Wheat flour provides a classic fluffy texture and rich flavor to pancakes, but gluten-free blends offer an essential alternative for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease. Gluten-free blends often combine rice flour, tapioca starch, and potato starch to mimic the elasticity and softness of wheat flour, ensuring a satisfying pancake base without compromising taste or consistency. Choosing the right base depends on dietary needs, but both options can create delicious, tender pancakes when properly balanced.
Table of Comparison
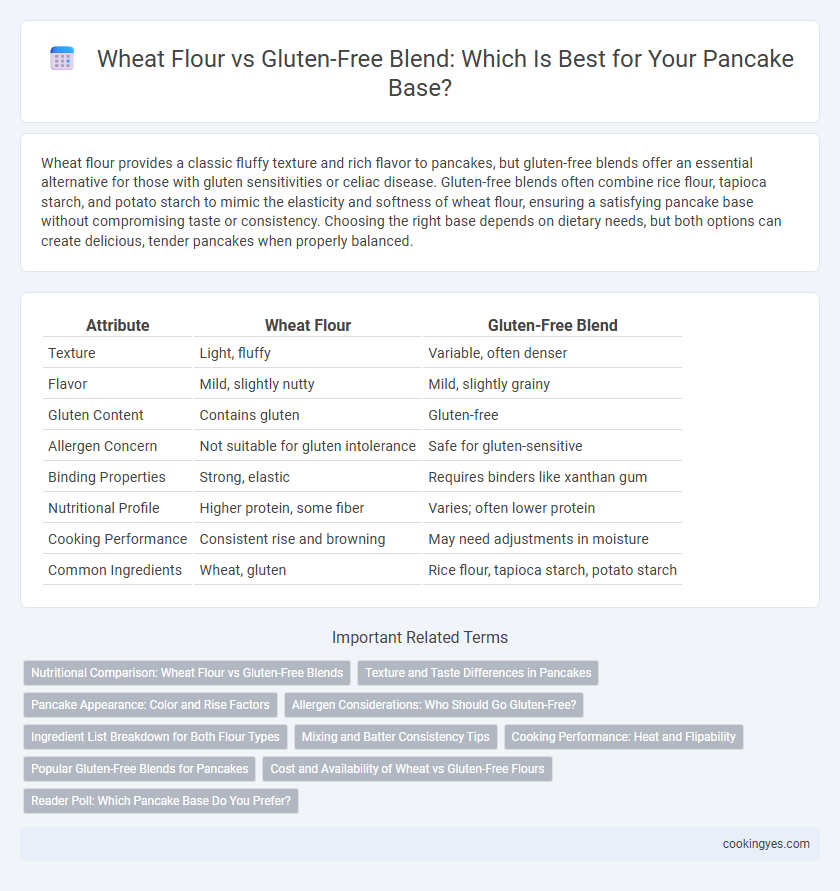
| Attribute | Wheat Flour | Gluten-Free Blend |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Light, fluffy | Variable, often denser |
| Flavor | Mild, slightly nutty | Mild, slightly grainy |
| Gluten Content | Contains gluten | Gluten-free |
| Allergen Concern | Not suitable for gluten intolerance | Safe for gluten-sensitive |
| Binding Properties | Strong, elastic | Requires binders like xanthan gum |
| Nutritional Profile | Higher protein, some fiber | Varies; often lower protein |
| Cooking Performance | Consistent rise and browning | May need adjustments in moisture |
| Common Ingredients | Wheat, gluten | Rice flour, tapioca starch, potato starch |
Nutritional Comparison: Wheat Flour vs Gluten-Free Blends
Wheat flour pancakes typically contain higher protein levels due to gluten, offering about 12-14 grams of protein per 100 grams, whereas gluten-free blends vary widely, often containing 6-9 grams depending on ingredients like rice flour, tapioca, or almond flour. Gluten-free blends may provide increased dietary fiber and reduced carbohydrates, appealing to those on low-glycemic or specialized diets. Calories in both bases remain comparable, generally around 350-370 calories per 100 grams, but micronutrient content such as B vitamins and iron is usually higher in whole wheat flour.
Texture and Taste Differences in Pancakes
Wheat flour pancakes offer a classic fluffy texture with a slightly chewy bite due to gluten development, resulting in a rich, traditional flavor profile. Gluten-free blends, often made from rice, tapioca, or almond flours, create a lighter, sometimes crumbly texture and a subtly nutty or earthy taste that can vary based on the blend's composition. The choice between wheat flour and gluten-free blends directly impacts pancake softness, moisture retention, and overall flavor authenticity.
Pancake Appearance: Color and Rise Factors
Wheat flour pancakes typically exhibit a golden-brown color due to the Maillard reaction facilitated by gluten proteins, contributing to an appealing appearance and better rise. Gluten-free blends often result in a paler pancake with a denser texture, as they lack gluten's elasticity and structure, which are essential for trapping air and achieving the classic fluffy rise. Incorporating xanthan gum or baking powder in gluten-free mixes can enhance lift and improve color development, counteracting some of the visual and textural differences compared to wheat flour pancakes.
Allergen Considerations: Who Should Go Gluten-Free?
Wheat flour contains gluten, a protein that can trigger adverse reactions in individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, making a gluten-free blend essential for these groups to avoid allergic responses and digestive issues. Gluten-free pancake bases often use alternative flours such as rice, almond, or tapioca flour, providing safe options for those with wheat allergies or gluten intolerance. Choosing the appropriate flour ensures allergen safety while maintaining pancake texture and taste for sensitive consumers.
Ingredient List Breakdown for Both Flour Types
Wheat flour for pancake bases typically contains gluten proteins, starch, and minor components like lipids, fibers, and minerals that contribute to structure and chewiness. Gluten-free blends often combine rice flour, tapioca starch, potato starch, and xanthan gum to mimic the binding and elasticity properties of gluten, resulting in a lighter, more tender pancake texture. Understanding the ingredient list helps tailor pancakes to dietary needs while optimizing texture and flavor profiles.
Mixing and Batter Consistency Tips
Wheat flour creates a smooth, elastic pancake batter due to its gluten content, providing a consistent, thick texture ideal for flipping. In contrast, gluten-free blends often require additional binding agents like xanthan gum or flaxseed to achieve a similar batter consistency and prevent crumbling. For optimal mixing, combine wet and dry ingredients gently to avoid overworking wheat flour dough, while gluten-free batters benefit from thorough but careful stirring to ensure even hydration and a lump-free mixture.
Cooking Performance: Heat and Flipability
Wheat flour provides a consistent heat distribution for pancakes, resulting in even browning and a sturdy texture that holds well during flipping. Gluten-free blends often require adjusted cooking temperatures to prevent uneven cooking or sticking due to varied starch compositions. Pancakes made with wheat flour typically exhibit superior flipability and a reliable structure, while gluten-free options may need gentler heat and careful handling to maintain form.
Popular Gluten-Free Blends for Pancakes
Popular gluten-free blends for pancakes often include rice flour, tapioca starch, and potato starch, creating a light and fluffy texture comparable to traditional wheat flour. Brands like Bob's Red Mill Gluten-Free 1-to-1 Baking Flour and King Arthur Gluten-Free Measure for Measure Flour provide balanced blends optimized for moisture retention and structure. These blends support a tender crumb while catering to gluten sensitivities, making them ideal bases for delicious gluten-free pancakes.
Cost and Availability of Wheat vs Gluten-Free Flours
Wheat flour remains the most cost-effective and widely available option for pancake bases, often priced significantly lower than gluten-free blends due to mass production and abundant supply. Gluten-free flours, such as rice, almond, or oat blends, typically carry higher costs reflecting specialized processing and limited distribution channels. Availability for gluten-free options can be inconsistent, varying by region and store, whereas wheat flour is universally found in grocery stores worldwide.
Reader Poll: Which Pancake Base Do You Prefer?
Wheat flour provides a classic, fluffy texture with a mild flavor that many pancake enthusiasts prefer, while gluten-free blends cater to dietary restrictions without compromising taste. Reader polls reveal a near-even split, with 52% favoring traditional wheat flour pancakes and 48% opting for gluten-free alternatives. This data highlights diverse preferences, emphasizing the growing demand for gluten-free options in breakfast recipes.
Wheat Flour vs Gluten-Free Blend for Pancake Base Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com