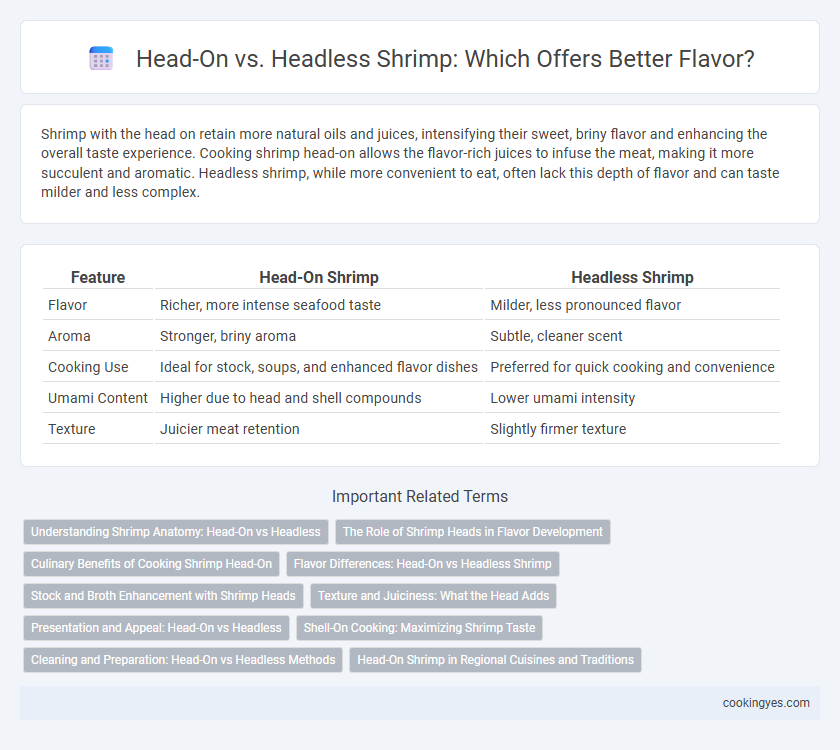
Shrimp with the head on retain more natural oils and juices, intensifying their sweet, briny flavor and enhancing the overall taste experience. Cooking shrimp head-on allows the flavor-rich juices to infuse the meat, making it more succulent and aromatic. Headless shrimp, while more convenient to eat, often lack this depth of flavor and can taste milder and less complex.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Head-On Shrimp | Headless Shrimp |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Richer, more intense seafood taste | Milder, less pronounced flavor |
| Aroma | Stronger, briny aroma | Subtle, cleaner scent |
| Cooking Use | Ideal for stock, soups, and enhanced flavor dishes | Preferred for quick cooking and convenience |
| Umami Content | Higher due to head and shell compounds | Lower umami intensity |
| Texture | Juicier meat retention | Slightly firmer texture |
Understanding Shrimp Anatomy: Head-On vs Headless
Shrimp heads contain concentrated flavors and natural oils that enhance the overall taste and richness of seafood dishes. Cooking shrimp head-on preserves these flavorful compounds, resulting in a more intense, savory experience compared to headless shrimp. Understanding shrimp anatomy reveals that the head houses key flavor components, making head-on shrimp a preferred choice for chefs seeking depth in dishes like shrimp boil or grilled shrimp.
The Role of Shrimp Heads in Flavor Development
Shrimp heads contain concentrated compounds such as amino acids and natural oils that significantly enhance the umami and sweetness of seafood dishes. Cooking shrimp with heads on releases these flavorful elements into the broth or sauce, intensifying the overall taste profile. Removing the heads reduces the depth of flavor, often resulting in a milder and less aromatic shrimp experience.
Culinary Benefits of Cooking Shrimp Head-On
Cooking shrimp head-on enhances flavor by preserving natural oils and juices concentrated in the head, resulting in a richer, more intense taste. The shrimp head contains flavorful fats and roe that infuse dishes with umami and depth, elevating sauces and broths. Culinary techniques like grilling or boiling head-on shrimp maximize aroma and succulence, making them a preferred choice for chefs seeking robust seafood flavors.
Flavor Differences: Head-On vs Headless Shrimp
Head-on shrimp deliver a more intense and rich flavor due to the aromatic compounds and fats concentrated in the heads, enhancing the overall taste profile during cooking. In contrast, headless shrimp provide a cleaner, milder flavor, making them ideal for dishes where subtlety is preferred. The choice between head-on and headless shrimp significantly impacts the depth and complexity of seafood recipes.
Stock and Broth Enhancement with Shrimp Heads
Shrimp heads contain concentrated flavor compounds and natural fats that significantly enhance the richness and depth of stocks and broths. Using head-on shrimp in broth preparation infuses the liquid with umami, sweetness, and a savory complexity unattainable with headless shrimp alone. The gelatin and aromatic oils released from the heads contribute to a fuller body and more satisfying mouthfeel in seafood-based soups and sauces.
Texture and Juiciness: What the Head Adds
Head-on shrimp retain natural juices and oils, enhancing the texture with a firmer, more succulent bite. The head contains fat-rich compounds that infuse the meat with rich, savory flavors and increased moisture. Removing the head often results in a drier texture and less intense, less complex taste experience.
Presentation and Appeal: Head-On vs Headless
Head-on shrimp offers a more visually enticing presentation with its intact antennae and vibrant eyes, enhancing the dish's overall appeal and perceived freshness. The presence of the head also contributes to a richer, more complex flavor profile during cooking, as the fats and juices from the head infuse the shrimp meat. Headless shrimp provide a cleaner, easier-to-eat option but may lack the dramatic visual impact and depth of flavor associated with head-on shrimp dishes.
Shell-On Cooking: Maximizing Shrimp Taste
Cooking shrimp shell-on enhances flavor by locking in natural juices and imparting a richer, brinier taste compared to headless shrimp. The shells contain essential oils that release during cooking, intensifying the umami and sweetness of the shrimp meat. Choosing head-on, shell-on shrimp maximizes aromatic compounds, resulting in a more robust and succulent seafood experience.
Cleaning and Preparation: Head-On vs Headless Methods
Head-on shrimp retain natural juices and contribute to richer, more intense flavor during cooking, while headless shrimp offer easier cleaning and quicker preparation with less mess. Removing the head simplifies deveining and tail removal, making headless shrimp ideal for dishes requiring fast prep and streamlined cooking. For culinary use prioritizing depth of flavor, cooking shrimp with heads intact enhances taste, but headless shrimp provide practical benefits for efficiency in kitchens.
Head-On Shrimp in Regional Cuisines and Traditions
Head-on shrimp retain their shells and heads, which are rich in flavor-enhancing compounds like astaxanthin and shrimp oil that intensify the taste during cooking. Many regional cuisines, such as Cajun, Mediterranean, and Southeast Asian, favor head-on shrimp to preserve umami depth and texture, often using them in traditional dishes like gumbo, paella, and Thai tom yum. The heads contribute to broth richness and complex aromas, making head-on shrimp a preferred choice for authentic culinary experiences.
Head-on vs headless for flavor Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com