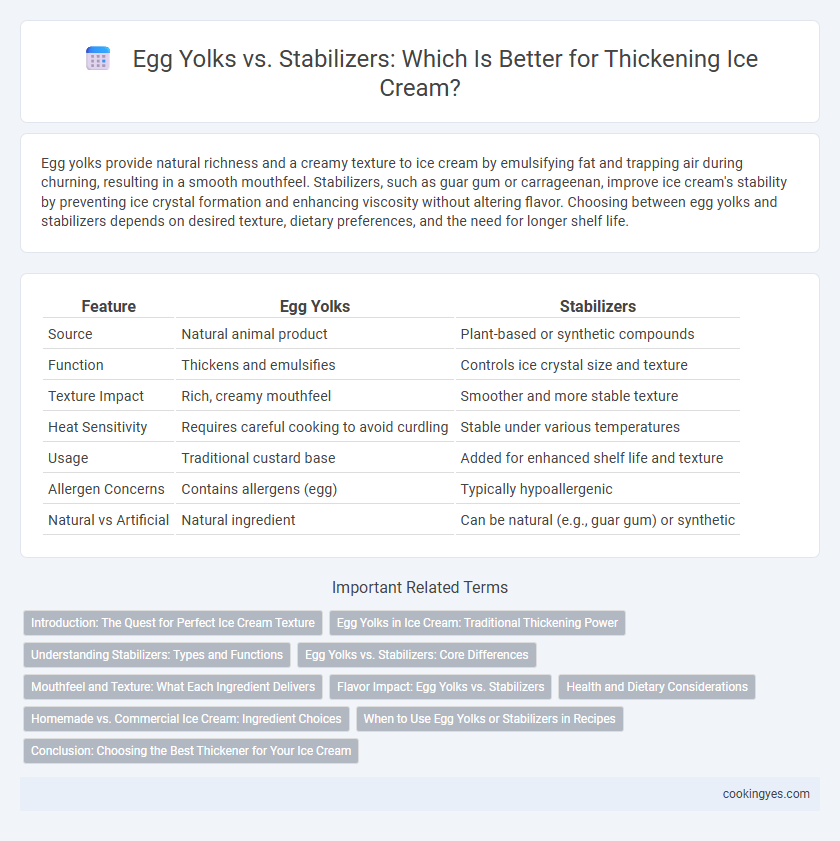
Egg yolks provide natural richness and a creamy texture to ice cream by emulsifying fat and trapping air during churning, resulting in a smooth mouthfeel. Stabilizers, such as guar gum or carrageenan, improve ice cream's stability by preventing ice crystal formation and enhancing viscosity without altering flavor. Choosing between egg yolks and stabilizers depends on desired texture, dietary preferences, and the need for longer shelf life.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Egg Yolks | Stabilizers |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural animal product | Plant-based or synthetic compounds |
| Function | Thickens and emulsifies | Controls ice crystal size and texture |
| Texture Impact | Rich, creamy mouthfeel | Smoother and more stable texture |
| Heat Sensitivity | Requires careful cooking to avoid curdling | Stable under various temperatures |
| Usage | Traditional custard base | Added for enhanced shelf life and texture |
| Allergen Concerns | Contains allergens (egg) | Typically hypoallergenic |
| Natural vs Artificial | Natural ingredient | Can be natural (e.g., guar gum) or synthetic |
Introduction: The Quest for Perfect Ice Cream Texture
Egg yolks provide natural emulsifying properties and rich creaminess, creating a smooth, velvety texture in ice cream. Stabilizers such as guar gum or carrageenan prevent ice crystal formation, enhancing creaminess and extending shelf life. Balancing egg yolks and stabilizers is crucial for achieving the ideal ice cream thickness and mouthfeel.
Egg Yolks in Ice Cream: Traditional Thickening Power
Egg yolks provide natural emulsifiers and lecithin, essential for creating a rich, creamy texture in traditional ice cream recipes. Their proteins coagulate during cooking, thickening the custard base and contributing to a smooth, velvety mouthfeel. Egg yolks also enhance flavor complexity while helping to stabilize air bubbles, improving ice cream's overall structure and melt quality.
Understanding Stabilizers: Types and Functions
Ice cream stabilizers such as guar gum, carrageenan, and xanthan gum are used to improve texture and prevent ice crystal formation, ensuring a smooth and creamy consistency. These hydrocolloids bind water and control the freezing process without affecting flavor, unlike egg yolks which provide emulsification and richness. Understanding the types and functions of stabilizers is essential for customizing ice cream formulations to achieve desired mouthfeel and shelf stability.
Egg Yolks vs. Stabilizers: Core Differences
Egg yolks provide natural emulsification and rich texture through lecithin, enhancing ice cream's creaminess and mouthfeel, while stabilizers like guar gum or carrageenan primarily increase viscosity and prevent ice crystal formation for smoother consistency. Egg yolks contribute to flavor complexity and color, whereas stabilizers maintain structural integrity during freezing and storage without adding taste. Understanding these core differences allows manufacturers to balance traditional richness with modern stability in ice cream production.
Mouthfeel and Texture: What Each Ingredient Delivers
Egg yolks contribute a rich, creamy mouthfeel and velvety texture to ice cream by providing natural emulsifiers like lecithin that stabilize fat and proteins. Stabilizers, such as guar gum or carrageenan, enhance smoothness and prevent ice crystal formation, resulting in a consistently soft texture over time. Combining egg yolks with stabilizers balances creaminess and durability, improving overall texture and mouthfeel in premium ice cream products.
Flavor Impact: Egg Yolks vs. Stabilizers
Egg yolks contribute a rich, creamy flavor and smooth texture to ice cream, enhancing its overall mouthfeel with natural fats and proteins. Stabilizers, often derived from plant or seaweed sources, provide thickening without altering flavor, preserving the pure taste of the ice cream base. While egg yolks add complexity and depth, stabilizers offer a neutral solution for texture that maintains the base ice cream's original flavor profile.
Health and Dietary Considerations
Egg yolks serve as natural emulsifiers in ice cream, providing richness and smooth texture while contributing essential nutrients like vitamins A and D. Stabilizers, often derived from plant-based sources such as guar gum or carrageenan, improve ice cream's viscosity without adding cholesterol or calories, making them suitable for vegan or low-fat diets. Choosing between egg yolks and stabilizers depends on dietary restrictions, with egg yolks being less ideal for those with cholesterol concerns and stabilizers offering a neutral, allergen-friendly alternative.
Homemade vs. Commercial Ice Cream: Ingredient Choices
Egg yolks serve as a natural thickening agent in homemade ice cream, providing rich texture and flavor through their lecithin content, while commercial ice creams often rely on stabilizers such as guar gum or carrageenan for consistent viscosity and extended shelf life. The emulsifying properties of egg yolks enhance creaminess but require precise temperature control during churning, contrasting with stabilizers that simplify production and maintain smoothness at various storage conditions. Consumers seeking artisanal quality prioritize egg yolks for authentic texture, whereas mass-produced ice creams incorporate stabilizers to optimize texture uniformity and prevent ice crystal formation.
When to Use Egg Yolks or Stabilizers in Recipes
Egg yolks provide natural creaminess and richness by emulsifying fats and forming a custard base, ideal for traditional, homemade ice cream recipes where flavor depth and texture are priorities. Stabilizers, such as guar gum or carrageenan, are preferred in commercial or low-fat ice creams to enhance texture, prevent ice crystal formation, and extend shelf life. Use egg yolks when aiming for a dense, creamy mouthfeel and stabilizers when requiring consistency, smoothness, and improved freeze-thaw stability in large batches or low-fat formulations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Thickener for Your Ice Cream
Egg yolks provide a rich texture and natural emulsification, enhancing the creaminess and flavor of ice cream, while stabilizers such as guar gum or carrageenan offer consistent thickening and improved shelf life without altering taste. For traditional, indulgent ice cream, egg yolks remain the ideal thickener, but stabilizers are preferred in commercial or dairy-free formulations due to their stability and ease of use. Selecting the best thickener depends on your recipe goals, whether prioritizing natural richness or extended texture stability.
Egg yolks vs Stabilizers for ice cream thickening Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com