Melted butter adds a rich, creamy flavor and enhances the texture of pancakes, making them tender and slightly crispy on the edges. Vegetable oil provides a neutral taste and creates a lighter, fluffier pancake by keeping the batter moist without altering the flavor. Choosing melted butter or vegetable oil impacts the overall taste and texture, with butter offering depth and oil ensuring softness.
Table of Comparison
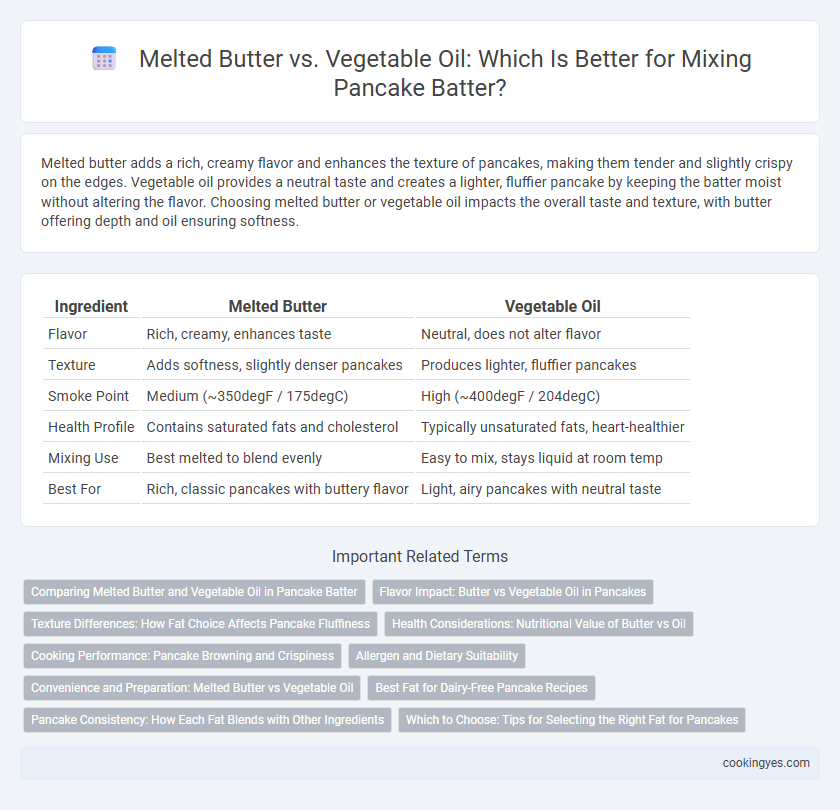
| Ingredient | Melted Butter | Vegetable Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Rich, creamy, enhances taste | Neutral, does not alter flavor |
| Texture | Adds softness, slightly denser pancakes | Produces lighter, fluffier pancakes |
| Smoke Point | Medium (~350degF / 175degC) | High (~400degF / 204degC) |
| Health Profile | Contains saturated fats and cholesterol | Typically unsaturated fats, heart-healthier |
| Mixing Use | Best melted to blend evenly | Easy to mix, stays liquid at room temp |
| Best For | Rich, classic pancakes with buttery flavor | Light, airy pancakes with neutral taste |
Comparing Melted Butter and Vegetable Oil in Pancake Batter
Melted butter adds rich flavor and a tender crumb to pancake batter, enhancing taste and texture with its creamy fat content. Vegetable oil provides a neutral taste and maintains moisture, resulting in lighter, fluffier pancakes with a consistent rise. Choosing between melted butter and vegetable oil depends on whether a richer flavor or a lighter texture is preferred in the final pancake.
Flavor Impact: Butter vs Vegetable Oil in Pancakes
Melted butter imparts a rich, creamy flavor and a slightly caramelized aroma to pancakes, enhancing their overall taste and providing a more indulgent mouthfeel. Vegetable oil, being neutral in flavor, allows other ingredients like vanilla or spices to shine but results in a lighter, less flavorful pancake. Choosing melted butter over vegetable oil significantly boosts the depth and complexity of pancake flavor.
Texture Differences: How Fat Choice Affects Pancake Fluffiness
Melted butter adds richness and a dense, tender crumb to pancakes, resulting in a slightly heavier texture with a buttery flavor. Vegetable oil creates a lighter, airier pancake by promoting a more uniform batter and preventing gluten from developing too much. Choosing butter enhances moistness and flavor, while oil prioritizes fluffiness and a softer bite.
Health Considerations: Nutritional Value of Butter vs Oil
Melted butter adds essential fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, and E to pancake batter, enhancing nutritional value while providing a rich flavor profile. Vegetable oil, especially varieties rich in unsaturated fats such as olive or canola oil, offers heart-healthy benefits by reducing saturated fat intake and supporting cholesterol management. Choosing between butter and vegetable oil impacts not only taste and texture but also the overall healthfulness of the pancakes based on fat quality and micronutrient content.
Cooking Performance: Pancake Browning and Crispiness
Melted butter in pancake batter enhances browning due to its milk solids, which promote Maillard reactions, creating a richer golden crust and crispier edges. Vegetable oil results in softer pancakes with less browning since it lacks proteins and sugars that aid in caramelization. For optimal cooking performance, using melted butter yields pancakes with superior crispiness and visually appealing, evenly browned surfaces.
Allergen and Dietary Suitability
Melted butter in pancake mixing provides a rich flavor but contains dairy allergens, making it unsuitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies. Vegetable oil offers a dairy-free alternative, enhancing dietary suitability for vegans and those with milk-related allergies while maintaining moisture in the batter. Choosing vegetable oil ensures allergen-conscious pancakes without compromising texture, ideal for allergen-sensitive and plant-based diets.
Convenience and Preparation: Melted Butter vs Vegetable Oil
Melted butter adds a rich flavor but requires melting and careful temperature control before mixing into pancake batter, making preparation slightly more involved. Vegetable oil offers greater convenience due to its liquid state at room temperature and easy integration directly into the batter without melting. Choosing vegetable oil streamlines the mixing process, ideal for quick and simple pancake preparation.
Best Fat for Dairy-Free Pancake Recipes
Melted butter offers a rich flavor and a tender texture to pancakes but contains dairy, making it unsuitable for dairy-free recipes. Vegetable oil, such as canola or sunflower oil, provides a neutral taste and keeps dairy-free pancakes moist and fluffy without compromising dietary restrictions. For the best dairy-free pancake results, vegetable oil is preferred due to its compatibility with non-dairy ingredients and consistent texture.
Pancake Consistency: How Each Fat Blends with Other Ingredients
Melted butter creates a richer, denser pancake batter by coating flour proteins and limiting gluten formation, resulting in a tender, moist texture. Vegetable oil blends more uniformly with wet ingredients, producing a smoother, thinner batter that yields lighter, fluffier pancakes. The choice between melted butter and vegetable oil directly influences batter viscosity and final pancake crumb structure.
Which to Choose: Tips for Selecting the Right Fat for Pancakes
Melted butter enhances pancake flavor with its rich, creamy taste and promotes a tender crumb, while vegetable oil offers a neutral profile that keeps pancakes moist and light. Choosing between the two depends on desired texture and flavor intensity, with butter providing a golden, slightly crisp edge and oil contributing to a softer, more uniform pancake surface. For optimal results, use melted butter to maximize flavor in classic recipes, or vegetable oil for a lighter, allergen-friendly alternative.
Melted Butter vs Vegetable Oil for Pancake Mixing Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com