Gluten-free cookies use alternative flours such as almond, coconut, or rice flour to provide a safe option for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, while regular cookies typically use wheat flour, which contains gluten for elasticity and structure. Gluten-free flours often result in a different texture and taste, sometimes requiring additional binding agents to mimic the chewiness of traditional cookies. Selecting the right flour depends on dietary needs and desired cookie characteristics, making gluten-free options a versatile and inclusive choice.
Table of Comparison
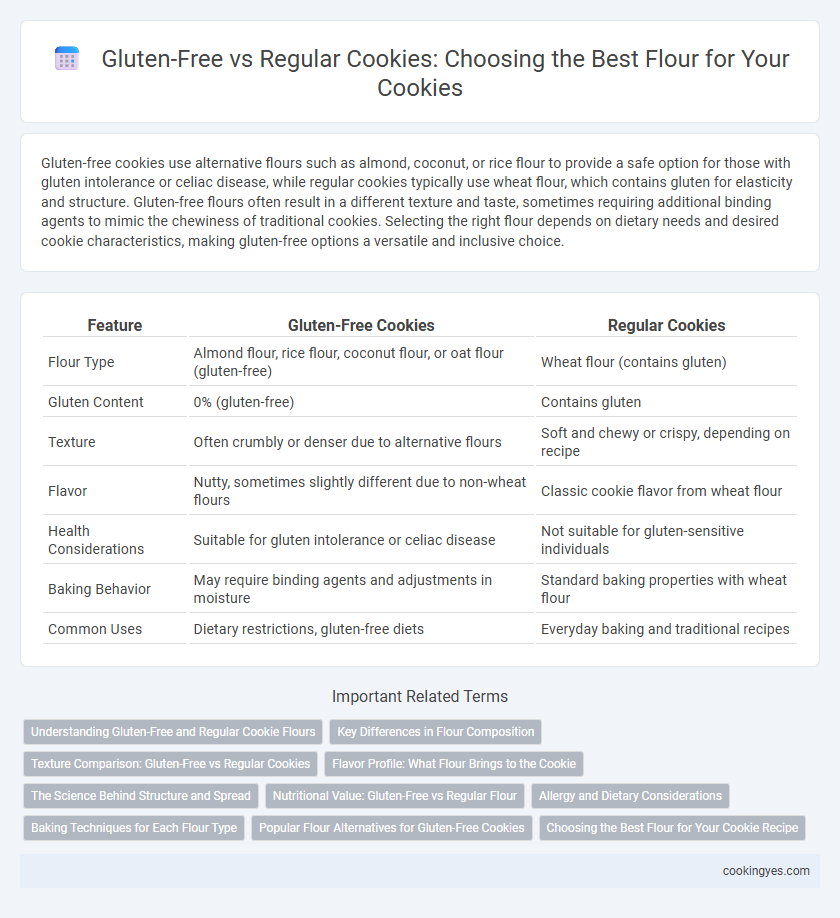
| Feature | Gluten-Free Cookies | Regular Cookies |
|---|---|---|
| Flour Type | Almond flour, rice flour, coconut flour, or oat flour (gluten-free) | Wheat flour (contains gluten) |
| Gluten Content | 0% (gluten-free) | Contains gluten |
| Texture | Often crumbly or denser due to alternative flours | Soft and chewy or crispy, depending on recipe |
| Flavor | Nutty, sometimes slightly different due to non-wheat flours | Classic cookie flavor from wheat flour |
| Health Considerations | Suitable for gluten intolerance or celiac disease | Not suitable for gluten-sensitive individuals |
| Baking Behavior | May require binding agents and adjustments in moisture | Standard baking properties with wheat flour |
| Common Uses | Dietary restrictions, gluten-free diets | Everyday baking and traditional recipes |
Understanding Gluten-Free and Regular Cookie Flours
Gluten-free cookies are made with alternative flours such as almond, rice, or oat flour, which lack the gluten protein found in traditional wheat flour used for regular cookies. The absence of gluten affects the texture and structure, often resulting in a denser, more crumbly cookie compared to the chewy and elastic qualities gluten provides in regular cookies. Understanding these differences helps bakers select appropriate flour blends and binding agents to achieve desired cookie consistency and flavor profiles.
Key Differences in Flour Composition
Gluten-free cookies typically use alternative flours such as almond, rice, or coconut flour, which lack gluten proteins found in wheat-based flour used in regular cookies. These gluten proteins contribute to the elasticity and chewiness in regular cookies, whereas gluten-free flours often require binding agents like xanthan gum to mimic texture. The difference in flour composition directly affects the structural integrity, moisture retention, and mouthfeel between gluten-free and regular cookies.
Texture Comparison: Gluten-Free vs Regular Cookies
Gluten-free cookies often rely on alternative flours like almond, rice, or tapioca flour, resulting in a denser and crumbly texture compared to regular cookies made with wheat flour that develop a chewy and soft bite due to gluten's elastic properties. The absence of gluten in gluten-free cookies can cause them to be more brittle and less able to retain moisture, affecting the overall mouthfeel and structural integrity. Baking techniques such as adding xanthan gum or psyllium husk are commonly used to mimic gluten's binding capabilities and improve the texture of gluten-free cookies.
Flavor Profile: What Flour Brings to the Cookie
Gluten-free cookies made with almond or rice flour often have a nuttier and slightly sweeter flavor profile compared to regular cookies that use wheat flour, which provides a classic, rich, and slightly malty taste. Wheat flour's gluten content contributes to a chewy texture that enhances the overall flavor release during baking, while gluten-free flours create a denser crumb and can highlight subtle natural flavors. The choice of flour directly impacts the cookie's taste complexity, with gluten-free options offering unique, earthy notes and regular wheat flour delivering the traditional cookie flavor preferred by many.
The Science Behind Structure and Spread
Gluten-free cookies rely on alternative flours like almond, rice, or tapioca, which lack the gluten protein responsible for elasticity and structure in regular cookies made with wheat flour. The absence of gluten leads to differences in dough hydration and protein interaction, causing gluten-free cookies to spread more and have a crumbly texture compared to the chewy, structured consistency of regular cookies. Understanding the role of gluten in forming a cohesive matrix helps bakers adjust moisture content, fat ratios, and binding agents to optimize the texture and spread of gluten-free cookies.
Nutritional Value: Gluten-Free vs Regular Flour
Gluten-free cookies often use alternative flours like almond, coconut, or rice flour, which can increase fiber and protein content compared to regular cookies made with wheat flour. Regular cookies typically contain gluten that provides structure and elasticity but may have lower fiber levels unless whole wheat flour is used. Nutritional differences include potential variations in carbohydrate impact, with gluten-free flours sometimes offering a lower glycemic index and added micronutrients depending on the flour blend.
Allergy and Dietary Considerations
Gluten-free cookies use alternative flours such as almond, coconut, or rice flour, making them safe for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. Regular cookies typically contain wheat flour, which includes gluten, posing a risk for those with gluten allergies or sensitivities. Choosing gluten-free options supports dietary needs while maintaining flavor and texture for allergy-conscious consumers.
Baking Techniques for Each Flour Type
Gluten-free cookies require the use of alternative flours like almond, rice, or coconut flour, which demand precise moisture adjustments and often the incorporation of binders such as xanthan gum to mimic gluten's elasticity. Regular cookies made with wheat flour benefit from gluten development through proper mixing and resting times, creating a chewy and structured texture. Baking temperature and time also vary, as gluten-free cookies typically need lower heat or slower baking to prevent dryness while achieving optimal softness.
Popular Flour Alternatives for Gluten-Free Cookies
Popular flour alternatives for gluten-free cookies include almond flour, coconut flour, and oat flour, which provide distinct textures and flavors while maintaining moisture. Almond flour offers a rich, nutty taste and helps achieve a tender crumb, whereas coconut flour absorbs more liquid, requiring recipe adjustments to prevent dryness. Oat flour contributes a mild, slightly sweet flavor and a chewy texture, making it a versatile replacement for traditional wheat flour in gluten-free cookie recipes.
Choosing the Best Flour for Your Cookie Recipe
Gluten-free cookies often rely on almond flour, coconut flour, or rice flour to mimic the texture provided by wheat flour in regular cookies. Choosing the best flour depends on desired cookie traits: almond flour offers a moist, chewy texture, while rice flour yields a lighter, crisper bite. For balanced flavor and structure, blending gluten-free flours with xanthan gum enhances elasticity similar to gluten in traditional wheat-based cookies.
Gluten-free cookies vs Regular cookies for flour choice Infographic
 cookingyes.com
cookingyes.com