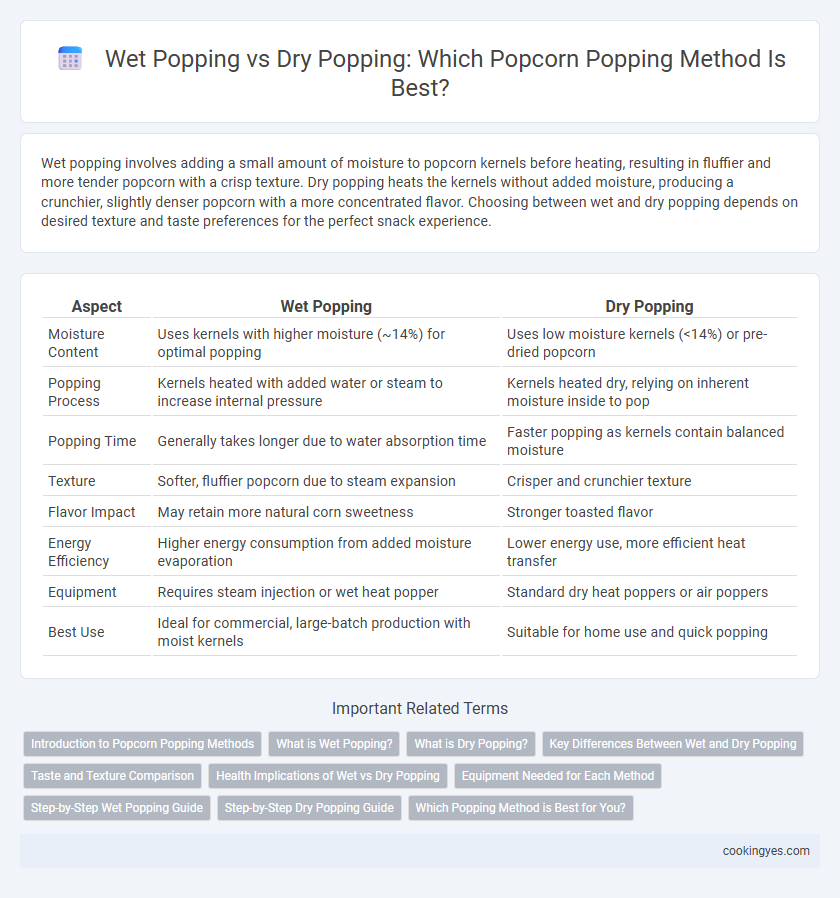
Wet popping involves adding a small amount of moisture to popcorn kernels before heating, resulting in fluffier and more tender popcorn with a crisp texture. Dry popping heats the kernels without added moisture, producing a crunchier, slightly denser popcorn with a more concentrated flavor. Choosing between wet and dry popping depends on desired texture and taste preferences for the perfect snack experience.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wet Popping | Dry Popping |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | Uses kernels with higher moisture (~14%) for optimal popping | Uses low moisture kernels (<14%) or pre-dried popcorn |
| Popping Process | Kernels heated with added water or steam to increase internal pressure | Kernels heated dry, relying on inherent moisture inside to pop |
| Popping Time | Generally takes longer due to water absorption time | Faster popping as kernels contain balanced moisture |
| Texture | Softer, fluffier popcorn due to steam expansion | Crisper and crunchier texture |
| Flavor Impact | May retain more natural corn sweetness | Stronger toasted flavor |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy consumption from added moisture evaporation | Lower energy use, more efficient heat transfer |
| Equipment | Requires steam injection or wet heat popper | Standard dry heat poppers or air poppers |
| Best Use | Ideal for commercial, large-batch production with moist kernels | Suitable for home use and quick popping |
Introduction to Popcorn Popping Methods
Wet popping uses popcorn kernels with higher moisture content, resulting in larger, fluffier popped kernels due to the steam pressure build-up inside the kernel. Dry popping involves kernels with lower moisture content, producing a crunchier texture but smaller popped pieces. Both methods affect the texture and volume of popcorn, influencing taste and cooking time.
What is Wet Popping?
Wet popping is a popcorn popping method where kernels are soaked in water or steam-treated before heating, allowing moisture to penetrate the hull. This process increases internal steam pressure during heating, resulting in a more even and fuller pop compared to dry popping. Wet-popped popcorn typically has a tender texture and larger, fluffier kernels.
What is Dry Popping?
Dry popping is a popcorn popping method that uses no oil or water, relying solely on heat to cause the kernels to burst. In this process, popcorn kernels are heated in a hot, dry pan or popcorn maker until they explode, producing a lighter, less greasy snack. Dry popped popcorn typically contains fewer calories and less fat compared to wet popping, making it a healthier option for consumers.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Popping
Wet popping involves adding water or oil to popcorn kernels before heating, resulting in a moister environment that can create fluffier and more tender popcorn. Dry popping relies solely on kernel moisture for expansion, producing a crisper texture with less oil absorption and often a healthier snack option. Key differences include texture variation, oil usage, and the final flavor profile influenced by the method chosen.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Wet popping retains moisture inside popcorn kernels, resulting in a tender, fluffy texture with a slightly sweeter and richer taste due to steam expansion. Dry popping uses hot air or oil without added moisture, producing a crispier, lighter crunch and a more neutral flavor that highlights the natural corn essence. Taste preferences vary as wet-popped popcorn offers softness and depth, while dry-popped popcorn delivers a clean, crunchy bite ideal for seasoning adherence.
Health Implications of Wet vs Dry Popping
Wet popping popcorn involves adding water or oil before heating, which can introduce extra calories and fats, potentially impacting cardiovascular health. Dry popping eliminates the use of added fats, making it a lower-calorie option with reduced risk of unhealthy fat consumption. Choosing dry popping promotes a healthier snack by minimizing exposure to added oils and maintaining the popcorn's natural fiber and nutrient content.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Wet popping requires steam generation equipment or a specialized wet popping pot to maintain moisture levels, whereas dry popping relies on a hot-air popper or a conventional stovetop pan without added moisture. Wet popping methods often involve lids with vent holes to control steam release, while dry popping equipment typically includes stirring mechanisms to prevent burning. Choosing the right equipment influences popcorn texture, with wet popping creating more tender kernels and dry popping producing crispier results.
Step-by-Step Wet Popping Guide
Wet popping involves adding a precise amount of water to popcorn kernels before heating, which helps increase the moisture content inside each kernel for optimal popping. Start by measuring 1 tablespoon of water per half cup of kernels, then mix thoroughly and let it sit for 10 minutes to evenly distribute moisture. Heat the kernels in a covered pot over medium-high heat, shaking frequently until popping slows, ensuring fluffy, fully popped corn with minimal unpopped kernels.
Step-by-Step Dry Popping Guide
Dry popping popcorn involves heating the kernels directly in a hot pan without oil or water, resulting in a lighter, less greasy snack. Begin by preheating a heavy-bottomed pan over medium-high heat, then pour in a single layer of kernels, shaking the pan occasionally to prevent burning. Once popping slows to several seconds between pops, promptly remove from heat to avoid scorching and enjoy crisp, airy popcorn.
Which Popping Method is Best for You?
Wet popping preserves moisture inside popcorn kernels, resulting in larger, fluffier popcorn with a tender texture, ideal for those who prefer soft, well-popped kernels. Dry popping uses no oil or water, producing healthier, crispier popcorn with less fat and calories, perfect for health-conscious individuals seeking a low-calorie snack. Choosing the best method depends on your taste preference and dietary goals, balancing texture and health benefits.
Wet popping vs Dry popping for popcorn popping method Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com