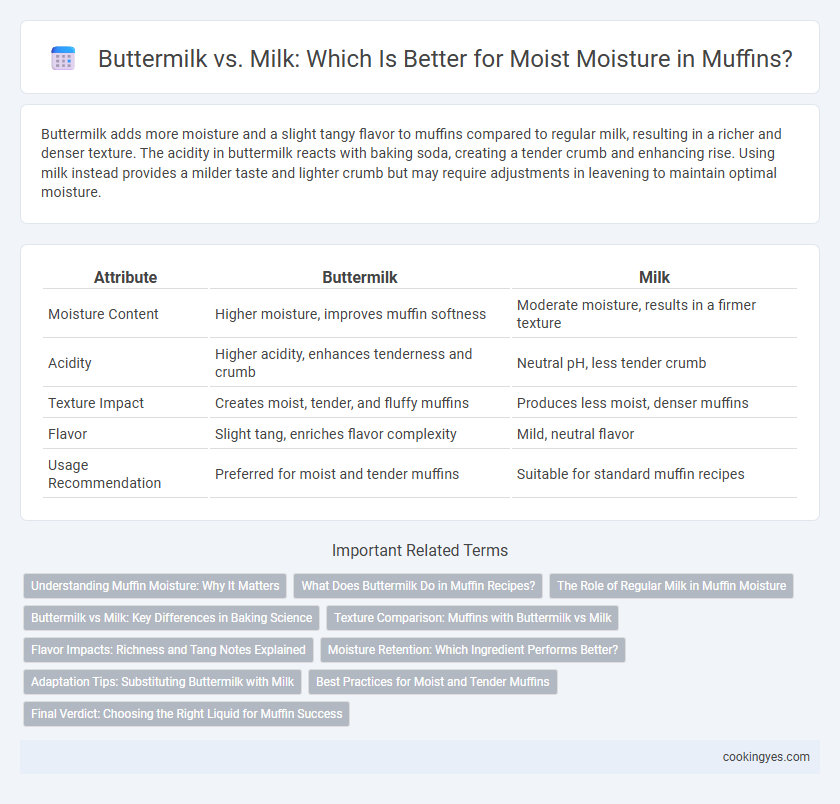
Buttermilk adds more moisture and a slight tangy flavor to muffins compared to regular milk, resulting in a richer and denser texture. The acidity in buttermilk reacts with baking soda, creating a tender crumb and enhancing rise. Using milk instead provides a milder taste and lighter crumb but may require adjustments in leavening to maintain optimal moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Buttermilk | Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | Higher moisture, improves muffin softness | Moderate moisture, results in a firmer texture |
| Acidity | Higher acidity, enhances tenderness and crumb | Neutral pH, less tender crumb |
| Texture Impact | Creates moist, tender, and fluffy muffins | Produces less moist, denser muffins |
| Flavor | Slight tang, enriches flavor complexity | Mild, neutral flavor |
| Usage Recommendation | Preferred for moist and tender muffins | Suitable for standard muffin recipes |
Understanding Muffin Moisture: Why It Matters
Buttermilk enhances muffin moisture by providing acidity that reacts with baking soda, creating a tender crumb and richer texture compared to regular milk. The higher fat content and lower pH in buttermilk help retain moisture longer, resulting in a soft, moist muffin. Understanding these chemical interactions is crucial for achieving optimal muffin texture and moisture retention.
What Does Buttermilk Do in Muffin Recipes?
Buttermilk enhances muffin moisture by reacting with baking soda to create carbon dioxide, which helps muffins rise and develop a tender crumb. Its acidic properties break down gluten, resulting in a softer texture compared to using regular milk. The slight tanginess of buttermilk also adds depth of flavor, making muffins more moist and flavorful.
The Role of Regular Milk in Muffin Moisture
Regular milk contributes essential moisture to muffins by providing a balanced liquid content that hydrates dry ingredients effectively. Its natural sugars and proteins help create a tender crumb, while the moderate fat content enhances softness without overpowering the batter. Unlike buttermilk, regular milk offers a neutral pH that maintains consistent texture and rise in muffins.
Buttermilk vs Milk: Key Differences in Baking Science
Buttermilk's acidity reacts with baking soda to create carbon dioxide bubbles, resulting in lighter, moister muffins compared to regular milk. The higher fat content and tangy flavor of buttermilk also enhance tenderness and depth, whereas milk produces denser textures. Using buttermilk instead of milk improves muffin crumb structure through its unique chemical properties in baking.
Texture Comparison: Muffins with Buttermilk vs Milk
Muffins made with buttermilk have a denser, tender crumb due to the acid reacting with baking soda, which creates a finer, moist texture. In contrast, muffins using milk tend to be lighter but slightly drier because milk lacks the acidity that enhances leavening and moisture retention. The acidity in buttermilk also helps break down gluten, resulting in softer, more delicate muffins compared to the firmer texture of milk-based muffins.
Flavor Impacts: Richness and Tang Notes Explained
Buttermilk enhances muffin moisture by adding a rich, tangy flavor that milk lacks, resulting in a more complex taste profile. The acidity in buttermilk reacts with leavening agents, creating a tender crumb and subtly sharp notes that balance sweetness. Using milk yields a milder, creamier texture but misses the depth and slight tang that buttermilk provides for flavor complexity.
Moisture Retention: Which Ingredient Performs Better?
Buttermilk outperforms milk in muffin moisture retention due to its higher acidity and fat content, which tenderizes gluten and helps retain moisture during baking. The lactic acid in buttermilk breaks down proteins, resulting in a softer crumb that stays moist longer compared to muffins made with regular milk. Studies show that muffins made with buttermilk exhibit greater shelf-life moisture levels, enhancing overall texture and freshness.
Adaptation Tips: Substituting Buttermilk with Milk
When substituting buttermilk with milk in muffin recipes, adding 1 tablespoon of lemon juice or vinegar per cup of milk helps mimic buttermilk's acidity, enhancing moisture and tenderness. Using whole milk instead of skim milk improves fat content, which contributes to a richer crumb and prevents dryness. Adjusting baking soda quantities by reducing it slightly ensures proper rise and texture when replacing buttermilk with milk.
Best Practices for Moist and Tender Muffins
Using buttermilk instead of milk in muffin recipes enhances moisture and tenderness due to its acidity, which reacts with baking soda to create a lighter, fluffier texture. Buttermilk's fat content and acidity help break down gluten, resulting in softer crumb structure and improved moisture retention. For best results, replace milk with an equal amount of buttermilk and adjust leavening agents accordingly to maintain balanced rise and optimal muffin texture.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Liquid for Muffin Success
Buttermilk enhances muffin moisture by providing acidity that tenderizes gluten, resulting in a softer crumb compared to regular milk. Milk contributes to a mild flavor and slightly denser texture but lacks the tenderizing effect of buttermilk. For optimal muffin success, buttermilk is the preferred liquid to achieve moistness and a tender bite.
Buttermilk vs milk for muffin moisture Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com