Sashimi and carpaccio both highlight the freshness of raw fish but differ in preparation and presentation. Sashimi consists of thinly sliced raw fish served plain, often accompanied by soy sauce, wasabi, and pickled ginger to enhance its natural flavors. Carpaccio, originally a dish of thinly sliced raw beef, is adapted for fish by dressing the slices with citrus, olive oil, herbs, or other seasonings, offering a more complex and zesty taste experience.
Table of Comparison
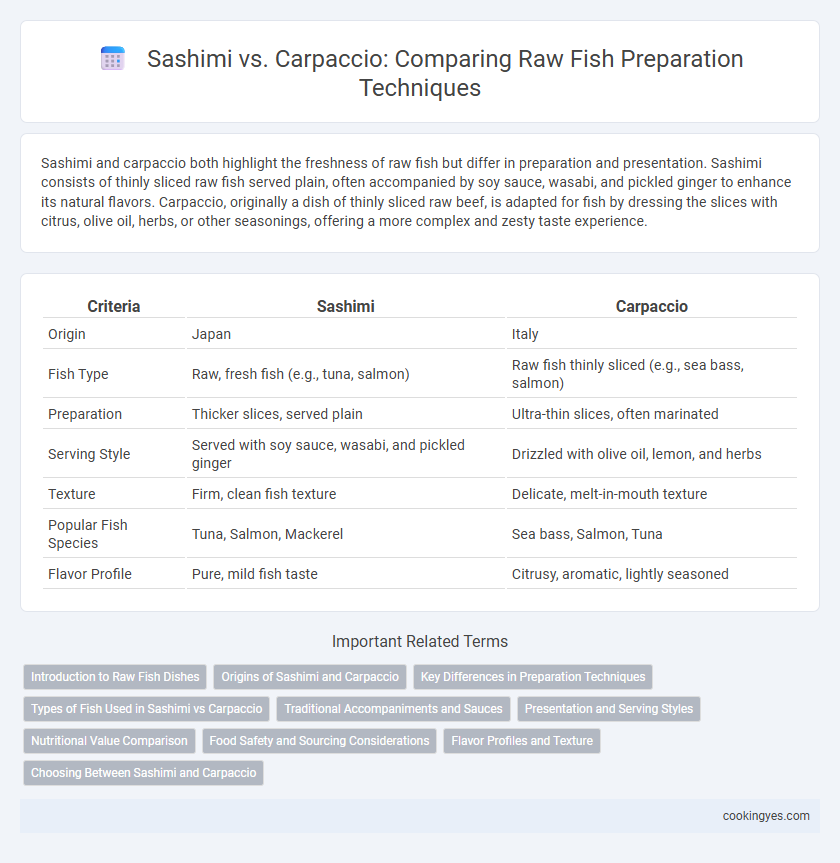
| Criteria | Sashimi | Carpaccio |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Japan | Italy |
| Fish Type | Raw, fresh fish (e.g., tuna, salmon) | Raw fish thinly sliced (e.g., sea bass, salmon) |
| Preparation | Thicker slices, served plain | Ultra-thin slices, often marinated |
| Serving Style | Served with soy sauce, wasabi, and pickled ginger | Drizzled with olive oil, lemon, and herbs |
| Texture | Firm, clean fish texture | Delicate, melt-in-mouth texture |
| Popular Fish Species | Tuna, Salmon, Mackerel | Sea bass, Salmon, Tuna |
| Flavor Profile | Pure, mild fish taste | Citrusy, aromatic, lightly seasoned |
Introduction to Raw Fish Dishes
Sashimi showcases pristine slices of raw fish, emphasizing freshness and texture, typically served without additional ingredients to highlight the natural flavors. Carpaccio features thinly sliced raw fish drizzled with olive oil, citrus, or vinegar, blending the fish's natural taste with subtle seasoning to enhance complexity. Both dishes celebrate raw fish preparation, with sashimi rooted in Japanese cuisine and carpaccio stemming from Italian culinary traditions.
Origins of Sashimi and Carpaccio
Sashimi, a traditional Japanese dish, traces its origins back to the Edo period, where thinly sliced raw fish was appreciated for its freshness and delicate flavor. Carpaccio originated in early 20th-century Venice, Italy, initially as a preparation of thinly sliced raw beef, later adapted to seafood including raw fish, combining Mediterranean ingredients like olive oil and lemon juice. Both methods emphasize the texture and natural taste of raw fish, though rooted in distinct cultural culinary traditions.
Key Differences in Preparation Techniques
Sashimi features thinly sliced raw fish, typically served fresh without additional ingredients, highlighting the fish's natural flavor and texture through precise knife skills. Carpaccio involves paper-thin slices of raw fish, often marinated or dressed with acidic components like lemon juice or olive oil, enhancing flavor complexity and tenderizing the fish. The key difference lies in sashimi's simplicity and emphasis on pure freshness, while carpaccio incorporates bold seasoning and textural contrast.
Types of Fish Used in Sashimi vs Carpaccio
Sashimi primarily features fish like tuna, salmon, yellowtail, and mackerel, chosen for their texture and flavor when served raw. Carpaccio, though originally referring to thinly sliced raw beef, adapts to fish varieties such as sea bass, halibut, or swordfish, often emphasizing a thinner cut and lighter marinade. Sashimi's focus is on purity and freshness, while carpaccio highlights subtle seasonings that complement more delicate or lean fish types.
Traditional Accompaniments and Sauces
Sashimi, a Japanese delicacy, is traditionally accompanied by soy sauce, wasabi, and pickled ginger, enhancing the natural flavors of raw fish like tuna or salmon. Carpaccio, an Italian adaptation of raw fish preparation, is typically served with olive oil, lemon juice, capers, and shaved Parmesan, adding a tangy and savory profile to thinly sliced fish such as sea bass or halibut. Both methods highlight delicate textures but differ significantly in their regional seasoning and presentation styles.
Presentation and Serving Styles
Sashimi showcases expertly sliced raw fish arranged meticulously on a chilled platter, often accompanied by daikon radish, shiso leaves, and wasabi to enhance visual appeal and flavor balance. Carpaccio presents thinly sliced raw fish drizzled with olive oil, citrus juices, and garnished with capers, microgreens, or thinly sliced vegetables, emphasizing a vibrant and colorful plating style. The serving style of sashimi is traditionally minimalist and refined, while carpaccio offers a more textured and layered presentation, appealing to diverse sensory experiences.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Sashimi and carpaccio both offer high-protein, low-fat options ideal for raw fish consumption, with sashimi typically featuring nutrient-rich fish like tuna or salmon that provide essential omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins D and B12. Carpaccio, often prepared with thinly sliced white fish such as sea bass or halibut, delivers a lighter calorie profile while maintaining antioxidants and mineral content. Both preparations retain the fish's natural benefits, but sashimi generally delivers higher amounts of healthy fats and fat-soluble vitamins essential for heart and brain health.
Food Safety and Sourcing Considerations
Sashimi, a traditional Japanese dish, requires fish that is specifically labeled as "sashimi-grade" or "sushi-grade," indicating it has been frozen at temperatures that kill parasites, ensuring food safety. Carpaccio, though also served raw, often involves thin slices of raw fish marinated or dressed, demanding equally rigorous sourcing standards to prevent bacterial contamination. Both preparations rely heavily on fresh, high-quality fish sourced from reputable suppliers following strict handling and storage protocols to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Flavor Profiles and Texture
Sashimi showcases the pure, delicate flavor of fresh fish with a silky, melt-in-the-mouth texture, highlighting the natural sweetness and subtle umami of raw seafood. Carpaccio, often thinly sliced and marinated with citrus, olive oil, or vinegar, offers a more complex flavor profile with tangy, bright notes that complement a slightly firmer texture. Both preparations emphasize freshness but cater to different palate preferences--sashimi for clean, unadulterated taste and carpaccio for a layered, zesty experience.
Choosing Between Sashimi and Carpaccio
Choosing between sashimi and carpaccio hinges on the desired texture and flavor profile of raw fish; sashimi offers thick, skillfully sliced pieces showcasing the fish's pure, fresh taste, while carpaccio features thinly sliced fish served with dressings, emphasizing delicate flavors enhanced by citrus or olive oil. Sashimi is traditionally served without accompaniment, ideal for highlighting premium fish quality, whereas carpaccio provides a more diverse sensory experience through its garnishes and seasoning. Selecting sashimi suits those seeking an authentic Japanese raw fish experience, while carpaccio appeals to diners who prefer a fusion of textures and vibrant, complementary tastes.
Sashimi vs Carpaccio for Raw Fish Preparation Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com