Full-fat paneer offers a richer source of healthy fats and calories, making it ideal for those needing higher energy intake and fat-soluble vitamins like A and D. Low-fat paneer contains fewer calories and saturated fats, supporting weight management and heart health while still providing substantial protein and calcium. Choosing between full-fat and low-fat paneer depends on individual dietary goals and nutritional needs.
Table of Comparison
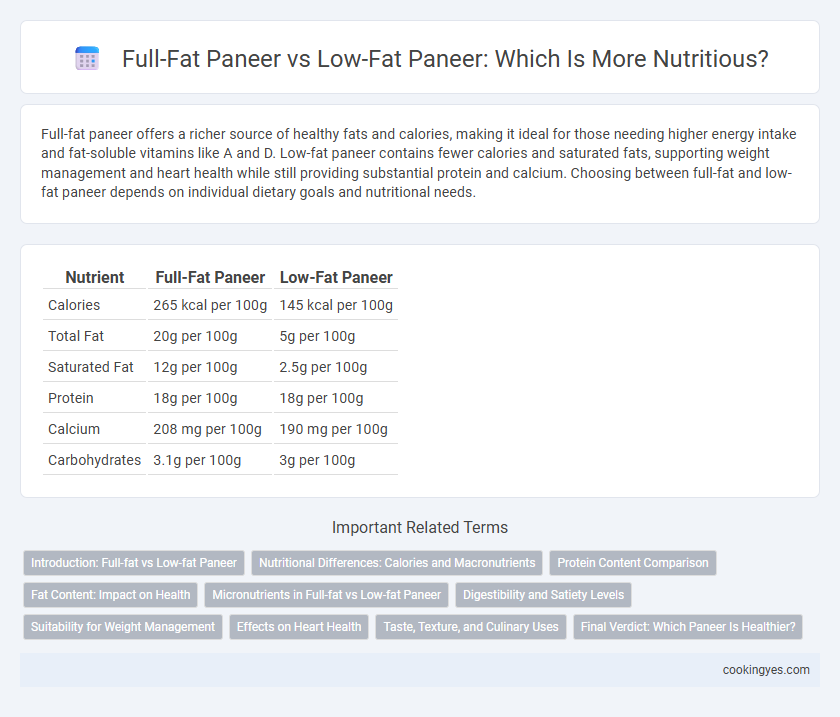
| Nutrient | Full-Fat Paneer | Low-Fat Paneer |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 265 kcal per 100g | 145 kcal per 100g |
| Total Fat | 20g per 100g | 5g per 100g |
| Saturated Fat | 12g per 100g | 2.5g per 100g |
| Protein | 18g per 100g | 18g per 100g |
| Calcium | 208 mg per 100g | 190 mg per 100g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.1g per 100g | 3g per 100g |
Introduction: Full-fat vs Low-fat Paneer
Full-fat paneer contains higher levels of saturated fats and calories, making it richer and creamier, which supports energy-dense diets and muscle repair. Low-fat paneer offers a leaner protein source with reduced fat content, ideal for weight management and heart health. Both types supply essential nutrients like calcium and casein protein but cater to different dietary needs and preferences.
Nutritional Differences: Calories and Macronutrients
Full-fat paneer contains approximately 265 calories and 20 grams of fat per 100 grams, providing a rich source of saturated fats and protein, ideal for energy-dense diets. Low-fat paneer typically offers around 150 calories and 8 grams of fat per 100 grams, reducing overall calorie intake while maintaining high protein content, making it suitable for weight management. Both types provide essential macronutrients like protein and calcium, but full-fat paneer delivers higher calorie levels due to increased fat content.
Protein Content Comparison
Full-fat paneer contains approximately 18 grams of protein per 100 grams, offering a rich source of complete proteins essential for muscle repair and growth. Low-fat paneer typically provides slightly higher protein concentration, around 19 grams per 100 grams, due to reduced fat content, making it a preferred choice for calorie-conscious individuals seeking high protein intake. The retention of essential amino acids in both varieties ensures that paneer remains an excellent plant-based protein option for vegetarians and fitness enthusiasts alike.
Fat Content: Impact on Health
Full-fat paneer contains higher levels of saturated fat, which may contribute to increased cholesterol and cardiovascular risks if consumed excessively. Low-fat paneer offers a reduced fat content, making it a healthier option for weight management and heart health without compromising protein and calcium benefits. Choosing low-fat paneer supports a balanced diet by lowering overall calorie intake while still providing essential nutrients for bone strength and muscle repair.
Micronutrients in Full-fat vs Low-fat Paneer
Full-fat paneer contains higher levels of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A and vitamin D compared to low-fat paneer, enhancing its micronutrient density. Low-fat paneer provides reduced calories and fat content but may have lower concentrations of essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus. Choosing between full-fat and low-fat paneer depends on balancing calorie intake with the need for vital micronutrients crucial for bone health and immune function.
Digestibility and Satiety Levels
Full-fat paneer contains higher fat content, which enhances satiety by promoting slower digestion and prolonged feelings of fullness. Low-fat paneer, with reduced fat levels, is easier to digest due to lower fat content but may result in quicker hunger return. Choosing between full-fat and low-fat paneer depends on individual digestion capacity and appetite control preferences.
Suitability for Weight Management
Full-fat paneer contains higher levels of calories and saturated fats, making it less suitable for weight management compared to low-fat paneer, which offers reduced fat content without significantly compromising protein levels. Low-fat paneer provides a nutritious, lower-calorie option ideal for those seeking to control caloric intake while maintaining muscle mass. Choosing low-fat paneer supports weight loss goals by delivering essential nutrients with fewer calories and less saturated fat.
Effects on Heart Health
Full-fat paneer contains higher levels of saturated fats, which may increase LDL cholesterol and contribute to heart disease risk when consumed in excess. Low-fat paneer offers reduced saturated fat content, making it a heart-healthier option while still providing essential protein and calcium. Choosing low-fat paneer can help support cardiovascular health by managing cholesterol levels and reducing overall fat intake.
Taste, Texture, and Culinary Uses
Full-fat paneer offers a rich, creamy taste and a soft, crumbly texture ideal for indulgent dishes like paneer butter masala and kebabs. Low-fat paneer has a milder flavor and firmer texture, making it suitable for salads, wraps, and health-conscious recipes. Nutritionally, full-fat paneer delivers higher calories and fat content, while low-fat paneer provides a leaner protein source with reduced saturated fat.
Final Verdict: Which Paneer Is Healthier?
Full-fat paneer contains higher levels of calories and saturated fats, supporting energy needs and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Low-fat paneer offers reduced calorie and fat content, benefiting weight management and heart health without compromising protein levels. Choosing between full-fat and low-fat paneer depends on individual nutritional goals, with low-fat paneer generally preferred for healthier, balanced diets.
Full-fat Paneer vs Low-fat Paneer for nutrition Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com