Bronze-cut pasta features rough, porous surfaces that hold sauces better, resulting in a more authentic, al dente texture preferred by many chefs. Teflon-cut pasta, produced with non-stick molds, has a smoother finish that cooks more evenly but may lack the robust bite and sauce absorption of bronze-cut varieties. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize traditional texture and sauce adherence or a sleek, consistent appearance.
Table of Comparison
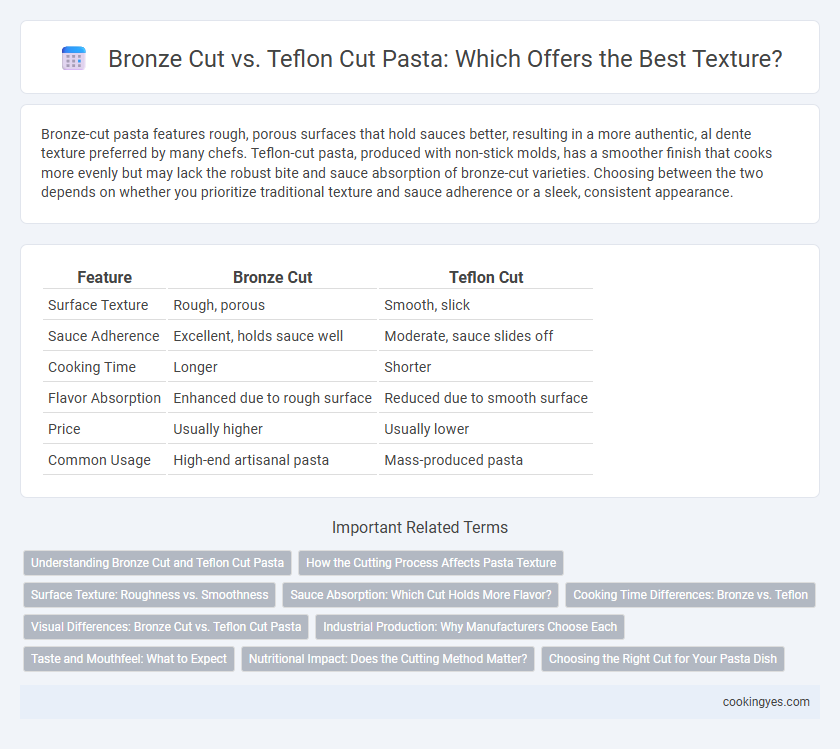
| Feature | Bronze Cut | Teflon Cut |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Texture | Rough, porous | Smooth, slick |
| Sauce Adherence | Excellent, holds sauce well | Moderate, sauce slides off |
| Cooking Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Flavor Absorption | Enhanced due to rough surface | Reduced due to smooth surface |
| Price | Usually higher | Usually lower |
| Common Usage | High-end artisanal pasta | Mass-produced pasta |
Understanding Bronze Cut and Teflon Cut Pasta
Bronze cut pasta features a rough, porous surface created by bronze dies that enhances sauce adhesion and provides a traditional, rustic texture favored in artisanal pasta. Teflon cut pasta, made using non-stick Teflon dies, results in a smoother surface that yields a more uniform and polished appearance but may offer less sauce grip. Understanding the distinction between bronze and Teflon cut pasta is essential for selecting pasta that complements specific sauces and desired mouthfeel in culinary applications.
How the Cutting Process Affects Pasta Texture
Bronze cut pasta features rough, porous surfaces that allow sauces to cling better, enhancing flavor absorption and creating a firmer texture after cooking. Teflon cut pasta has smoother, shinier surfaces that result in a silkier, less porous texture, leading to a more delicate bite and reduced sauce adherence. The cutting process directly influences the pasta's surface roughness, which plays a critical role in texture, cooking time, and sauce compatibility.
Surface Texture: Roughness vs. Smoothness
Bronze-cut pasta features a rough surface texture that enhances sauce adhesion, resulting in a more flavorful dish as the sauce clings to the pasta's porous exterior. In contrast, Teflon-cut pasta has a smooth finish which causes sauces to slide off, often leading to less intense flavor integration. This difference in surface roughness between bronze and Teflon-cut pasta directly influences the overall taste experience and sauce retention.
Sauce Absorption: Which Cut Holds More Flavor?
Bronze cut pasta features a rough, porous surface that allows sauces to cling effectively, enhancing flavor absorption and overall taste. Teflon cut pasta, with its smooth surface, tends to repel sauces, resulting in a lighter coating and less intense flavor. Consequently, bronze cut pasta is preferred for dishes requiring robust sauce adherence and richer flavor profiles.
Cooking Time Differences: Bronze vs. Teflon
Bronze cut pasta has a rougher surface that allows sauce to cling better but generally requires longer cooking times compared to Teflon cut pasta. Teflon cut pasta features a smoother texture, resulting in faster cooking due to reduced surface friction and water absorption. The cooking time difference can range from one to three minutes, with bronze cut pasta typically needing more time to achieve the desired al dente texture.
Visual Differences: Bronze Cut vs. Teflon Cut Pasta
Bronze cut pasta features a rougher, matte surface with pronounced ridges that effectively hold onto sauces, while teflon cut pasta has a smoother, shinier appearance with less texture. The porous nature of bronze cut pasta creates a rustic look and enhances flavor absorption, whereas teflon cut yields a more polished, sleek finish. These visual differences impact both the pasta's tactile quality and its ability to complement different types of sauces.
Industrial Production: Why Manufacturers Choose Each
Bronze cut pasta features a rougher surface created by bronze dies that enhances sauce adhesion and provides a traditional, artisanal texture preferred for premium products. Teflon cut pasta, produced using non-stick Teflon dies, offers a smoother finish that facilitates faster production and easier unmolding, making it ideal for large-scale industrial manufacturing focused on efficiency. Manufacturers select bronze cut for high-quality, rustic products, while Teflon cut is favored for mass production due to its streamlined processing and cost-effectiveness.
Taste and Mouthfeel: What to Expect
Bronze cut pasta has a rough, porous surface that retains sauce better and provides a firmer, more textured bite, enhancing the overall taste and mouthfeel. Teflon cut pasta is smoother and glossier, resulting in a silkier texture but less grip for sauces, which can lead to a subtler flavor experience. Choosing bronze cut pasta intensifies the savory notes and creates a satisfying chewy texture preferred in traditional Italian cooking.
Nutritional Impact: Does the Cutting Method Matter?
Bronze cut pasta features a rougher texture that holds sauce better and allows for slightly slower starch release, potentially aiding in a more gradual blood sugar response compared to the smoother Teflon cut. The porous surface of bronze cut pasta may increase the pasta's ability to retain nutrients like proteins and micronutrients during cooking. However, the cutting method has minimal direct impact on the overall nutritional profile, with factors like pasta type and cooking time playing a more significant role in nutrient retention.
Choosing the Right Cut for Your Pasta Dish
Bronze-cut pasta surfaces create a rougher texture that holds sauce more effectively, enhancing flavor absorption and providing a traditional, artisan-quality mouthfeel. Teflon-cut pasta produces a smoother finish, resulting in a silkier texture that works well with lighter, cream-based sauces. Selecting the right cut depends on the sauce type and desired texture, with bronze-cut ideal for hearty, chunky sauces and Teflon-cut suited for delicate, emulsified blends.
Bronze cut vs Teflon cut for pasta texture Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com