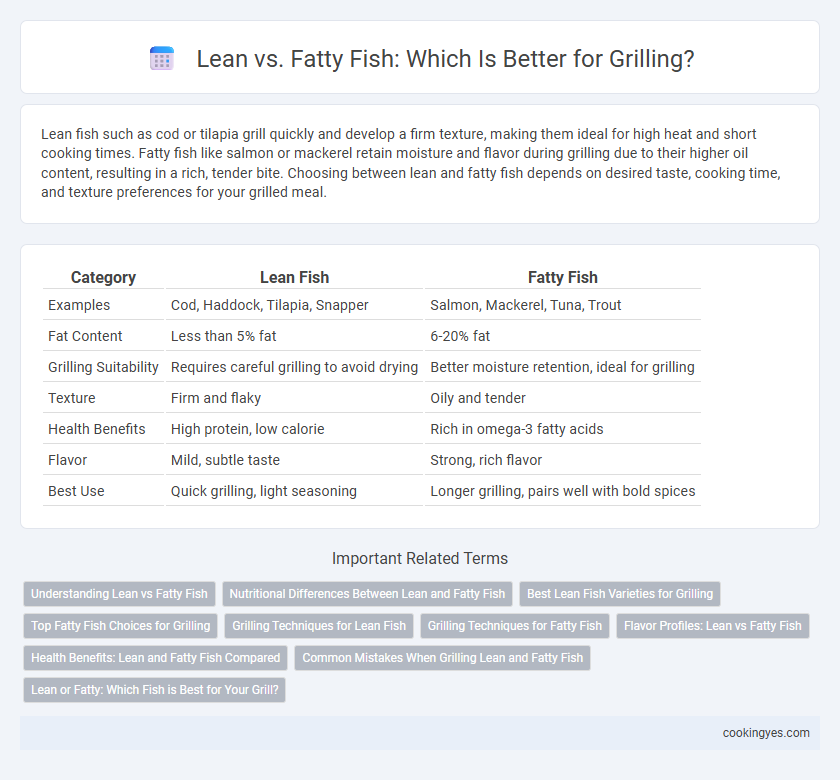
Lean fish such as cod or tilapia grill quickly and develop a firm texture, making them ideal for high heat and short cooking times. Fatty fish like salmon or mackerel retain moisture and flavor during grilling due to their higher oil content, resulting in a rich, tender bite. Choosing between lean and fatty fish depends on desired taste, cooking time, and texture preferences for your grilled meal.
Table of Comparison
| Category | Lean Fish | Fatty Fish |
|---|---|---|
| Examples | Cod, Haddock, Tilapia, Snapper | Salmon, Mackerel, Tuna, Trout |
| Fat Content | Less than 5% fat | 6-20% fat |
| Grilling Suitability | Requires careful grilling to avoid drying | Better moisture retention, ideal for grilling |
| Texture | Firm and flaky | Oily and tender |
| Health Benefits | High protein, low calorie | Rich in omega-3 fatty acids |
| Flavor | Mild, subtle taste | Strong, rich flavor |
| Best Use | Quick grilling, light seasoning | Longer grilling, pairs well with bold spices |
Understanding Lean vs Fatty Fish
Lean fish such as cod and tilapia contain lower oil content, making them ideal for quick grilling with a mild, delicate flavor and firm texture that holds well under high heat. Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, providing a moist, rich taste that remains tender and flavorful when grilled. Choosing between lean and fatty fish depends on desired taste, cooking time, and nutritional benefits, with lean fish offering lower calories and fat, and fatty fish delivering essential healthy fats.
Nutritional Differences Between Lean and Fatty Fish
Lean fish such as cod and tilapia contain lower fat content, making them rich sources of high-quality protein with fewer calories, ideal for those seeking a lighter grilling option. Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel provide higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health and reduce inflammation, along with fat-soluble vitamins A and D. Nutritionally, choosing between lean and fatty fish depends on balancing protein intake with beneficial fats, as fatty fish offer more essential nutrients that promote overall wellness.
Best Lean Fish Varieties for Grilling
Best lean fish varieties for grilling include cod, tilapia, and haddock, prized for their firm texture and mild flavor that hold up well to high heat. These fish have lower fat content, making them ideal for a healthier grilled meal with a flaky yet sturdy consistency. Grilling lean fish requires careful timing to prevent drying out, often complemented by marinades or light seasoning to enhance their natural taste.
Top Fatty Fish Choices for Grilling
Top fatty fish choices for grilling include salmon, mackerel, and swordfish, prized for their rich omega-3 fatty acids and firm texture that withstands high heat. These species offer a moist, flavorful experience, with oil content helping prevent drying out on the grill. Their dense flesh and healthy fats make them ideal for achieving a crispy exterior while retaining juiciness inside.
Grilling Techniques for Lean Fish
Lean fish like cod, halibut, and tilapia require careful grilling techniques due to their delicate texture and lower fat content. To prevent sticking and drying out, marinate lean fish before grilling and use a well-oiled, preheated grill for even cooking. Cooking lean fish over medium heat and flipping gently ensures a moist, flaky result without overcooking.
Grilling Techniques for Fatty Fish
Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel contain higher oil content, making them ideal for grilling due to their moisture retention and rich flavor. To prevent sticking and ensure even cooking, use a well-oiled grill grate and moderate heat, turning the fish only once during grilling. Employ techniques such as indirect grilling or grilling with a cedar plank to enhance flavor while avoiding flare-ups caused by dripping oils.
Flavor Profiles: Lean vs Fatty Fish
Lean fish like cod and tilapia offer a mild, delicate flavor that absorbs marinades well but can dry out quickly on the grill. Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel deliver a rich, buttery taste with higher oil content, which helps retain moisture and enhances natural smoky flavors during grilling. Understanding these flavor profiles allows for better pairing of seasoning and cooking techniques to maximize the taste and texture of grilled fish.
Health Benefits: Lean and Fatty Fish Compared
Grilling lean fish like cod and tilapia offers a low-calorie source of high-quality protein with minimal fat content, making it ideal for heart health and weight management. Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel provide abundant omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for reducing inflammation, improving brain function, and lowering the risk of chronic diseases. Choosing between lean and fatty fish for grilling depends on balancing calorie intake with the need for beneficial fats, promoting overall cardiovascular and cognitive health.
Common Mistakes When Grilling Lean and Fatty Fish
Common mistakes when grilling lean fish include overcooking, which leads to dryness due to low fat content, and failing to oil the grill or fish, causing sticking. For fatty fish like salmon or mackerel, excessive heat can cause flare-ups from dripping fat, resulting in burnt exteriors and uneven cooking. Proper temperature control and pre-oiling are crucial to retain moisture and achieve even grilling for both lean and fatty fish varieties.
Lean or Fatty: Which Fish is Best for Your Grill?
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and trout are ideal for grilling due to their higher oil content, which keeps the flesh moist and flavorful under high heat. Lean fish like cod, tilapia, and sole tend to dry out quickly on the grill and require careful monitoring or marinating to maintain tenderness. Choosing fatty fish ensures a more succulent and less fragile grilling experience, making them the preferred option for barbecue enthusiasts.
Lean vs Fatty fish for grilling Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com