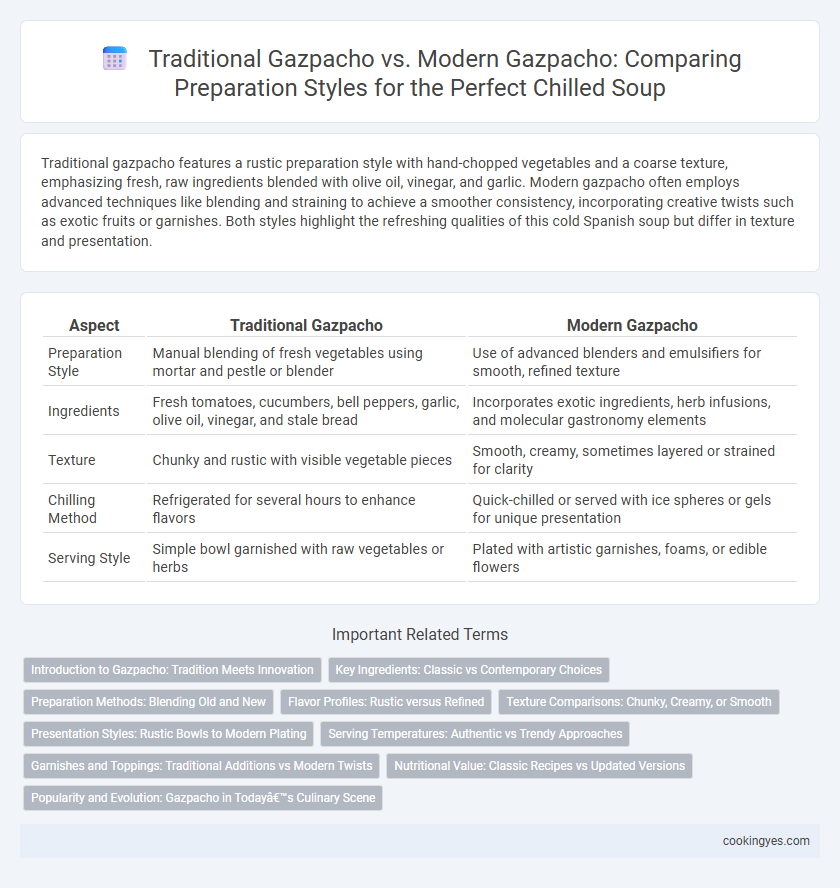
Traditional gazpacho features a rustic preparation style with hand-chopped vegetables and a coarse texture, emphasizing fresh, raw ingredients blended with olive oil, vinegar, and garlic. Modern gazpacho often employs advanced techniques like blending and straining to achieve a smoother consistency, incorporating creative twists such as exotic fruits or garnishes. Both styles highlight the refreshing qualities of this cold Spanish soup but differ in texture and presentation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Gazpacho | Modern Gazpacho |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Style | Manual blending of fresh vegetables using mortar and pestle or blender | Use of advanced blenders and emulsifiers for smooth, refined texture |
| Ingredients | Fresh tomatoes, cucumbers, bell peppers, garlic, olive oil, vinegar, and stale bread | Incorporates exotic ingredients, herb infusions, and molecular gastronomy elements |
| Texture | Chunky and rustic with visible vegetable pieces | Smooth, creamy, sometimes layered or strained for clarity |
| Chilling Method | Refrigerated for several hours to enhance flavors | Quick-chilled or served with ice spheres or gels for unique presentation |
| Serving Style | Simple bowl garnished with raw vegetables or herbs | Plated with artistic garnishes, foams, or edible flowers |
Introduction to Gazpacho: Tradition Meets Innovation
Traditional gazpacho features a rustic preparation style with raw vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers blended to create a refreshing cold soup rooted in Andalusian heritage. Modern gazpacho innovations introduce variations such as roasting vegetables for enhanced depth, incorporating fruits like watermelon or strawberries for sweetness, and adding spices or dairy elements to diversify texture and flavor profiles. This fusion of tradition and innovation highlights gazpacho's evolving culinary identity while maintaining its essential freshness and vibrant character.
Key Ingredients: Classic vs Contemporary Choices
Traditional gazpacho features key ingredients such as ripe tomatoes, cucumbers, green peppers, garlic, stale bread, olive oil, vinegar, and water, blended to create a refreshing cold soup with rustic textures. Modern gazpacho often incorporates contemporary choices like heirloom tomatoes, roasted red peppers, avocado, or fruit additions such as watermelon or mango, resulting in varied flavors and smoother consistencies. Preparation styles differ as traditional recipes emphasize hand-chopping and soaking stale bread for thickness, while modern versions typically use high-speed blenders for a silkier texture and innovative ingredient blends.
Preparation Methods: Blending Old and New
Traditional gazpacho relies on manual techniques such as crushing ripe tomatoes, cucumbers, and bell peppers using a mortar and pestle, emphasizing natural textures and slow melding of flavors. Modern gazpacho often employs high-speed blenders or food processors to achieve a smoother consistency and faster preparation while maintaining the freshness of raw ingredients. Combining these methods allows chefs to balance authentic, rustic flavors with contemporary convenience and presentation.
Flavor Profiles: Rustic versus Refined
Traditional gazpacho features a rustic preparation style, blending coarsely chopped tomatoes, cucumbers, onions, and garlic to create a chunky, robust flavor profile rooted in Andalusian culinary heritage. Modern gazpacho employs refined techniques such as straining and emulsifying ingredients to achieve a smooth, velvety texture with balanced acidity and enhanced subtlety in flavors. The contrast between rustic and refined gazpacho highlights the evolution from hearty, straightforward tastes to sophisticated, nuanced flavor experiences.
Texture Comparisons: Chunky, Creamy, or Smooth
Traditional gazpacho features a chunky texture with coarsely chopped vegetables like cucumbers, tomatoes, and peppers, providing a rustic and refreshing bite. Modern gazpacho often opts for a creamy or smooth consistency achieved by blending and straining the ingredients, resulting in a velvety finish that enhances the flavors. These texture variations define the sensory experience, blending heritage with contemporary culinary techniques.
Presentation Styles: Rustic Bowls to Modern Plating
Traditional gazpacho is served in rustic bowls, highlighting its roots as a simple, cold Spanish soup made from blended tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and bread, often garnished with chopped vegetables for a hearty texture. Modern gazpacho embraces contemporary presentation styles, featuring smooth purees plated elegantly in shallow, wide dishes or even glasses, garnished with microgreens, edible flowers, or drizzles of high-quality olive oil to enhance visual appeal. This shift in preparation style emphasizes refinement and creativity while preserving the fresh, vibrant flavors characteristic of gazpacho.
Serving Temperatures: Authentic vs Trendy Approaches
Traditional gazpacho is served ice-cold, emphasizing its refreshing qualities, prepared by blending raw vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, and bell peppers without cooking. Modern gazpacho variations often experiment with warmer serving temperatures or incorporate cooked ingredients, blending classic flavors with innovative techniques. This evolution in serving style reflects a trend toward diverse sensory experiences while maintaining the core essence of this Spanish cold soup.
Garnishes and Toppings: Traditional Additions vs Modern Twists
Traditional gazpacho features classic garnishes such as diced cucumbers, chopped tomatoes, green peppers, fresh herbs, and crusty bread croutons that enhance its fresh, raw vegetable flavors. Modern gazpacho incorporates innovative toppings like avocado slices, smoked paprika, microgreens, toasted nuts, and even seafood elements to add texture and bold, unexpected flavors. Both styles prioritize vibrant, complementary ingredients, but modern variations emphasize creative presentation and diverse textures beyond the original rustic simplicity.
Nutritional Value: Classic Recipes vs Updated Versions
Traditional gazpacho recipes emphasize raw, fresh vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers, preserving their natural vitamins and antioxidants with minimal processing. Modern gazpacho variations often incorporate added ingredients such as avocado, nuts, or olive oil to boost healthy fats and enhance nutrient density. These updated versions typically provide higher levels of monounsaturated fats and fiber, contributing to improved heart health and digestion compared to classic recipes.
Popularity and Evolution: Gazpacho in Today’s Culinary Scene
Traditional gazpacho, originating from Andalusia, is characterized by its raw vegetable ingredients like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers, blended with olive oil and vinegar for a refreshing, rustic flavor. Modern gazpacho variations often incorporate innovative ingredients and techniques such as fruit infusions, creamier textures, and chilled presentation styles that cater to contemporary palates. The evolution of gazpacho has increased its global popularity, making it a staple in gourmet summer menus and reflecting its adaptability within today's culinary scene.
Traditional gazpacho vs Modern gazpacho for preparation style Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com