Bronze-cut macaroni features a rougher surface texture that enhances sauce adherence, allowing flavors to cling better and creating a more satisfying bite. Teflon-cut macaroni has a smoother finish which can cause sauces to slide off, resulting in less flavorful dishes. Choosing bronze-cut pasta is ideal for recipes where sauce absorption and retention are essential for taste and texture.
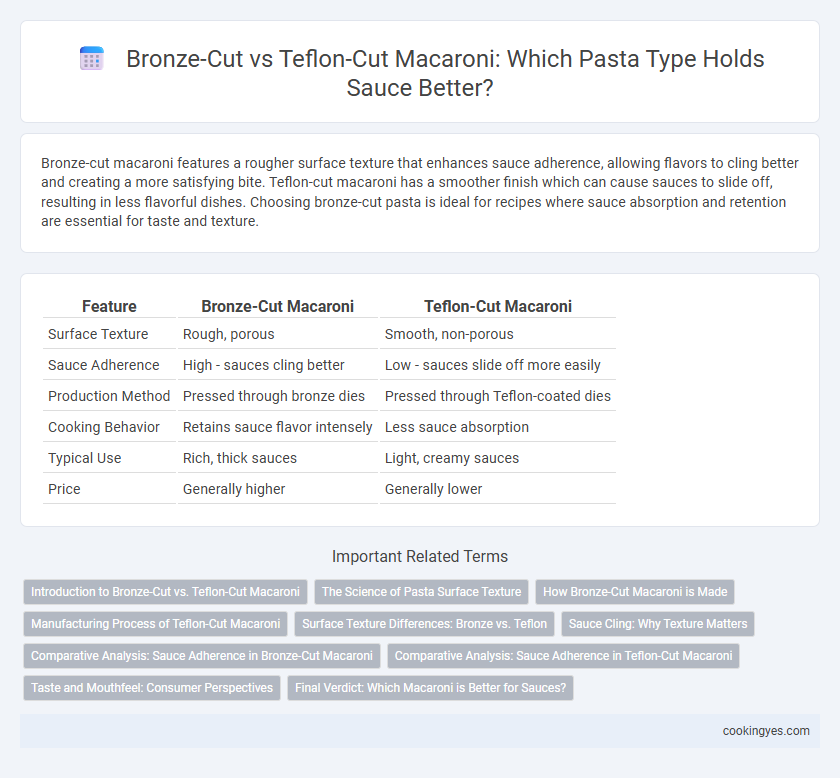
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bronze-Cut Macaroni | Teflon-Cut Macaroni |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Texture | Rough, porous | Smooth, non-porous |
| Sauce Adherence | High - sauces cling better | Low - sauces slide off more easily |
| Production Method | Pressed through bronze dies | Pressed through Teflon-coated dies |
| Cooking Behavior | Retains sauce flavor intensely | Less sauce absorption |
| Typical Use | Rich, thick sauces | Light, creamy sauces |
| Price | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to Bronze-Cut vs. Teflon-Cut Macaroni
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rough, porous surface created by traditional bronze dies, enhancing sauce adherence and delivering a more textured bite. Teflon-cut macaroni, produced with smooth non-stick dies, has a slick exterior that can cause sauces to slide off more easily, resulting in a less flavorful experience. The choice between bronze and Teflon-cut pasta significantly impacts the overall sauce retention and taste profile of the dish.
The Science of Pasta Surface Texture
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rougher, porous surface due to the traditional bronze die extrusion, which enhances sauce adherence by creating microscopic grooves that trap and cling to the sauce. In contrast, Teflon-cut macaroni has a smoother, more polished texture from non-stick dies, resulting in less sauce retention and a more slippery bite. The science of pasta surface texture underscores that the increased surface roughness of bronze-cut pasta allows for better flavor integration and an improved overall culinary experience.
How Bronze-Cut Macaroni is Made
Bronze-cut macaroni is crafted using traditional bronze dies that create a rough, porous surface ideal for sauce adherence, enhancing flavor retention with every bite. This artisanal method involves extruding dough through bronze molds, resulting in a textured pasta that holds sauces better than smooth, Teflon-cut counterparts. The coarse texture of bronze-cut macaroni allows sauces to cling effectively, making it the preferred choice for rich, hearty dishes.
Manufacturing Process of Teflon-Cut Macaroni
Teflon-cut macaroni is produced using non-stick Teflon-coated dies that create smooth, uniform pasta surfaces, resulting in less sauce adherence compared to bronze-cut varieties. The manufacturing process involves extrusion through these Teflon dies at controlled temperatures, minimizing roughness and enhancing pasta release. This method ensures a polished texture but reduces the key grooves that typically capture and hold sauce.
Surface Texture Differences: Bronze vs. Teflon
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rough, porous surface texture created by traditional bronze dies, which enhances sauce adherence by allowing the sauce to cling more effectively. Teflon-cut macaroni, produced with smooth, non-stick Teflon dies, results in a polished, slick surface that typically causes sauces to slide off rather than adhere. This fundamental difference in surface texture directly impacts the flavor and overall mouthfeel of pasta dishes, making bronze-cut varieties preferred for rich, thick sauces.
Sauce Cling: Why Texture Matters
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rough, porous surface created by traditional bronze dies, promoting superior sauce adherence compared to the smooth, slippery finish of Teflon-cut pasta. The textured exterior allows sauces to cling effectively, enhancing flavor distribution and overall mouthfeel. Choosing bronze-cut pasta ensures a richer, more cohesive dish due to its improved sauce retention properties.
Comparative Analysis: Sauce Adherence in Bronze-Cut Macaroni
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rough, porous surface created by traditional bronze dies, significantly enhancing sauce adherence compared to the smooth, non-stick texture of Teflon-cut pasta. This textured surface traps more sauce, making dishes richer and more flavorful, especially with thicker or chunkier sauces like Bolognese or Arrabbiata. In contrast, Teflon-cut macaroni tends to repel sauce, resulting in a less cohesive bite and diminished flavor integration.
Comparative Analysis: Sauce Adherence in Teflon-Cut Macaroni
Teflon-cut macaroni features a smoother surface compared to bronze-cut, resulting in lower sauce adherence due to reduced texture grip. Despite its non-stick properties facilitating easier cleaning, Teflon-cut pasta may not hold thick or chunky sauces as effectively as bronze-cut varieties. This difference significantly impacts the flavor integration and overall sensory experience in pasta dishes.
Taste and Mouthfeel: Consumer Perspectives
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rough, porous surface that enhances sauce adherence, resulting in a richer, more flavorful taste and a satisfying, chewy mouthfeel favored by many consumers. Teflon-cut macaroni has a smooth, slippery texture that causes sauces to slide off easily, often leading to a blander flavor experience and a softer, less engaging bite. Consumer preferences consistently highlight the textured bronze-cut pasta as superior for capturing sauce and delivering a more authentic, enjoyable eating experience.
Final Verdict: Which Macaroni is Better for Sauces?
Bronze-cut macaroni features a rougher texture created by traditional bronze dies, which enhances sauce adherence by allowing sauces to cling better to the pasta surface. Teflon-cut macaroni, made with non-stick dies, results in a smoother surface that causes sauces to slide off more easily, reducing flavor absorption. For superior sauce retention and a more flavorful dish, bronze-cut macaroni is the preferred choice among chefs and pasta enthusiasts.
Bronze-cut macaroni vs Teflon-cut macaroni for sauce adherence Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com