Dairy fat in traditional ice cream provides a creamy texture and rich mouthfeel that is challenging to replicate. Non-dairy fats, such as coconut oil or almond milk fat, offer a plant-based alternative that caters to vegan preferences while maintaining smoothness and flavor. Choosing the right non-dairy fat is essential for creating vegan ice cream that mimics the indulgence of dairy without compromising on taste or texture.
Table of Comparison
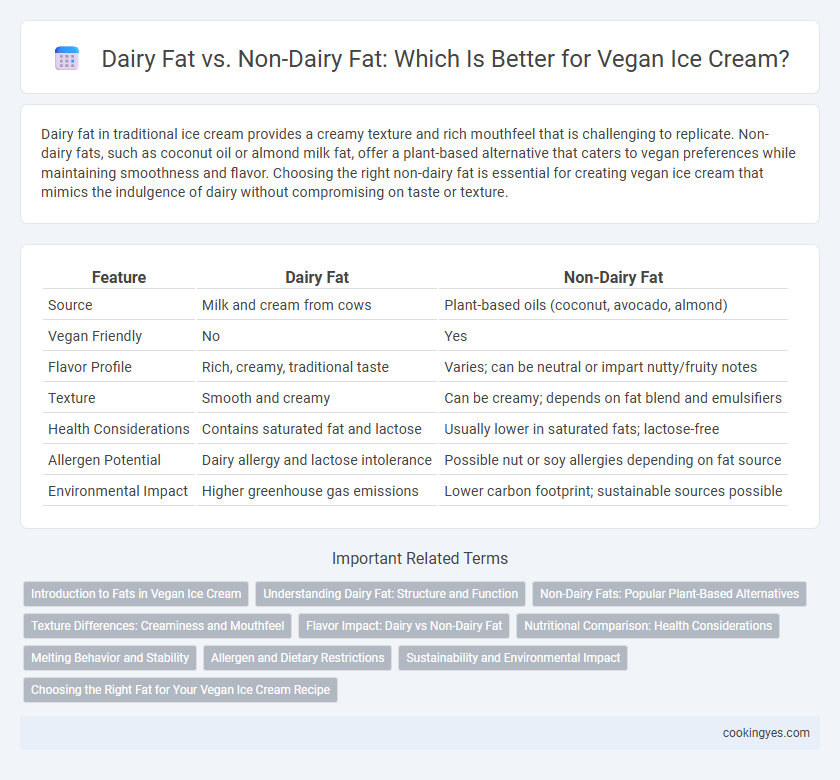
| Feature | Dairy Fat | Non-Dairy Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Milk and cream from cows | Plant-based oils (coconut, avocado, almond) |
| Vegan Friendly | No | Yes |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, creamy, traditional taste | Varies; can be neutral or impart nutty/fruity notes |
| Texture | Smooth and creamy | Can be creamy; depends on fat blend and emulsifiers |
| Health Considerations | Contains saturated fat and lactose | Usually lower in saturated fats; lactose-free |
| Allergen Potential | Dairy allergy and lactose intolerance | Possible nut or soy allergies depending on fat source |
| Environmental Impact | Higher greenhouse gas emissions | Lower carbon footprint; sustainable sources possible |
Introduction to Fats in Vegan Ice Cream
Vegan ice cream utilizes non-dairy fats such as coconut oil, almond oil, and avocado fat to replicate the creamy texture achieved by dairy fat, which consists primarily of milk fat from cow's milk. These plant-based fats provide essential mouthfeel, richness, and stability while aligning with vegan dietary preferences. Understanding the molecular structure and melting points of these fats is crucial for optimizing texture and flavor in dairy-free frozen desserts.
Understanding Dairy Fat: Structure and Function
Dairy fat in ice cream consists primarily of triglycerides with a unique crystalline structure that provides a creamy texture and rich mouthfeel. Its functional properties include emulsification and stability during freezing, which contribute to smoothness and reduced iciness. Non-dairy fats often mimic these characteristics through plant-based oils but require specific processing to replicate the complex melting profile and creaminess of dairy fat.
Non-Dairy Fats: Popular Plant-Based Alternatives
Non-dairy fats in vegan ice cream commonly come from coconut oil, almond butter, and cashew cream, which provide rich texture and creamy mouthfeel similar to traditional dairy fat. These plant-based alternatives contain medium-chain triglycerides and unsaturated fats, contributing to better heart health and easier digestion. Leveraging ingredients like avocado and oat oil enhances the creaminess while supporting vegan, lactose-free, and cholesterol-free claims in frozen desserts.
Texture Differences: Creaminess and Mouthfeel
Dairy fat in ice cream contributes to a rich, creamy texture with a smooth mouthfeel due to its ability to form small fat crystals and create a stable emulsion. Non-dairy fats, such as coconut or almond oil, often produce a lighter texture but may lack the same creaminess, sometimes resulting in a slightly oily or waxy mouthfeel. Emulsifiers and stabilizers are commonly used in vegan ice cream formulations to improve texture and mimic the creamy characteristics of dairy fat.
Flavor Impact: Dairy vs Non-Dairy Fat
Dairy fat in ice cream provides a rich, creamy texture and enhances the depth of flavor through its natural milk solids and butterfat content, creating a distinctive, indulgent taste. Non-dairy fats, often derived from coconut, almond, or oat sources, offer a lighter mouthfeel and subtle nutty or fruity notes, but may lack the full-bodied creaminess associated with traditional dairy. Balancing the flavor profile in vegan ice cream requires carefully selecting non-dairy fats that complement the base flavors while mimicking the creamy richness of dairy fat to satisfy consumer expectations.
Nutritional Comparison: Health Considerations
Dairy fat in traditional ice cream provides a rich source of saturated fats and fat-soluble vitamins like A and D, but it may contribute to higher cholesterol levels and increased cardiovascular risk. Non-dairy fat in vegan ice cream, often derived from coconut, almond, or soy, usually contains healthier unsaturated fats and lower cholesterol, supporting better heart health and digestion. Nutritionally, non-dairy fats offer a suitable alternative for lactose-intolerant individuals and those seeking reduced saturated fat intake while maintaining creamy texture and flavor.
Melting Behavior and Stability
Dairy fat in ice cream contributes to a creamy texture and slow melting due to its crystallization properties, which enhance structural stability and mouthfeel. Non-dairy fat, often derived from plant oils like coconut or palm, melts at different rates and can lead to faster melting and less stable textures without proper emulsifiers. Optimizing the melting behavior and stability in vegan ice cream requires balancing fat type and emulsification to mimic the rich, stable consistency provided by dairy fat.
Allergen and Dietary Restrictions
Dairy fat in traditional ice cream contains lactose and casein, which are common allergens affecting individuals with lactose intolerance or milk protein allergies. Non-dairy fat alternatives, such as coconut oil or almond butter, provide allergen-friendly options suitable for vegans and those with dairy sensitivities. Choosing non-dairy fats ensures compliance with vegan diets and often accommodates a wider range of dietary restrictions, reducing the risk of allergic reactions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Dairy fat in ice cream contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and water usage, making it less sustainable compared to non-dairy fat alternatives such as coconut or almond oil. Non-dairy fats typically have a lower carbon footprint and require less land and water resources, aligning better with vegan and environmentally friendly practices. Choosing plant-based fats in vegan ice cream production supports reduced environmental impact and promotes sustainable food systems.
Choosing the Right Fat for Your Vegan Ice Cream Recipe
Dairy fat, rich in saturated fats and creamy texture, offers unmatched richness but is unsuitable for vegan ice cream. Non-dairy fats like coconut oil, avocado oil, and almond butter provide plant-based alternatives with varying melting points and mouthfeel essential for vegan recipes. Selecting the ideal fat depends on balancing flavor, creaminess, and freeze stability to achieve a smooth, satisfying vegan ice cream texture.
Dairy fat vs Non-dairy fat for vegan ice cream Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com