shrimp offer a milder taste and firmer texture, preferred for delicate dishes like ceviche or sushi. Choose brined shrimp when aiming for enhanced succulence and seasoning, while non-brined shrimp work best for recipes requiring a subtle shrimp flavor and firm bite.
Brined vs Non-brined for shrimp marination Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com